Multi DEG - Kan-E/RNAseqChef GitHub Wiki
Multi DEG detects and visualizes differentially expressed genes by LRT(likelihood ratio test) DESeq2.
Two types of raw count data formats can be used as input.
The analysis can only be performed with raw count data if the following conditions are fulfilled:
- The replication number is represented by the underline “_”.
- Do not use the underline "_" for anything else.
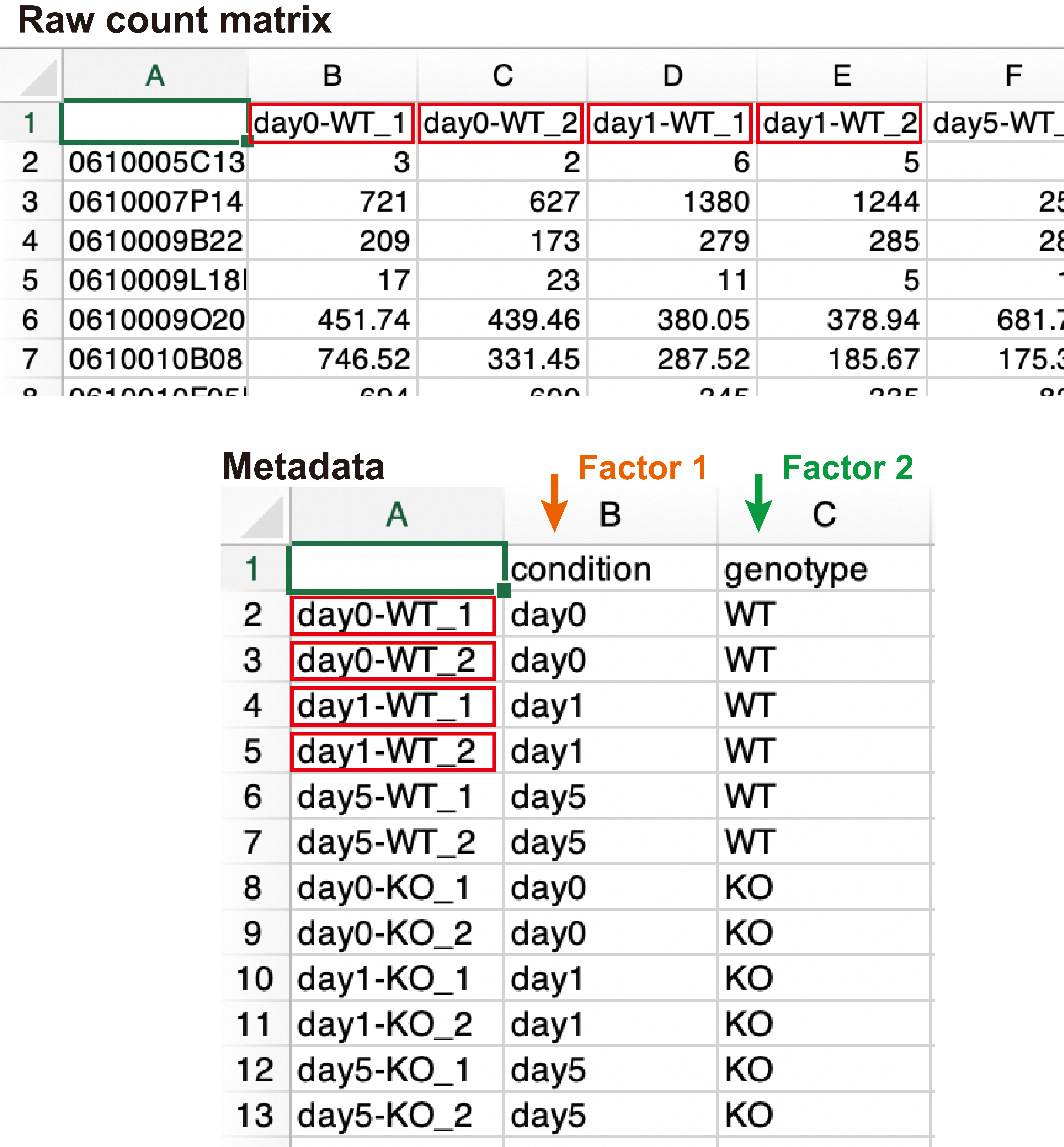
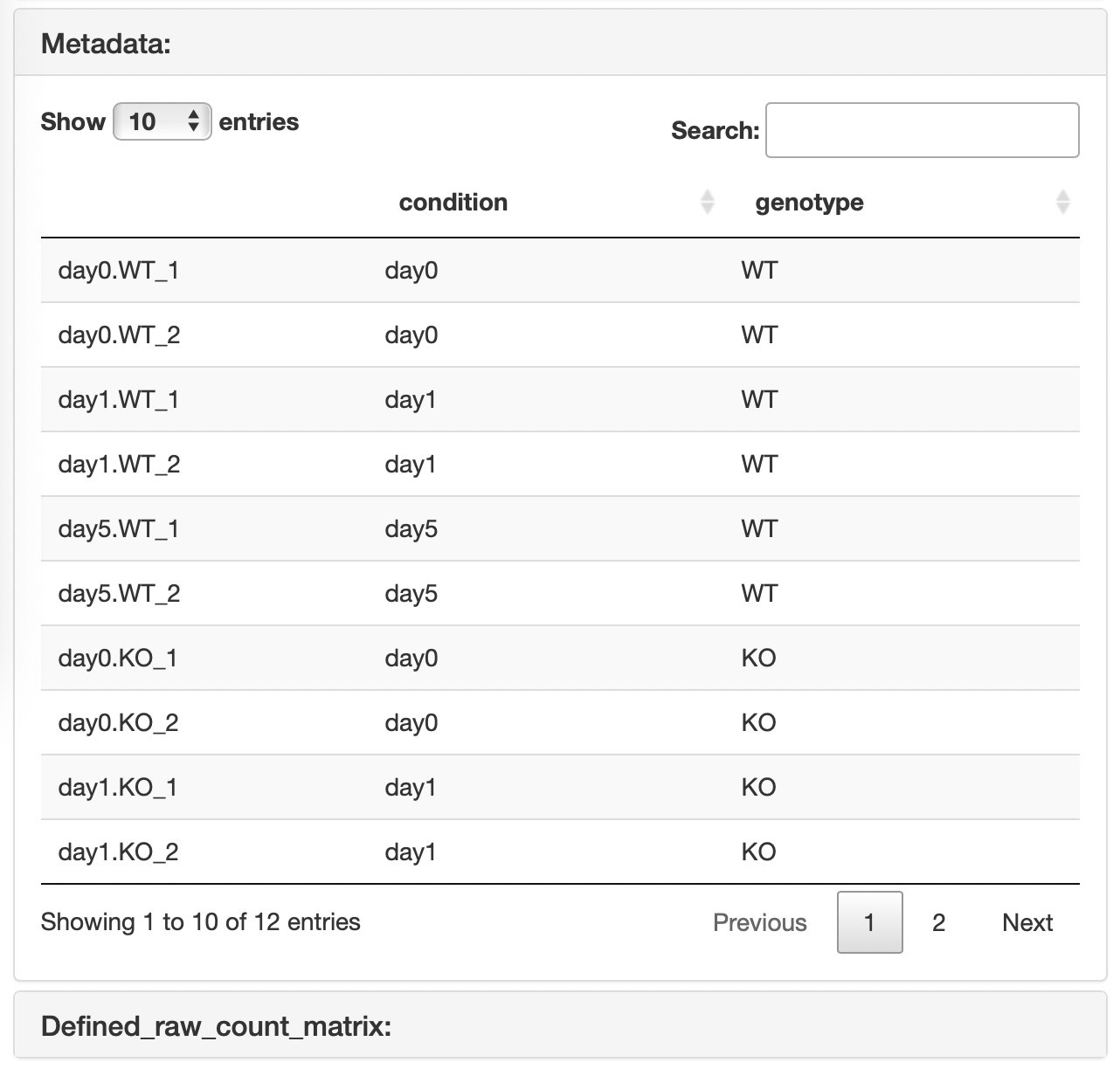
In this format, the results of a two-factor multiple comparison can be visualized. Metadata must contain the following information:
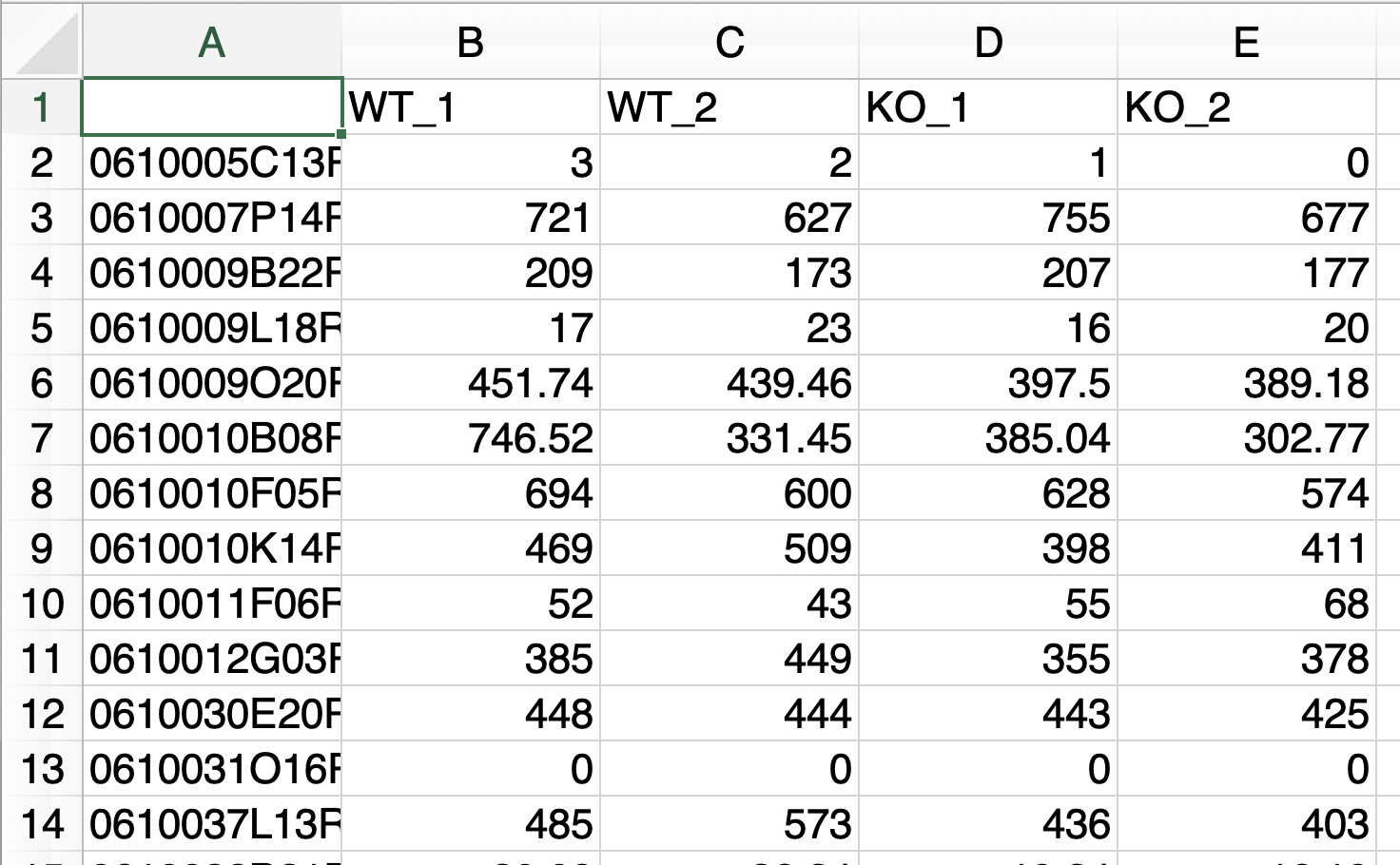
- The first column is the sample name used in the raw count data.
- In the first column, the replication number is represented by the underline “_”.
- The second column is the corresponding first condition name that matches the sample name in the first column.
- The third is the corresponding second condition name that matches the sample name in the first column.
