Python Advanced - LogeshVel/learning_resources GitHub Wiki
Strongly Typed vs. Weakly Typed
This distinction focuses on how strictly a language enforces type rules during execution.
Strongly Typed Languages
- Variables have a type, and you cannot perform operations that are not allowed for that type without explicit conversion.
- Errors occur when you try to mix incompatible types.
- Example: Python, Java, Ruby
x = "10"
y = 5
z = x + y # TypeError: can't add str and int in Python
- To make it work, you need explicit conversion:
z = int(x) + y # Correct
Weakly Typed Languages
- The language implicitly converts types when needed, even if it may lead to unexpected results.
- Example: JavaScript, PHP
x = "10";
y = 5;
z = x + y; // Output: "105" because JavaScript concatenates strings and numbers
Static Typing vs. Dynamic Typing
This distinction focuses on when type checking happens (compile time or runtime).
Statically Typed Languages
- Types of variables are determined at compile time.
- You must declare variable types explicitly, or they are inferred by the compiler.
- Example: C, C++, Java, Go, Rust
int x = 10; // Variable type explicitly declared
x = "hello"; // Compile-time error: incompatible type
Dynamically Typed Languages
- Types of variables are determined at runtime.
- You don't declare types explicitly; the language figures them out.
- Example: Python, JavaScript, Ruby
x = 10 # x is an integer
x = "hello" # Now x is a string; no error
How They Relate
- Strong vs. Weak Typing: Determines how strict type enforcement is during operations.
- Static vs. Dynamic Typing: Determines when the type information is applied and checked.
Examples of Combinations
-
Strongly Typed + Statically Typed: Rust, Java
- Errors occur at compile time, and types are strictly enforced.
-
Strongly Typed + Dynamically Typed: Python, Ruby
- Types are checked at runtime, but type rules are enforced strictly.
-
Weakly Typed + Dynamically Typed: JavaScript, PHP
- Types are flexible, and implicit conversions happen at runtime.
-
Weakly Typed + Statically Typed: C (arguably)
- Types are declared and checked at compile time, but you can bypass them using casts.
hash
Dynamic Attributes


Still we could change the value by self._x = "somevalue". But it is not intended to do that. Since _var in python means its private, eventhough we can change we should not do that.. thats the reason for that _var.

Advanced flow control
while else

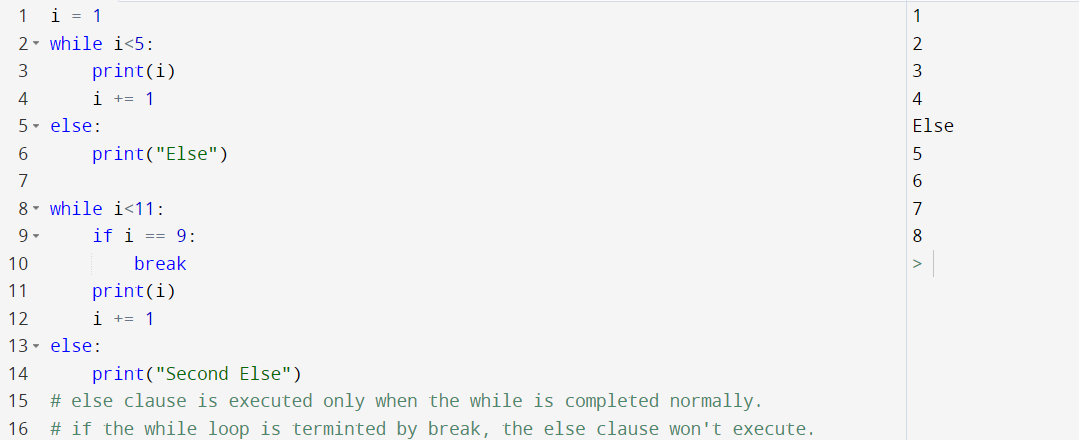
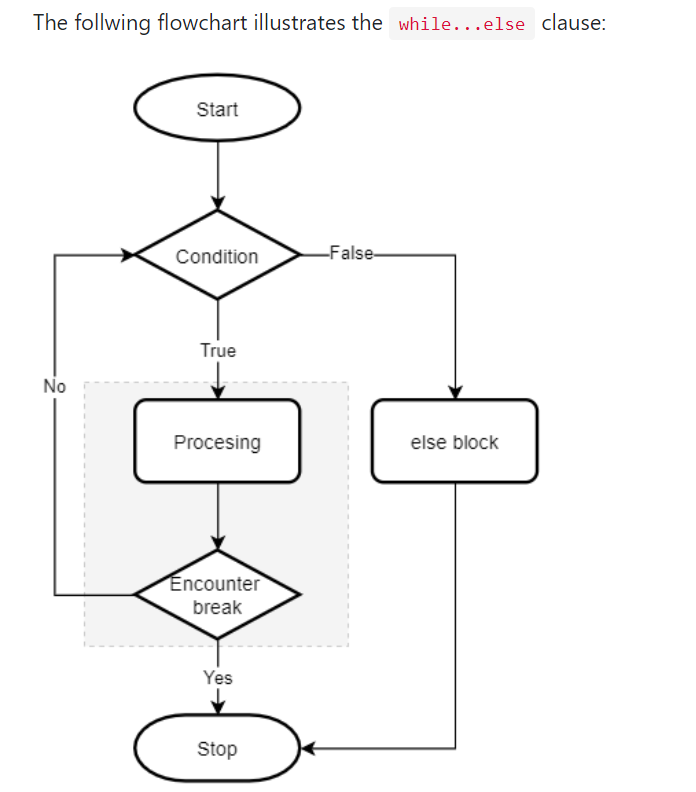
for else
The else clause executes after the loop completes normally. This means that the loop did not encounter a break statement.
Same as while else. but in the while else when the condition is false the else is executed and when the loop is terminated by break the else won't execute.
In simple words, under normal condition else clause is executed.
try else



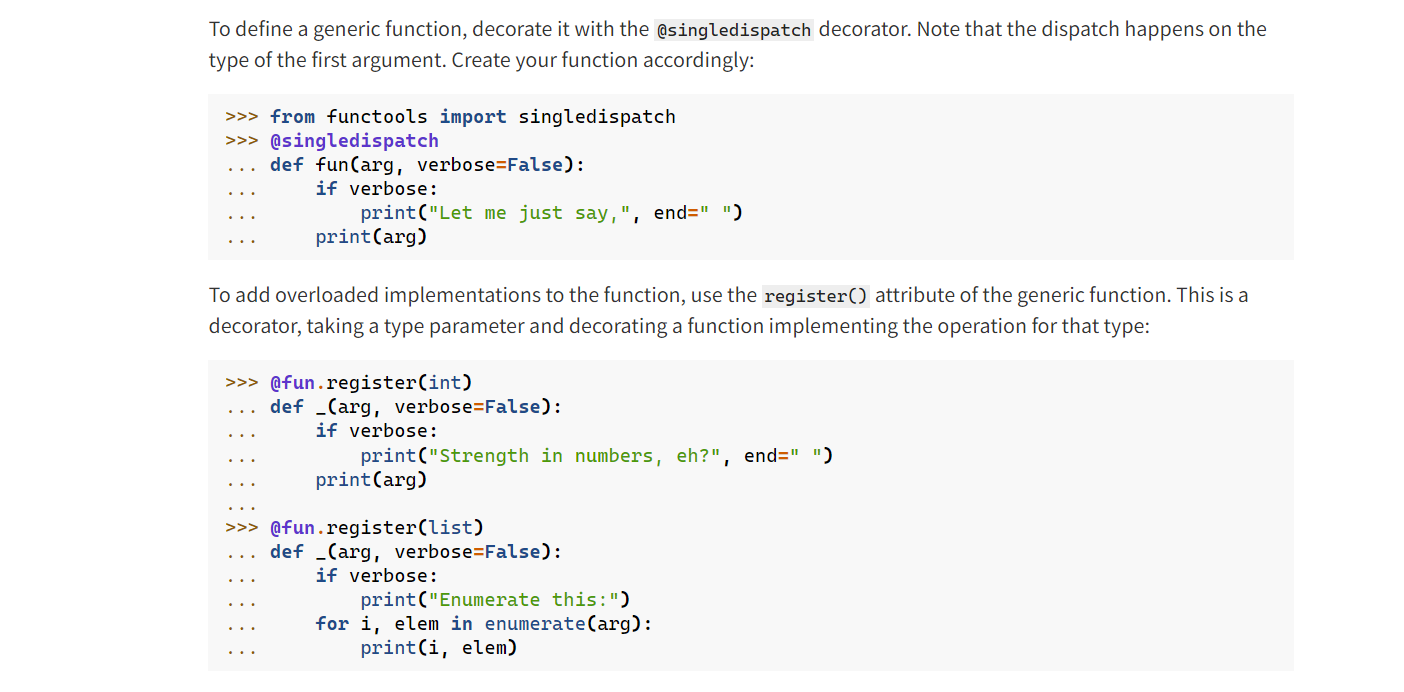
Single dispatch
When the implementation is chosen based on the type of a single argument, this is known as single dispatch.


