Contention Free and Contention based mechanism - LogeshVel/802.11 GitHub Wiki
Contention is a media access method that is used to share a broadcast medium. In contention, any computer in the network can transmit data at any time (first come-first served).
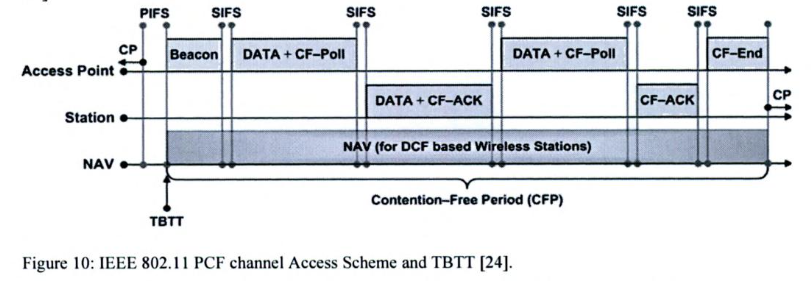
Contention Free Access using PCF

PCF media access method has the higher priority than the DCF scheme



PCF Mode


The polling list
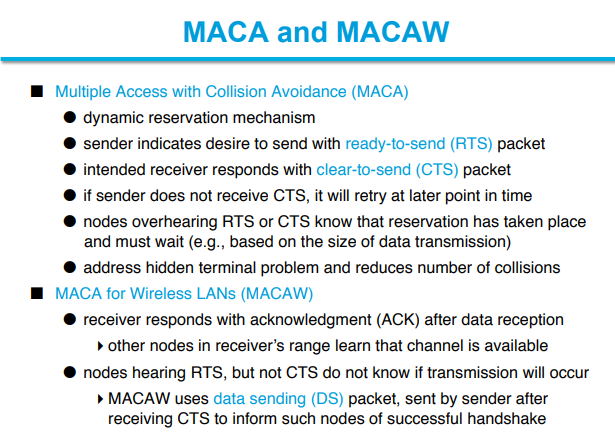
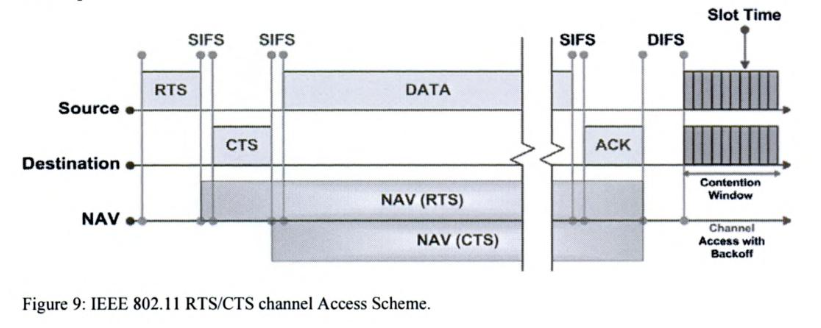
After the access point has gained control of the wireless medium, it polls any associated stations on a polling list for data transmissions. During the contention-free period, stations may transmit only if the access point solicits the transmission with a polling frame. Contention-free polling frames are often abbreviated CF-Poll. Each CF-Poll is a license to transmit one frame. Multiple frames can be transmitted only if the access point sends multiple poll requests.
The polling list is the list of privileged stations solicited for frames during the contention free period. Stations get on the polling list when they associate with the access point. The Association Request includes a field that indicates whether the station is capable of responding to polls during the contention-free period.
CF-Ack
This frame is used by stations to acknowledge the receipt of a frame when no data needs to be transmitted. Contention-free acknowledgments are longer than the standard control frame acknowledgment, so this frame may not be used in actual implementations.
CF-Poll
CF-Poll frames are sent by the access point to a mobile station to give the mobile station the right to transmit a single buffered frame. It is used when the access point does not have any data for the mobile station. When a frame for the mobile station is available, the access point uses the Data+CF-Poll frame type.