The following three types of FDR methods can be selected if the DEG analysis method is DESeq2 or edgeR.
- BH, Benjamini-Hochberg method (default)
- Qvalue, Storey method
-
IHW, Independent Hypothesis Weighting
The following analysis is performed by selecting the dataset species.
- Conversion to gene symbols if the gene name is ENSEMBL ID
- Enrichment analysis
Three types of thresholds can be set: fold change, FDR, and base mean.
The base mean cut-off can be set using the uploaded normalized count data, such as TPM counts.
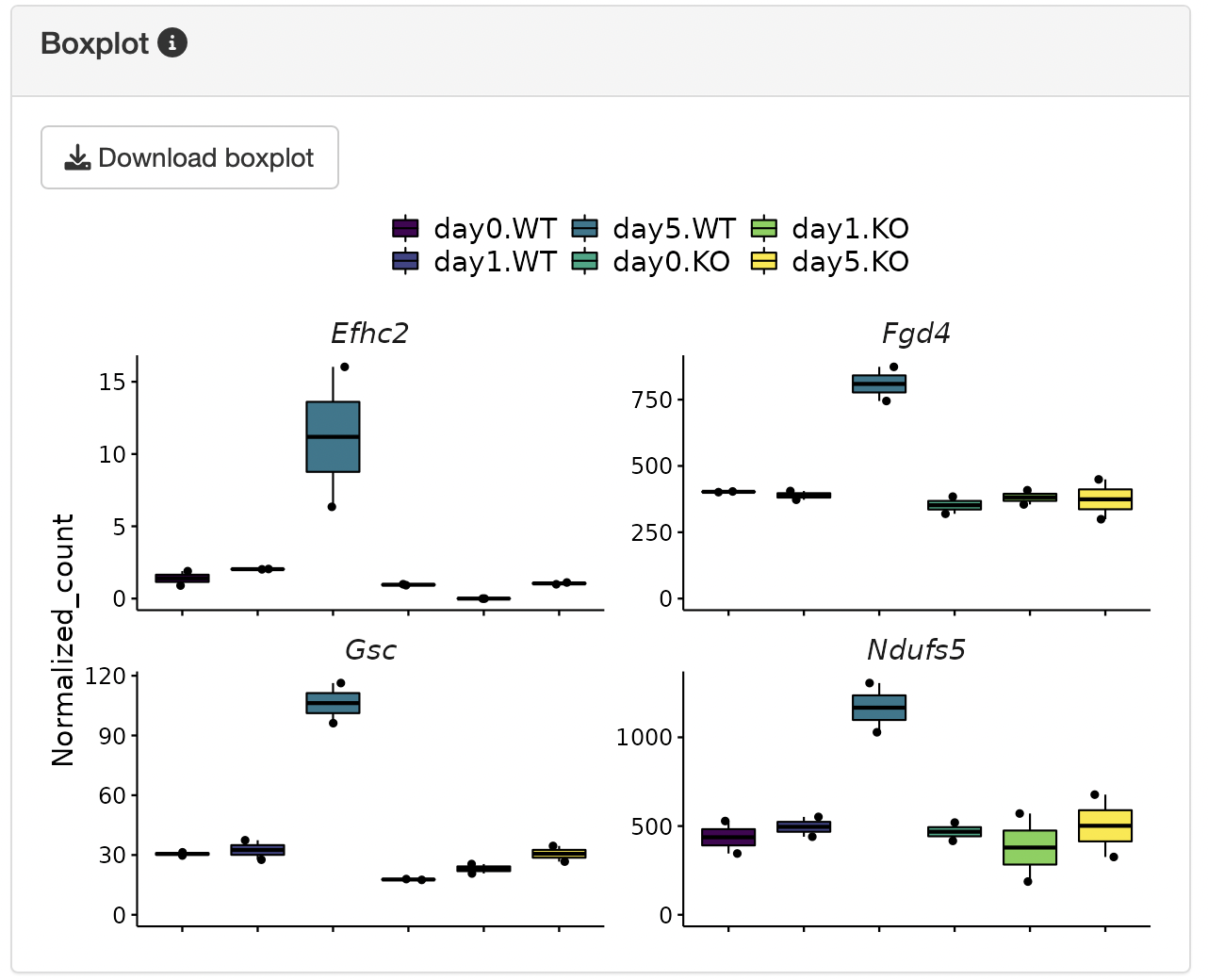
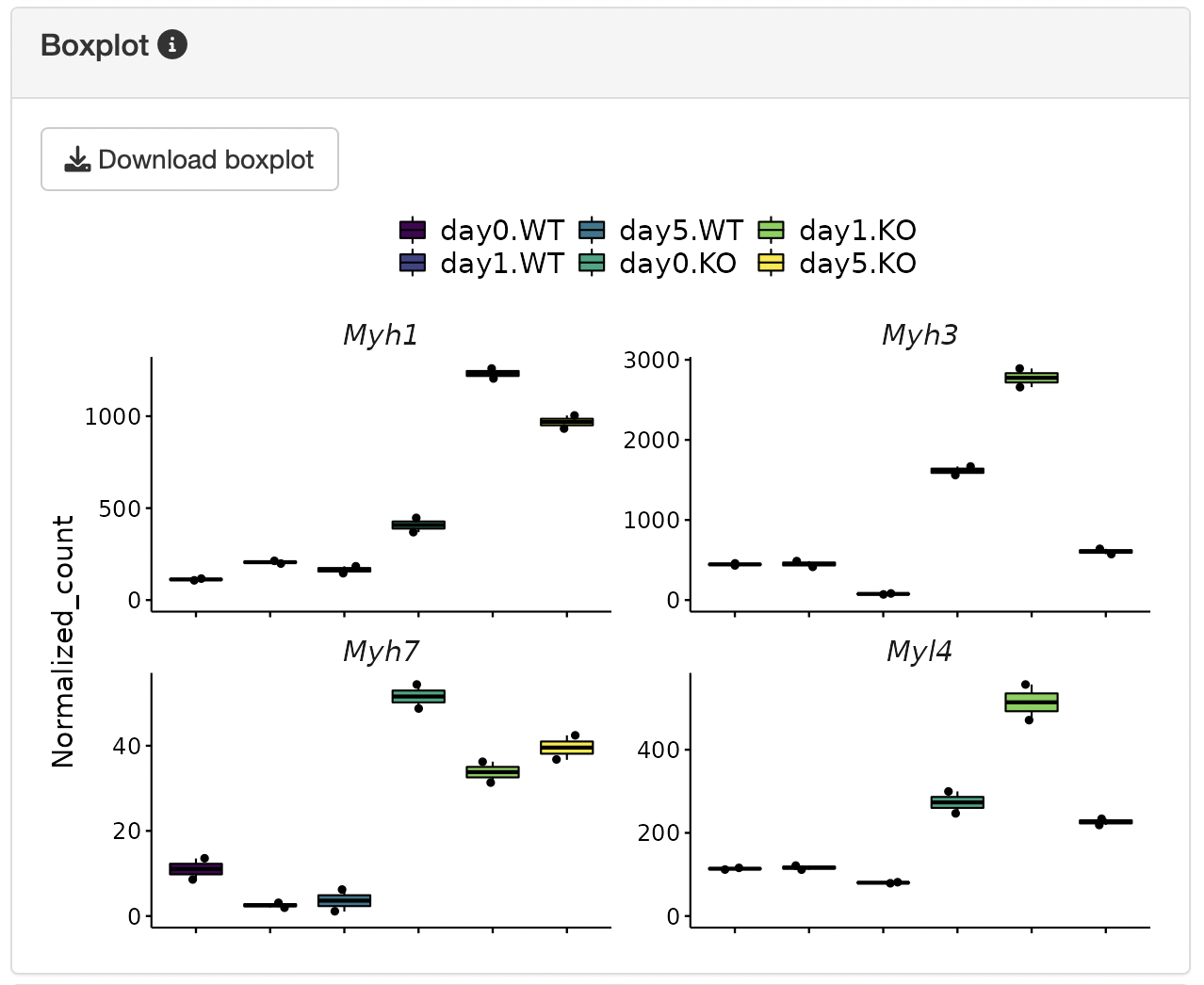
The y-axis of the boxplot can be displayed using the uploaded normalized count data.