bytes
bytes to str, hex


bytearray



Descriptors
Property decorator


Descriptors
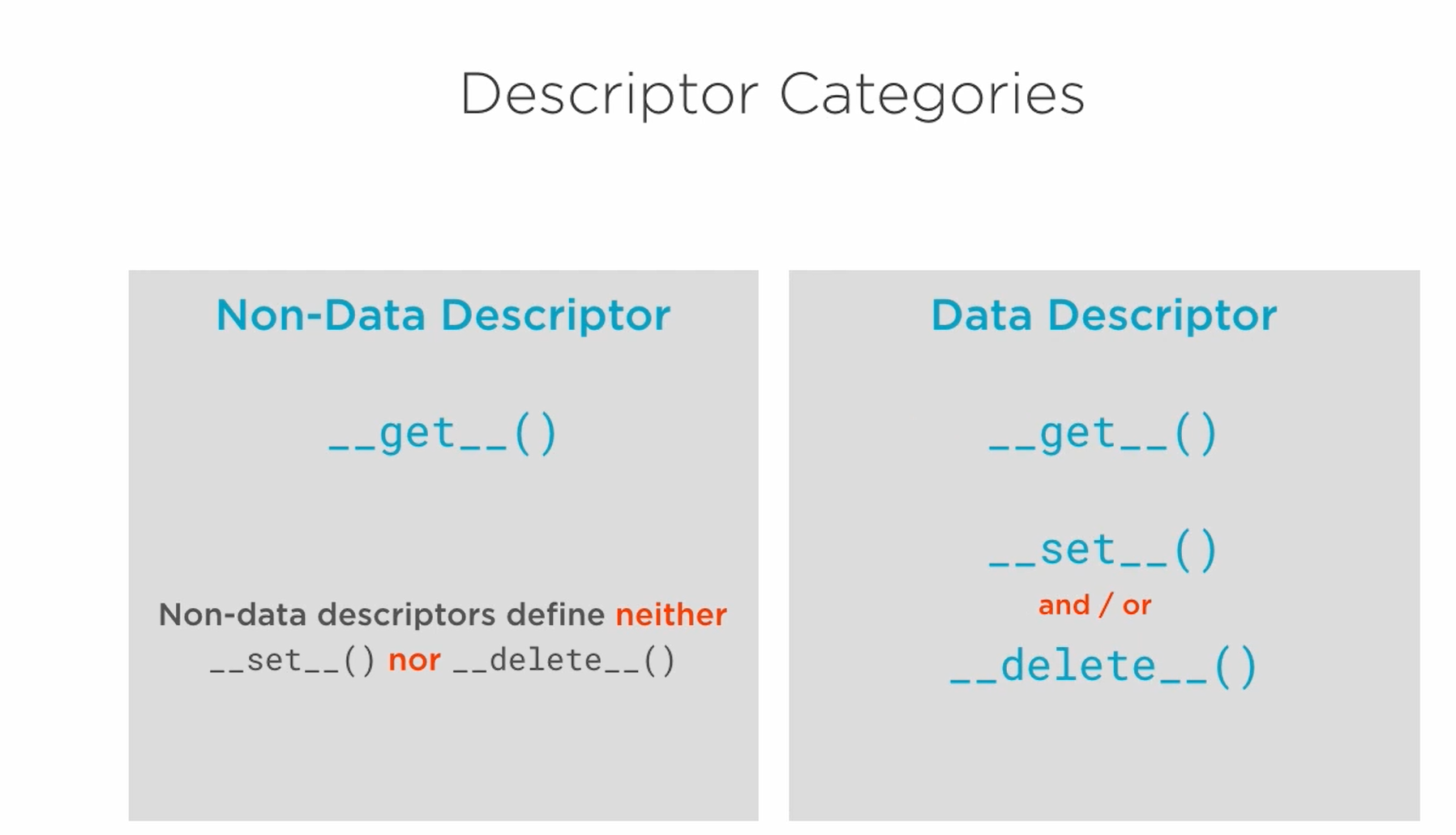
Any object which defines the methods __get__(), __set__(), or __delete__().
Property is a descriptor
property uses the decorator for the same result. But if we have 3 methods(get, set and del) and then give it to the proprty(fget, fset, fel, doc) then its the Descriptors.
descriptors are a low-level mechanism that lets you hook into an object's attributes being accessed. Properties are a high-level application of this; that is, properties are implemented using descriptors. Or, better yet, properties are descriptors that are already provided for you in the standard library.



*Note: Descriptors. We can bind getter, setter (and deleter) functions into a separate class, which denotes the property class
Descriptors - property( fget, fset, fdel, doc)
propperty = @property, @attr.setter,...