Data+CF-Ack
This frame combines data transmission with an acknowledgment. Data is directed to the frame recipient; the acknowledgment is for the previous frame transmitted and usually is not for the recipient of the data.
Data+CF-Poll
This frame is used by access points to transmit data to a mobile station and request one pending frame from the mobile station. The Data+CF-Poll can only be sent by the access point during the contention-free period.
CF-ACK+CF-Poll
This frame acknowledges the last frame from one of the access point's clients and requests a buffered frame from the next station on the polling list. It is directed to the next station on the polling list, though the acknowledgment may be intended for any mobile station associated with the access point.
Data+CF-ACK+CF-Poll
This frame brings together the data transmission, polling feature, and acknowledgment into one frame for maximum efficiency.
CF-End
This frame ends the contention-free period and returns control of the medium to the contention-based mechanisms of the DCF.
CF-End+CF-Ack
This is the same as the CF-End frame but also acknowledges the previously transmitted Data frame.
Examples
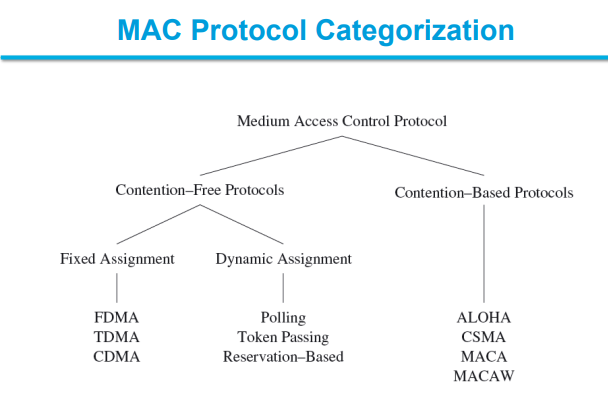
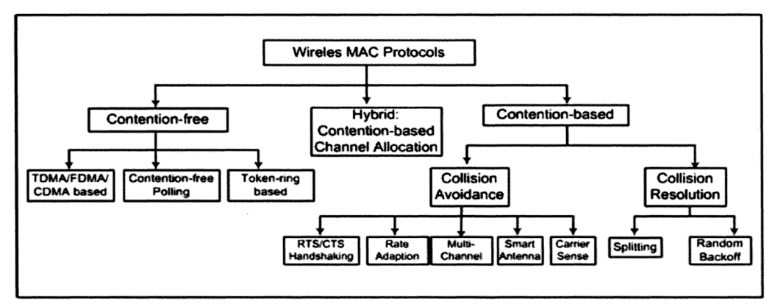
FDMA, CDMA, SDMA and TDMA are examples of contention-free MAC protocols.
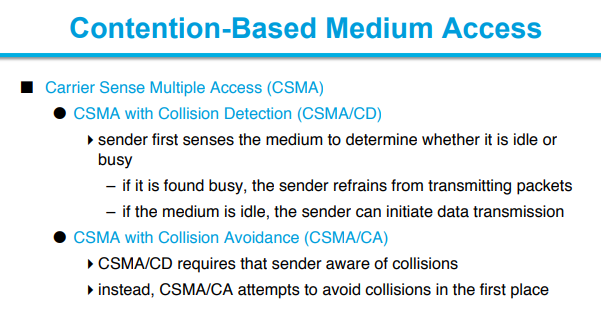
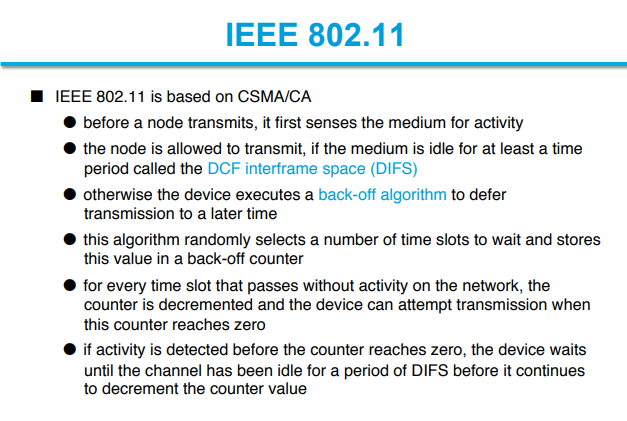
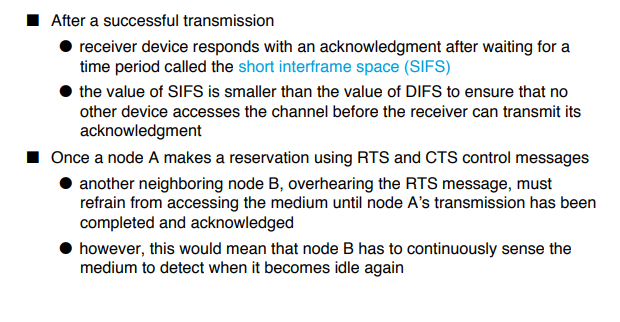
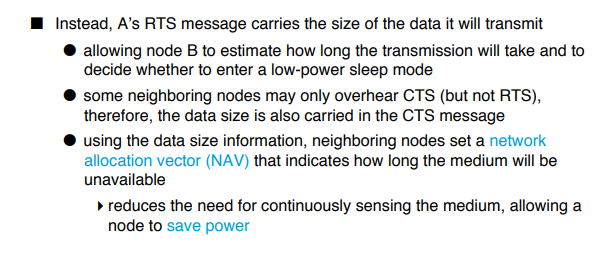
Contention Based Access using DCF
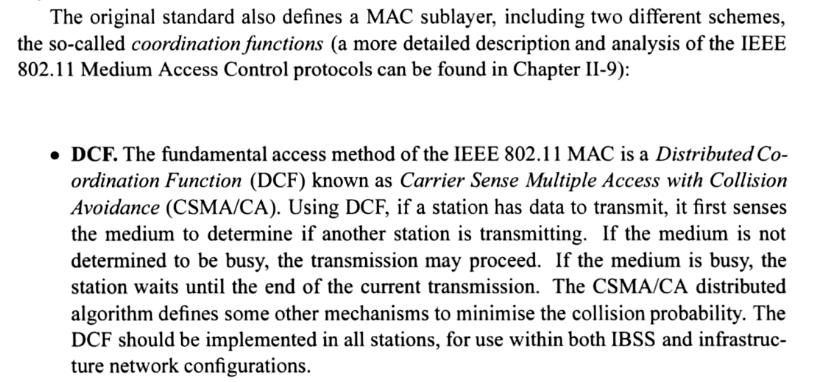
A contention-based protocol (CBP) is a communications protocol for operating wireless telecommunication equipment that allows many users to use the same radio channel without pre-coordination. The "listen before talk" operating procedure in IEEE 802.11 is the most well known contention-based protocol.