Note: Uploading raw count data is not unnecessary.
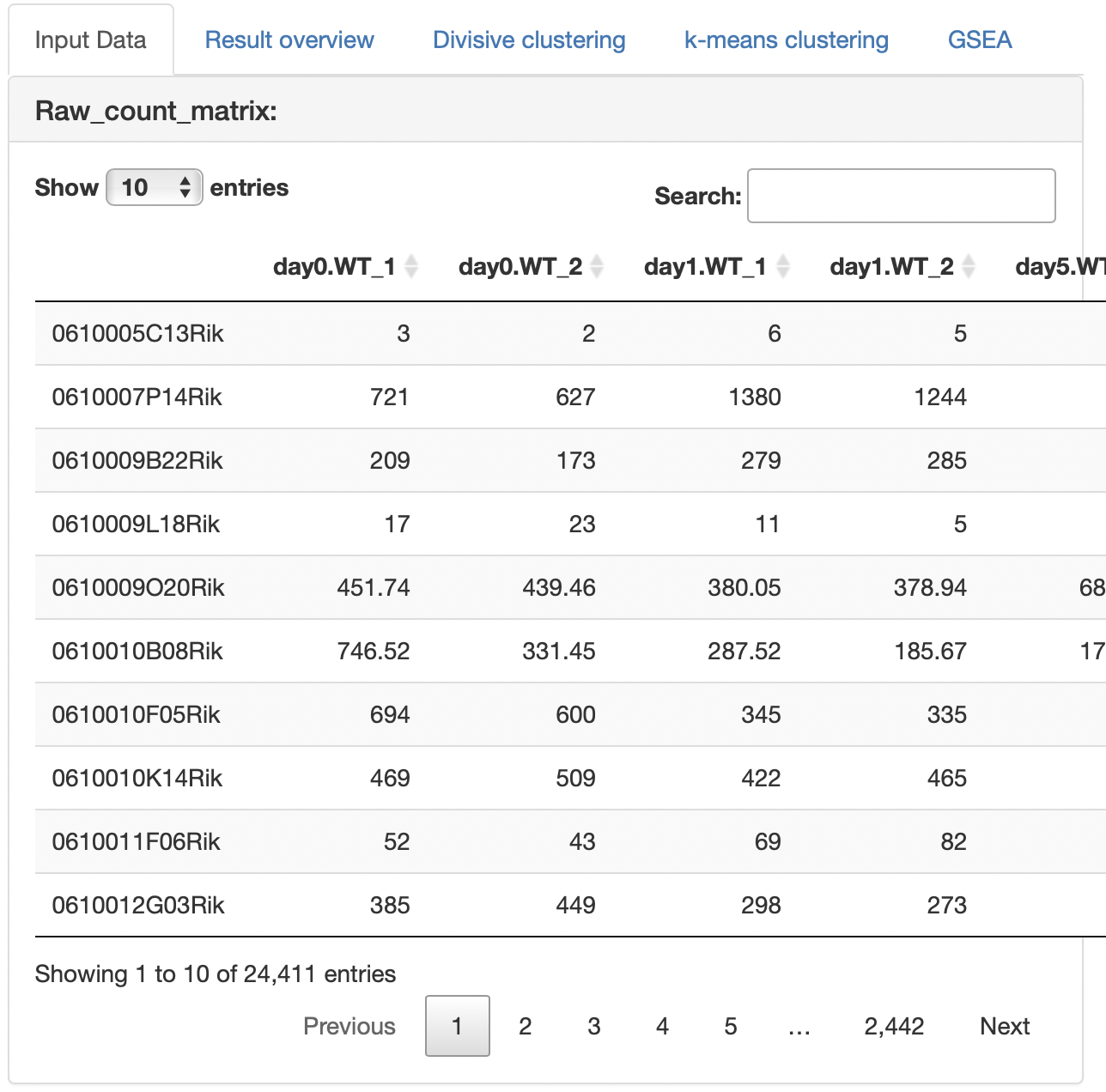
The uploaded raw count data are displayed.
In the case of the "Raw count data + metadata" format, the raw count data that is re-defined using the uploaded metadata.