implementing descriptor
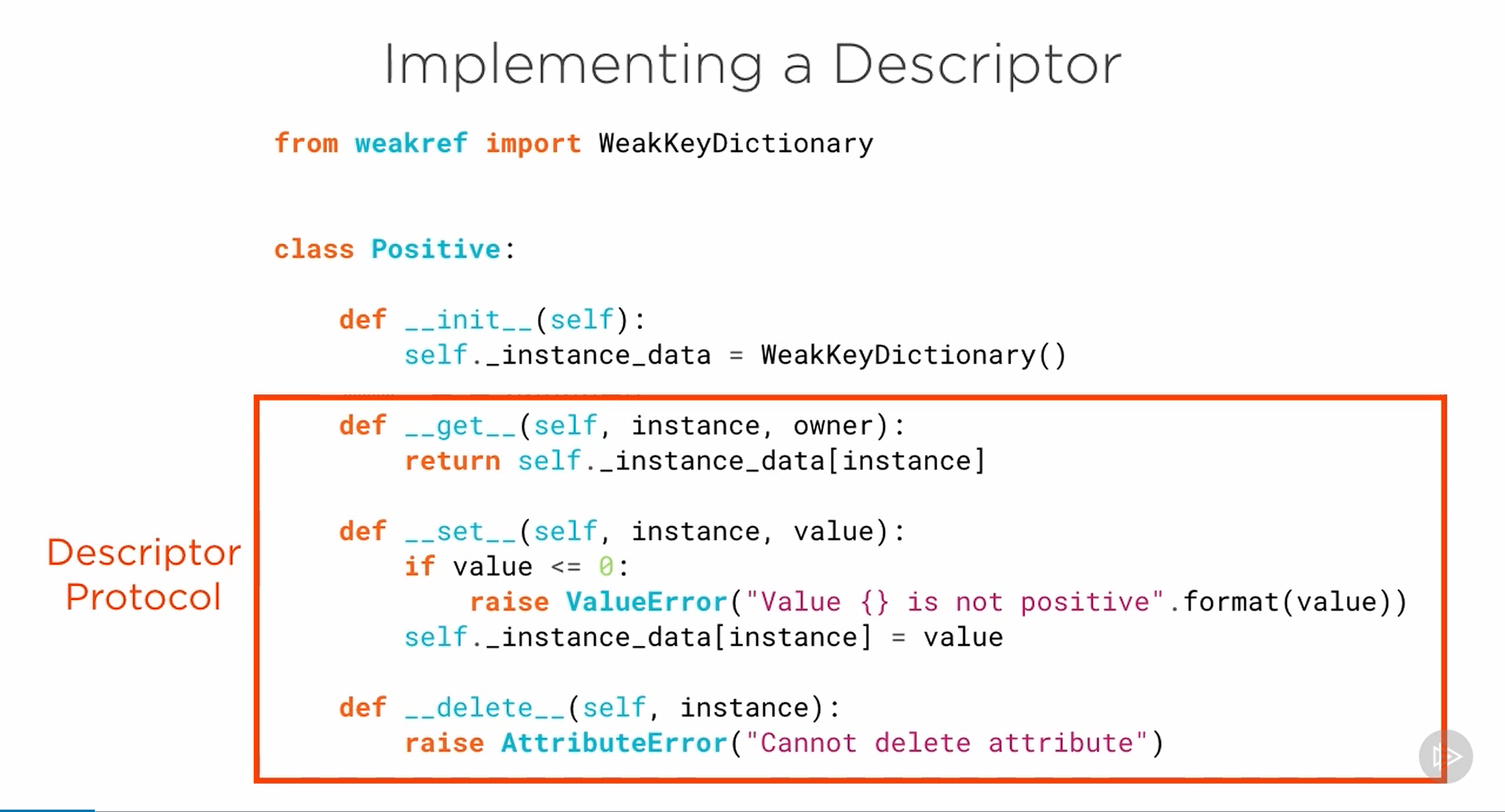
ex
in the above example we could see that the in the init the values are assigned for the property and in the body of the class the descriptors is created for that property. Positive() class has the get, set and del methods. So here, binding getter, setter (and deleter) functions into a separate class
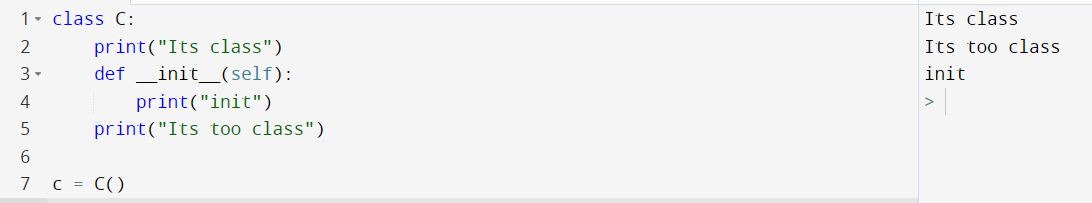
Also, the body of the class is first executed and then the init will be executed. So binding happens and then init will happen.
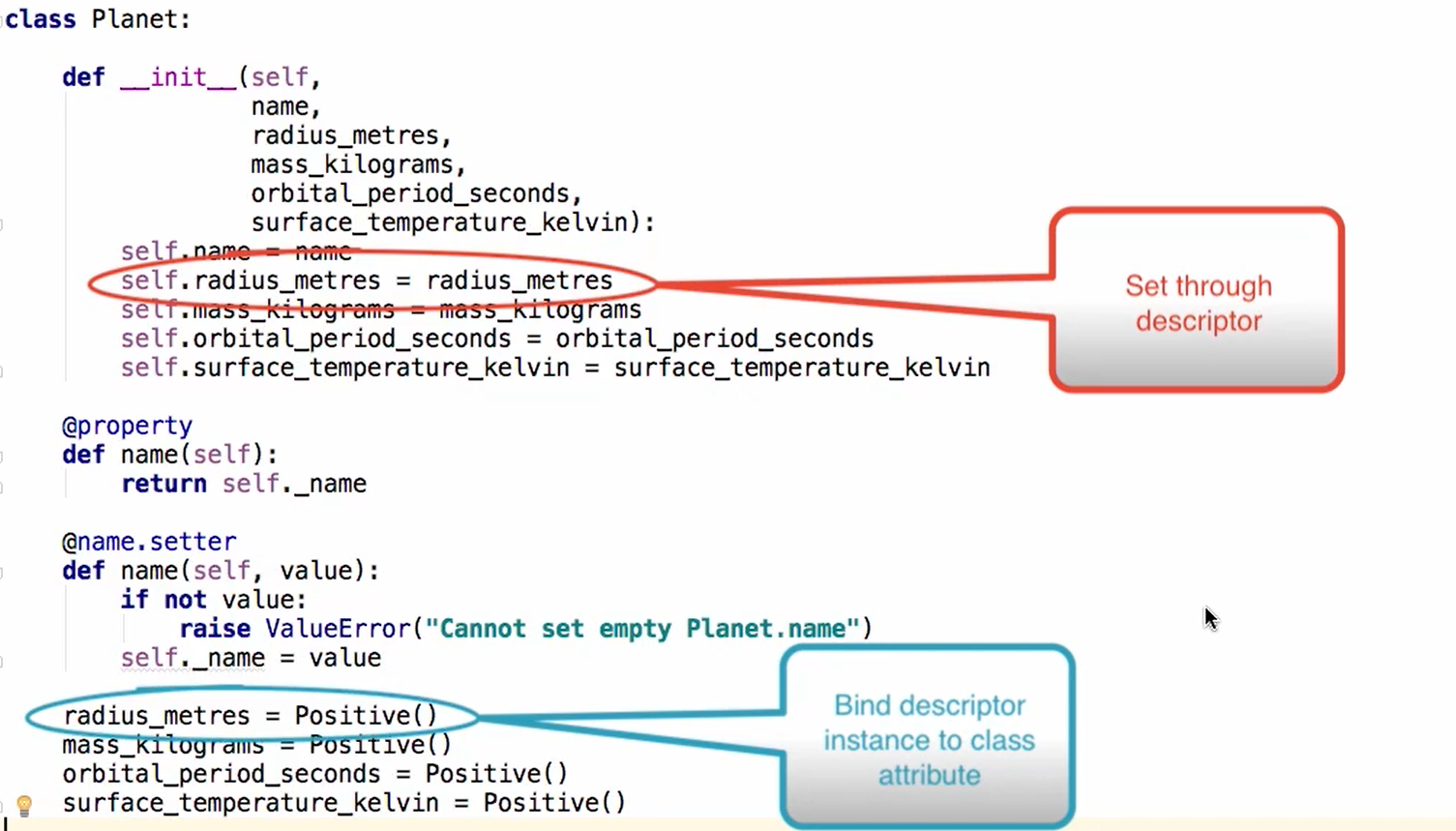
ex:
backend of descriptor

