Home - LogeshVel/learning_resources GitHub Wiki
Networking

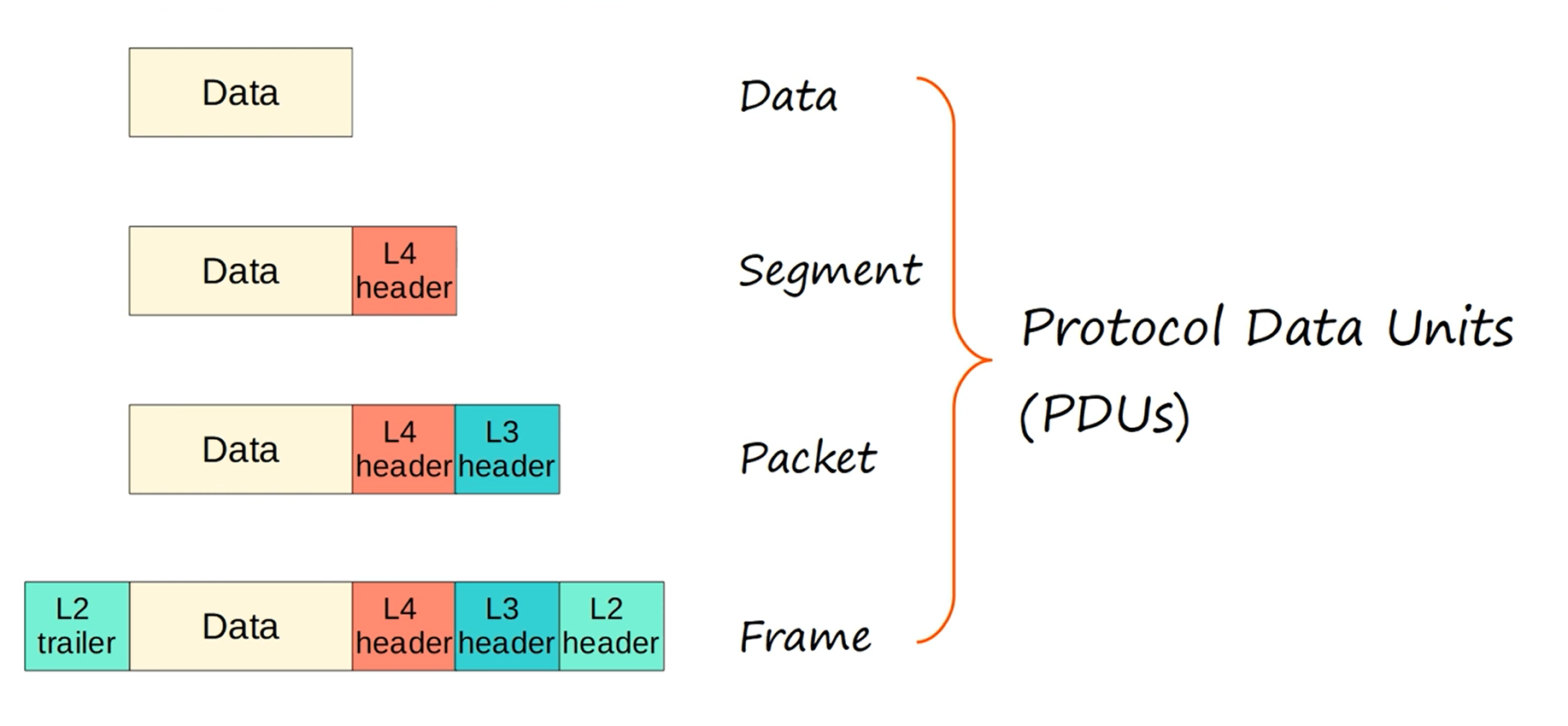
Header sizes
Ethernet headers are typically 14 bytes (Destination/Source MAC + Type) or 18 bytes with VLAN tags, while the IP header size varies: IPv4 is 20 bytes (minimum) to 60 bytes (with options), and IPv6 has a fixed 40-byte header, simplifying routing by removing variable fields like IHL and checksums, relying on extension headers instead.
Ethernet Header
• Standard Ethernet Header: 14 bytes (Destination MAC (6) + Source MAC (6) + Type (2)).
• With VLAN Tag (802.1Q): Adds 4 bytes, making the header 18 bytes.
• Note: The Preamble (7 bytes) and Start Frame Delimiter (SFD, 1 byte) are part of physical layer framing, not usually counted in the header size for MTU purposes.
IPv4 Header
• Minimum Size: 20 bytes (no options).
• Maximum Size: 60 bytes (with options, in 4-byte increments).
• Key Fields: Includes Internet Header Length (IHL) to define variable length, Header Checksum, Fragmentation fields.
IPv6 Header
• Fixed Size: 40 bytes.
• Key Changes from IPv4: No IHL, no Header Checksum, no Fragmentation fields (handled by source via extension headers), Flow Label introduced, Hop Limit (instead of TTL), Next Header (instead of Protocol).
Fundamentals
ACL
Short Forms
ALPN - Application Layer Protocol Negotiation