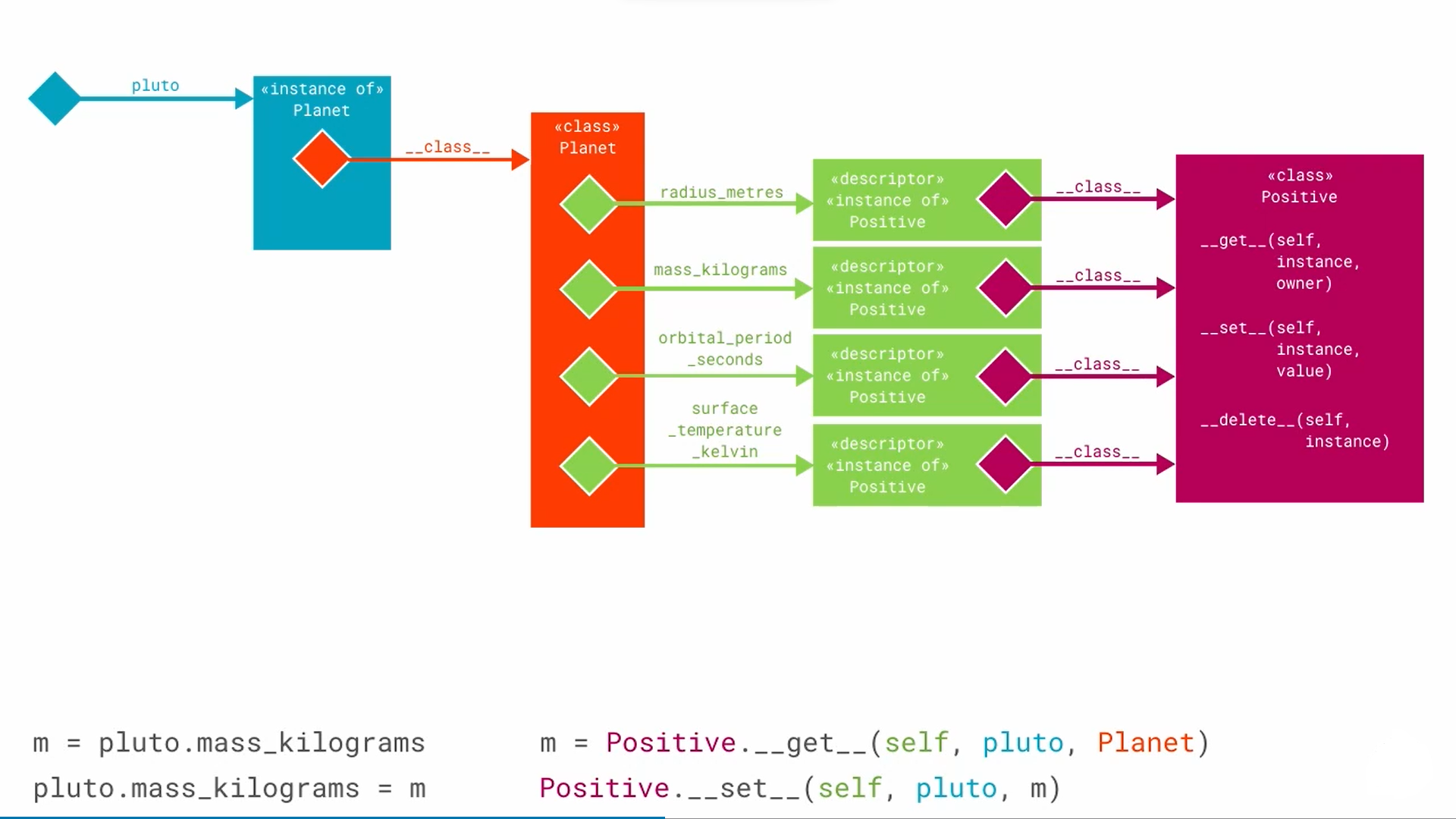
Data vs Non-Data descriptors
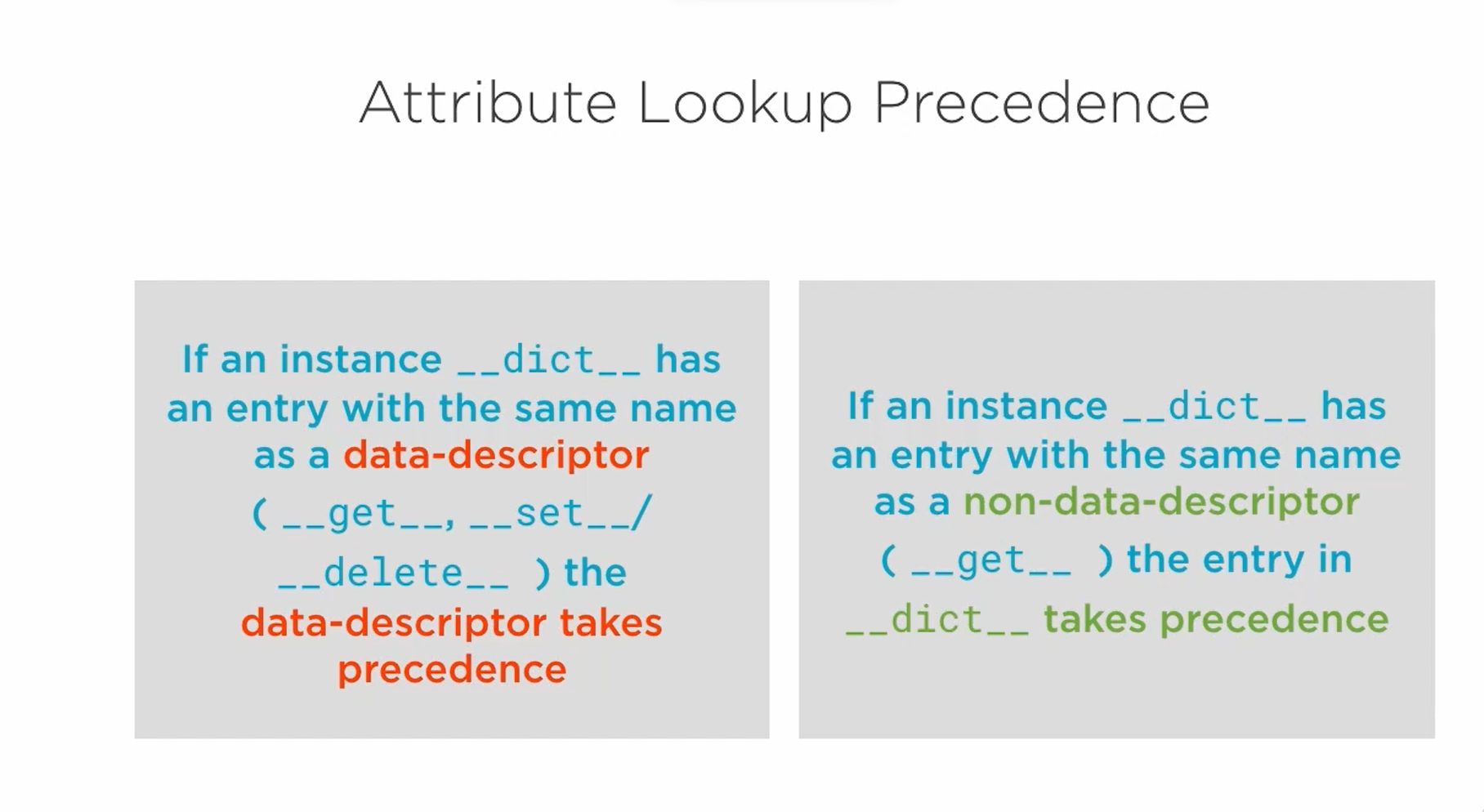
Attributes Lookup precedence

__new__
__new__ is a static method that returns the object for the class.
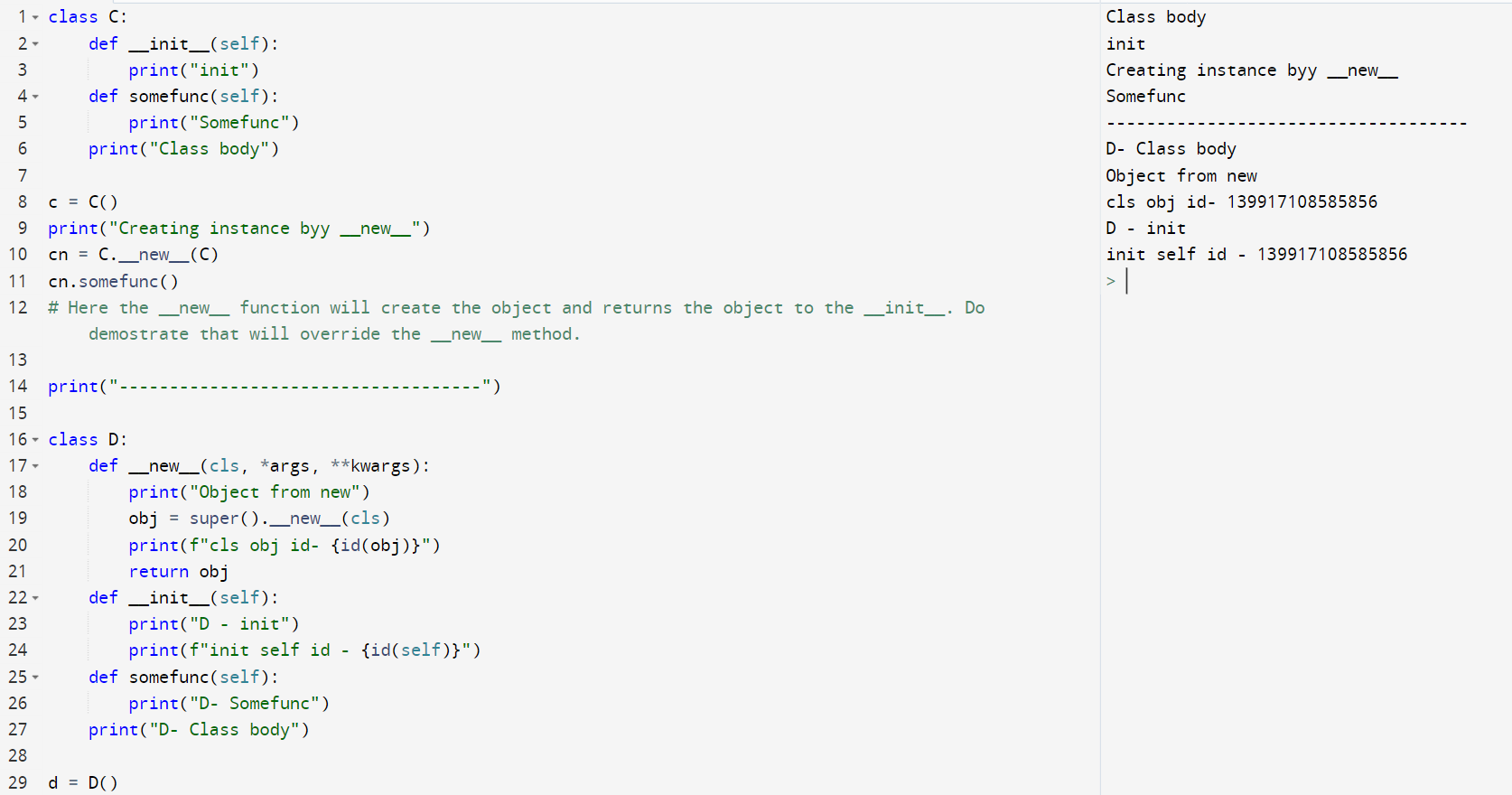
The Object created by the new method is been used by the init to initialize the values for the create instance.
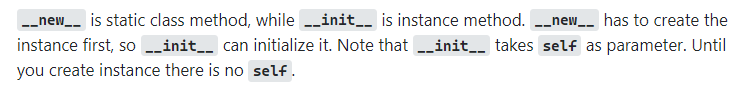
__new__ vs __init__
new - creation
init - initialization

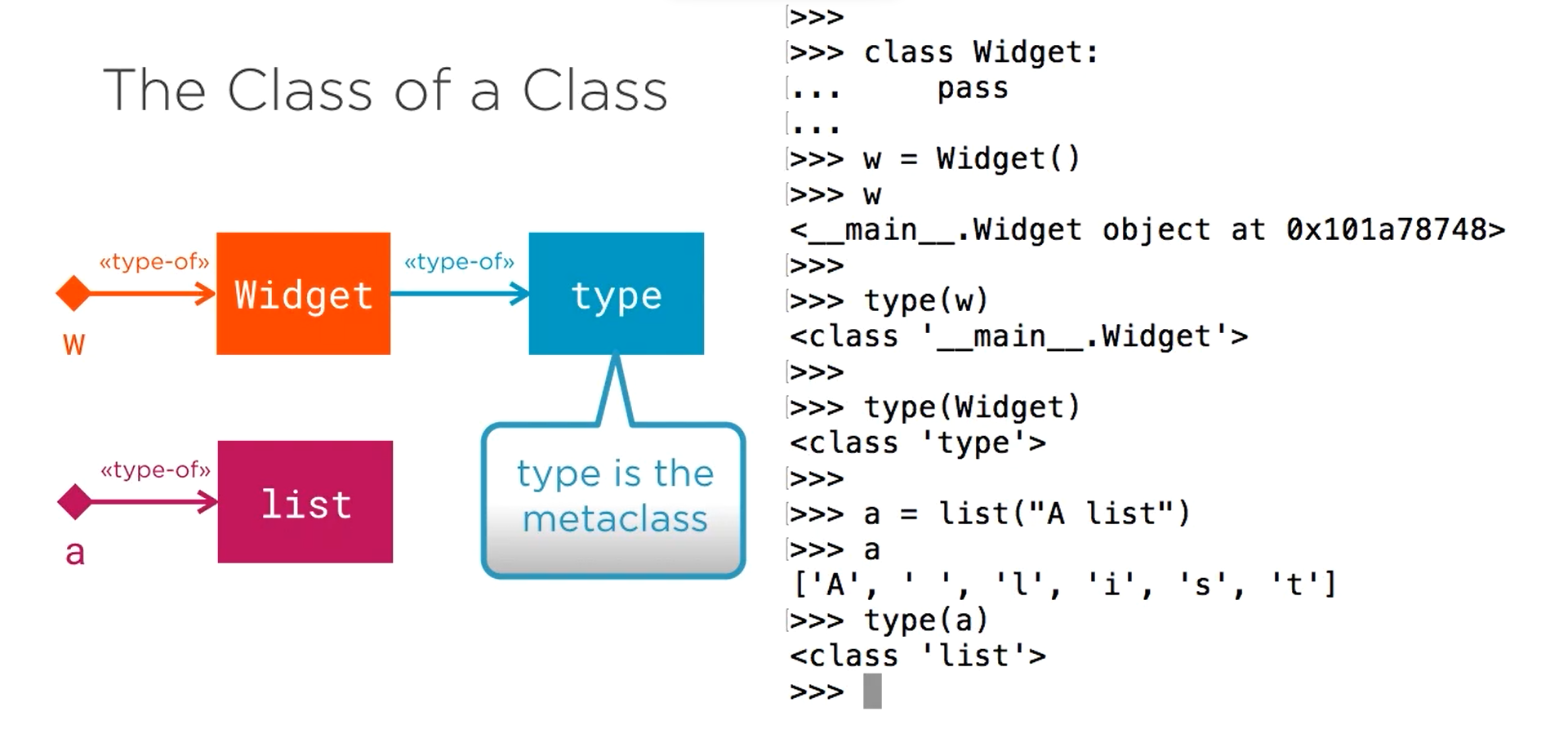
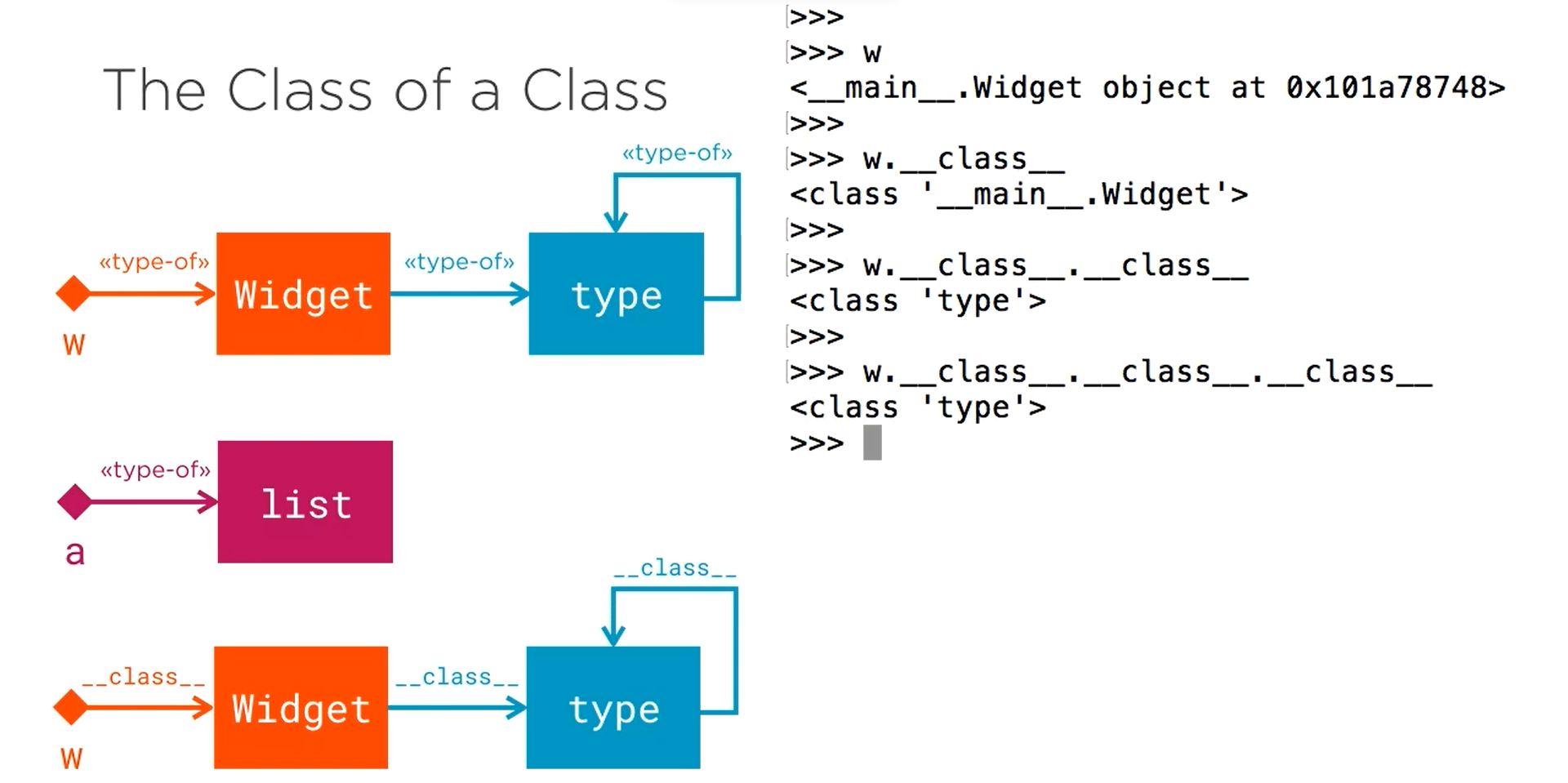
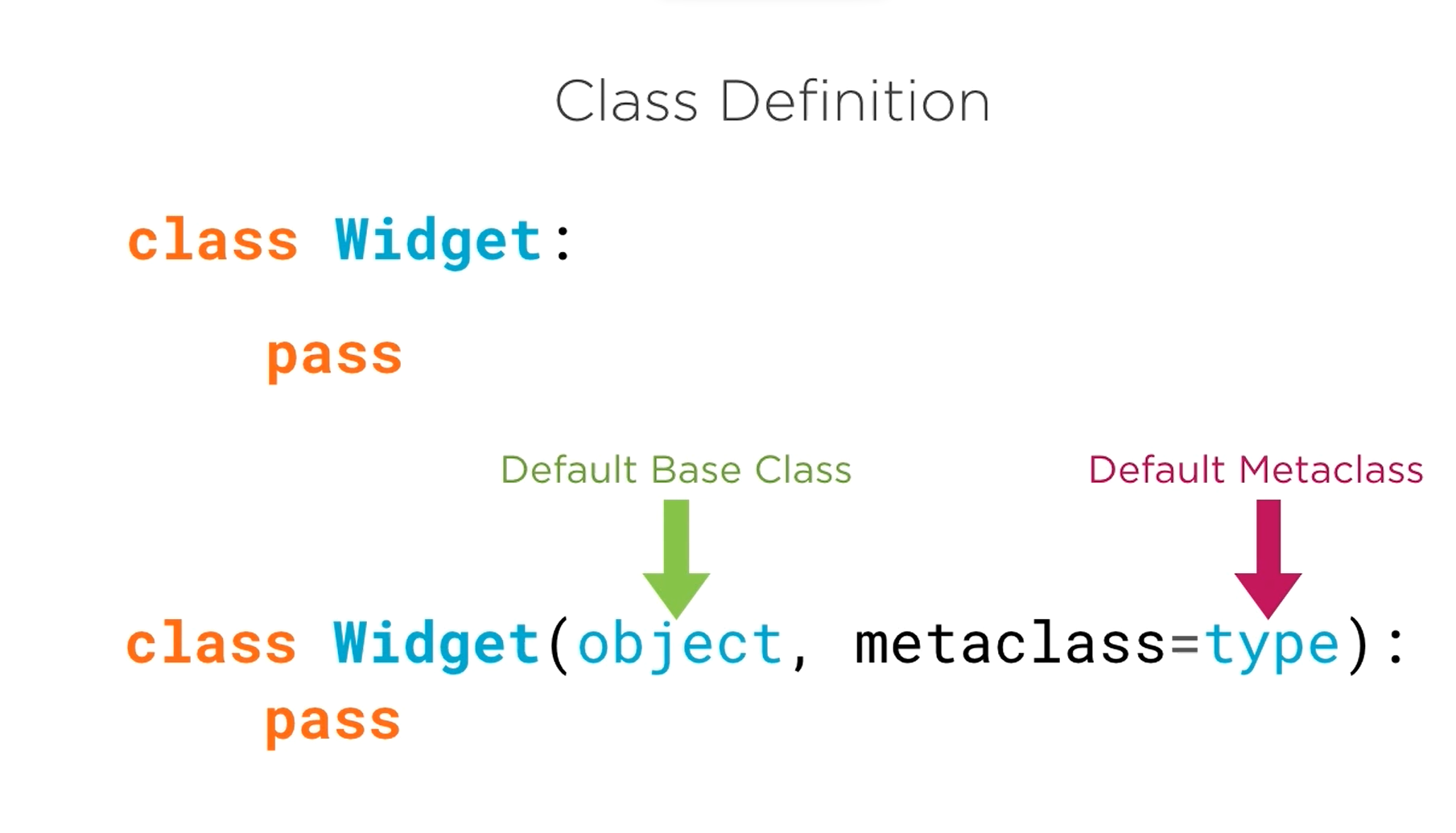
Metaclass
not much info i have provided
Abstract Class


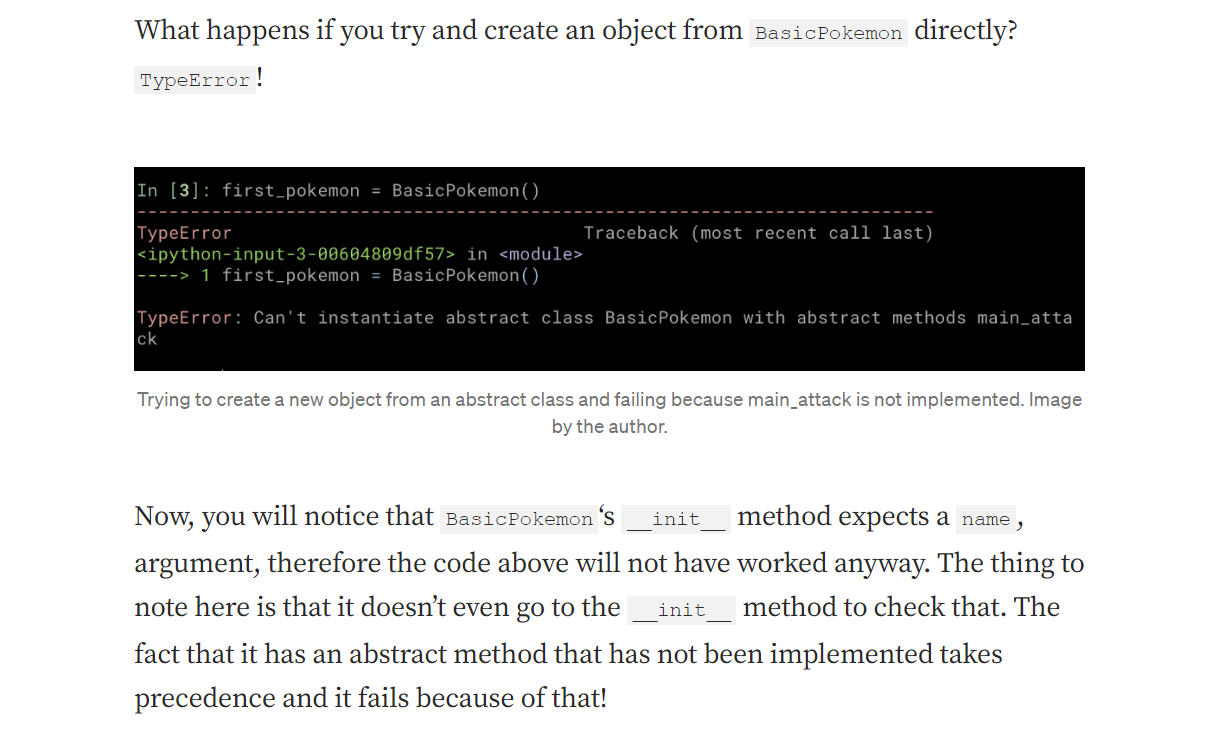




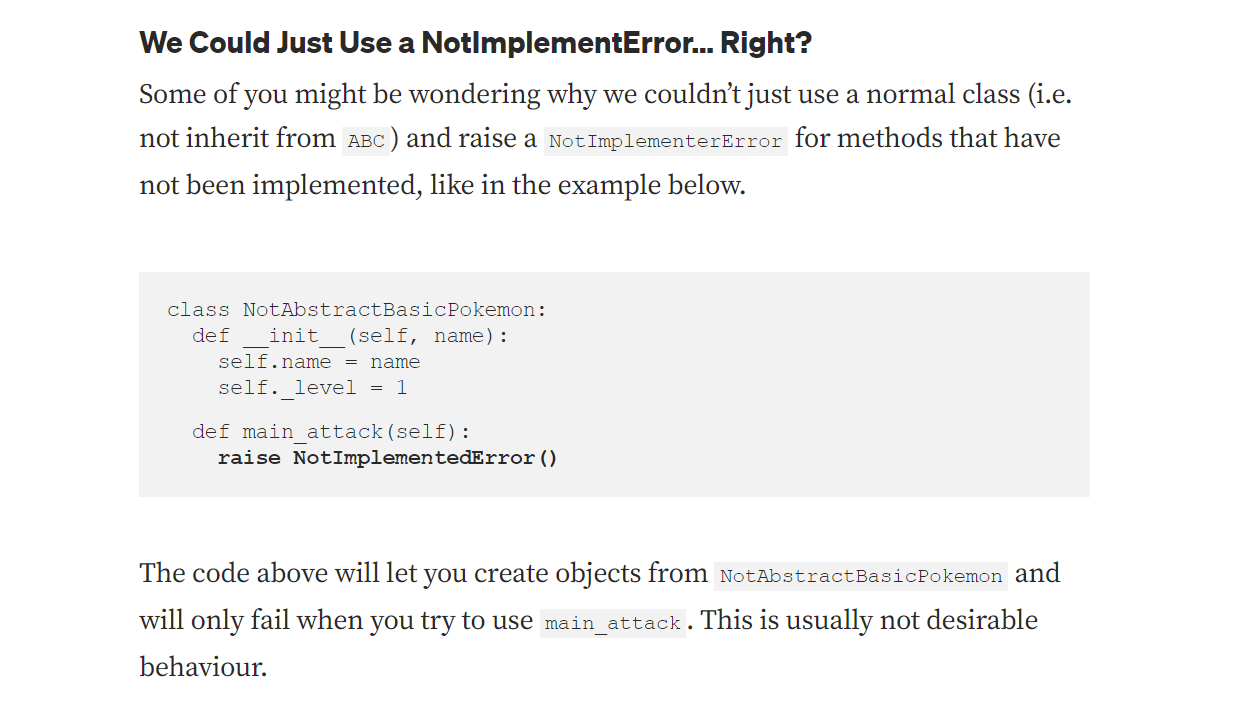
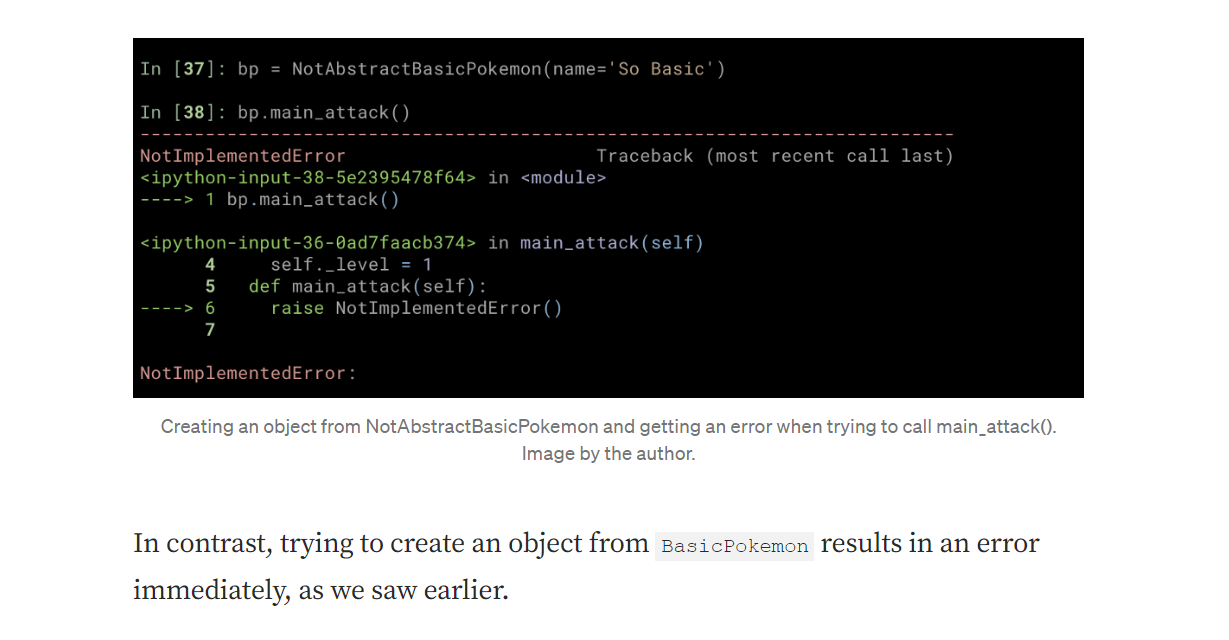

ABC library helps to create the Abstract class

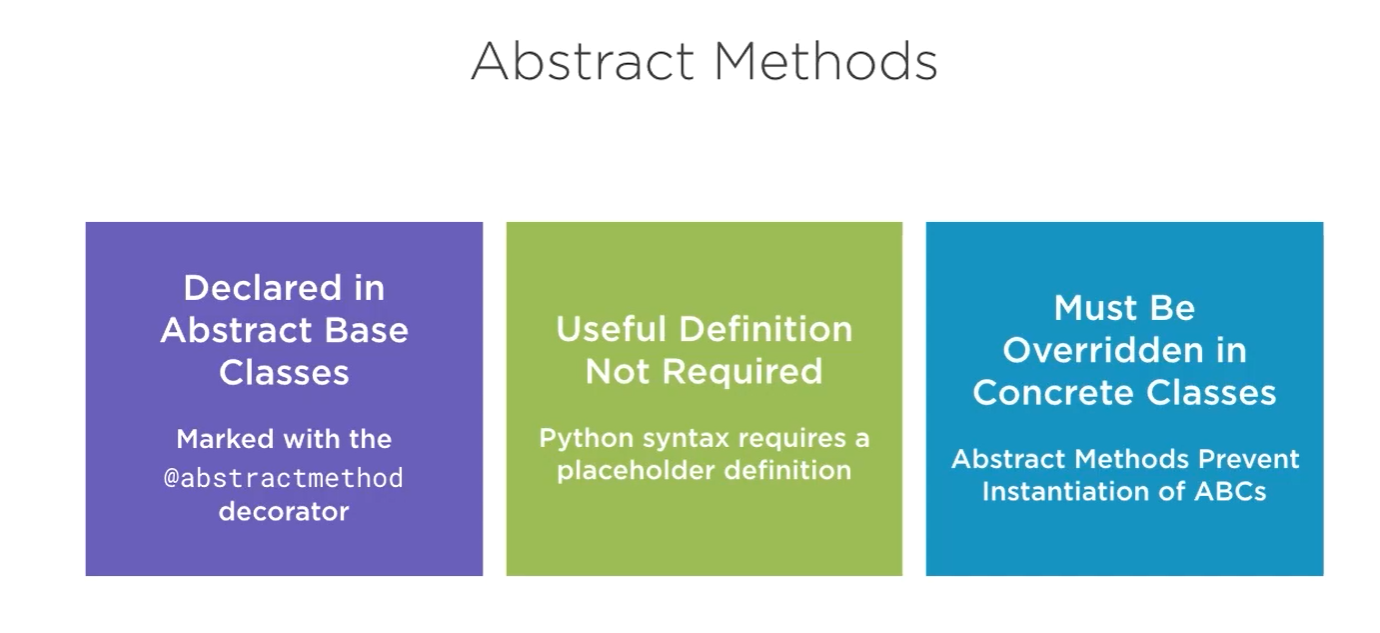
abstract method
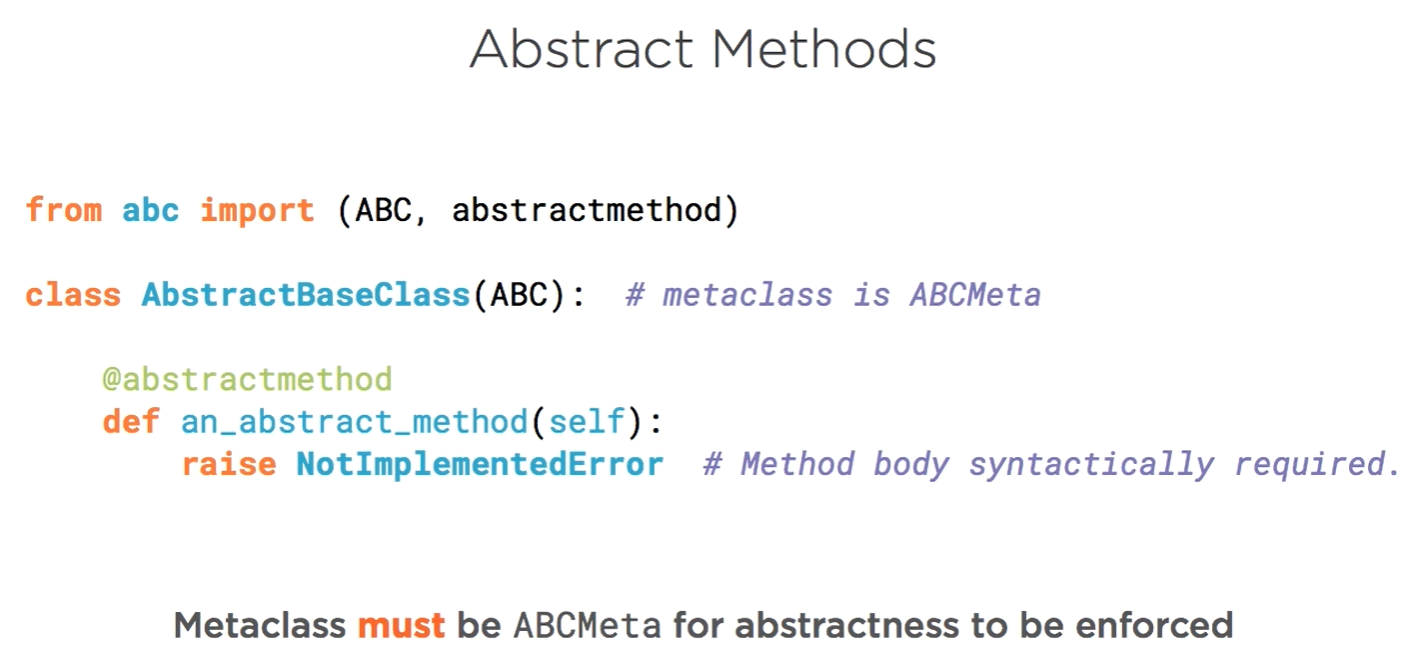
Concrete class
Opposite to the abstract class.. We can create object for the concrete class.