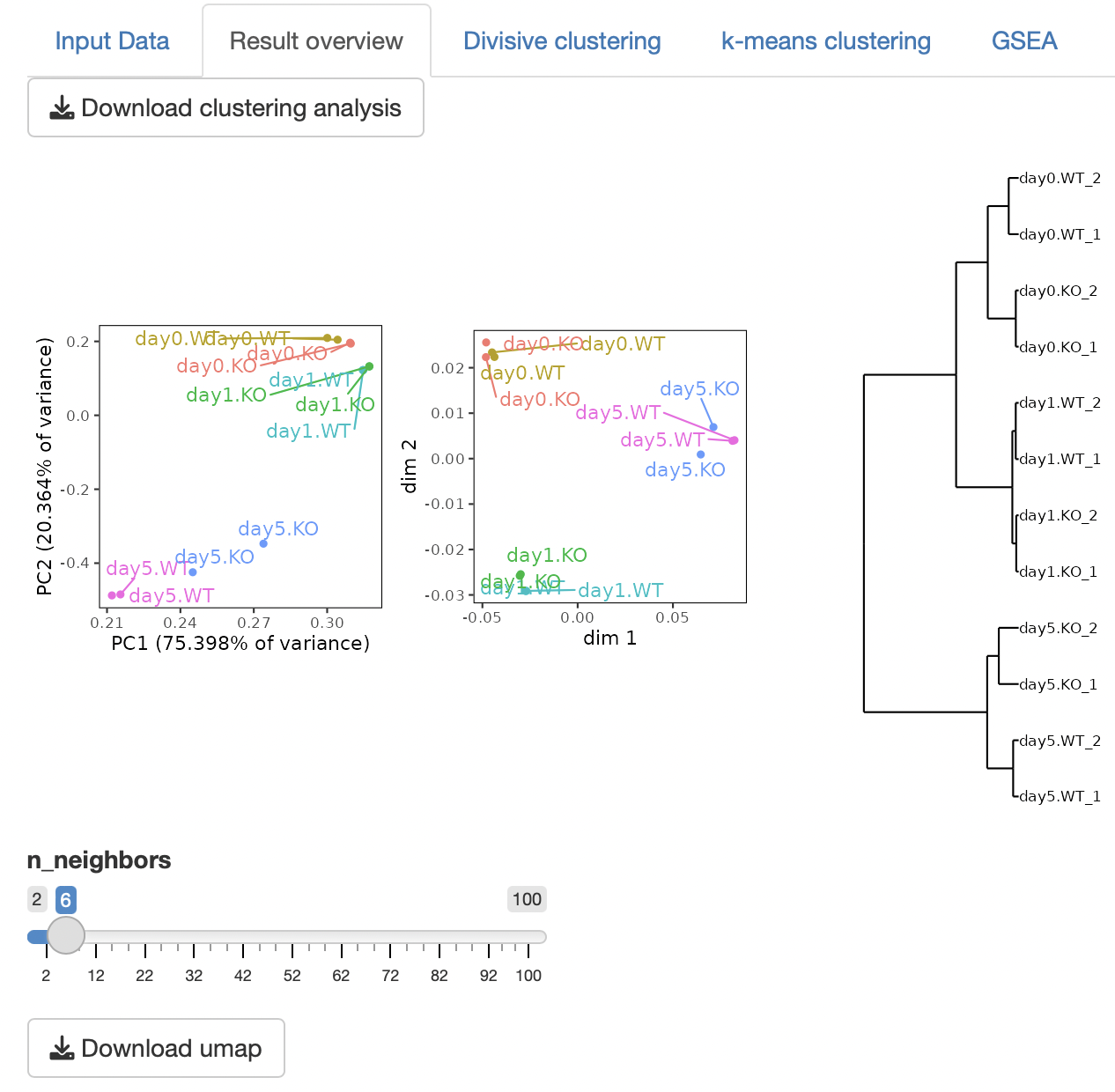
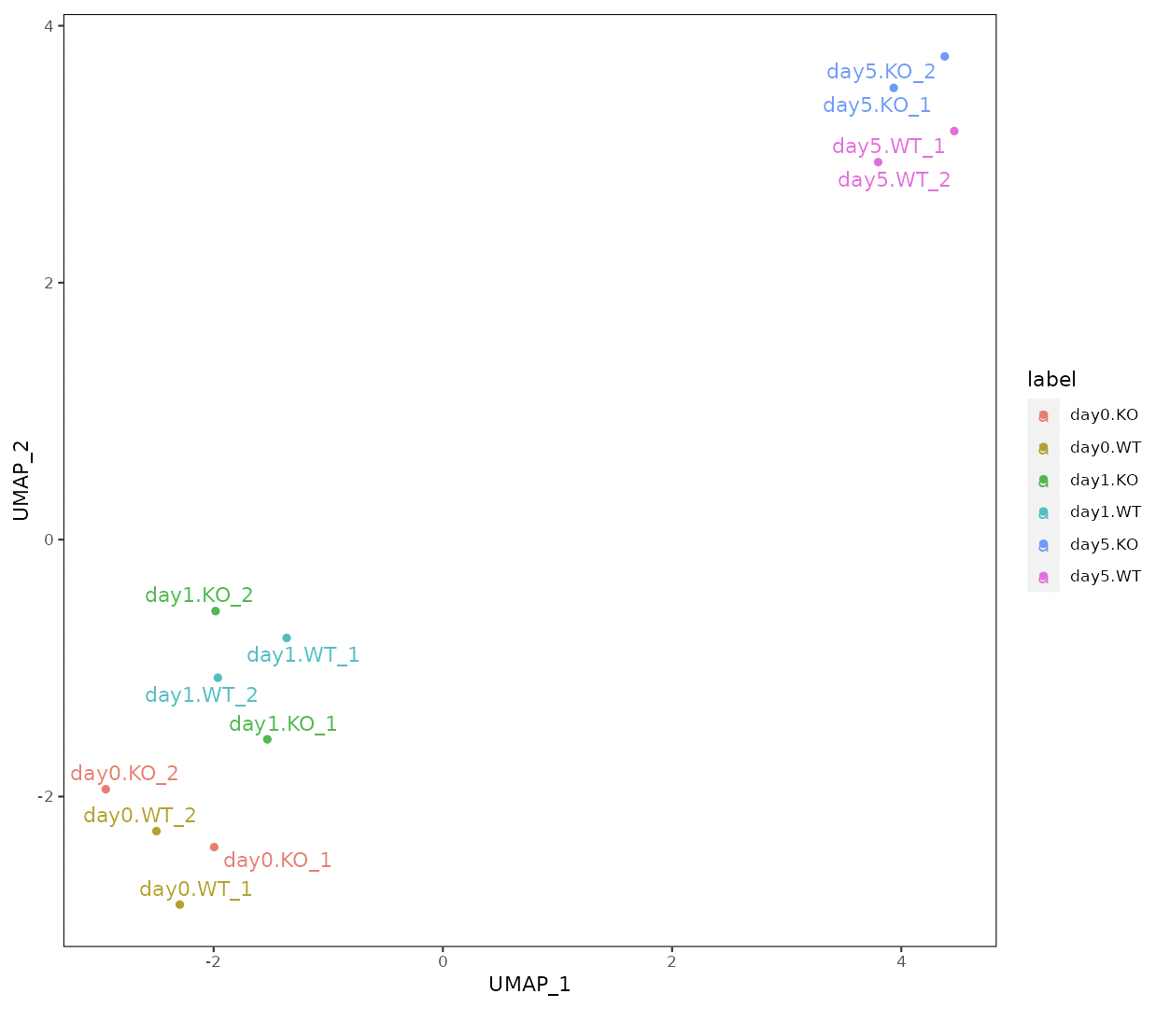
Four types of clustering analyses are performed: principal component analysis (PCA), multidimensional scaling (MDS), hierarchical clustering with ward.D2, and UMAP (uniform manifold approximation and projection).
The result table data of the DEG analysis are displayed.
n_neighbors in UMAP control how UMAP balances the local versus global structure in the data.
Low values of n_neighbors force UMAP to concentrate on very local structures, whereas large values push UMAP to look at the larger neighborhoods of each point.
In the case of a small number of samples, n_neighbors should be small.
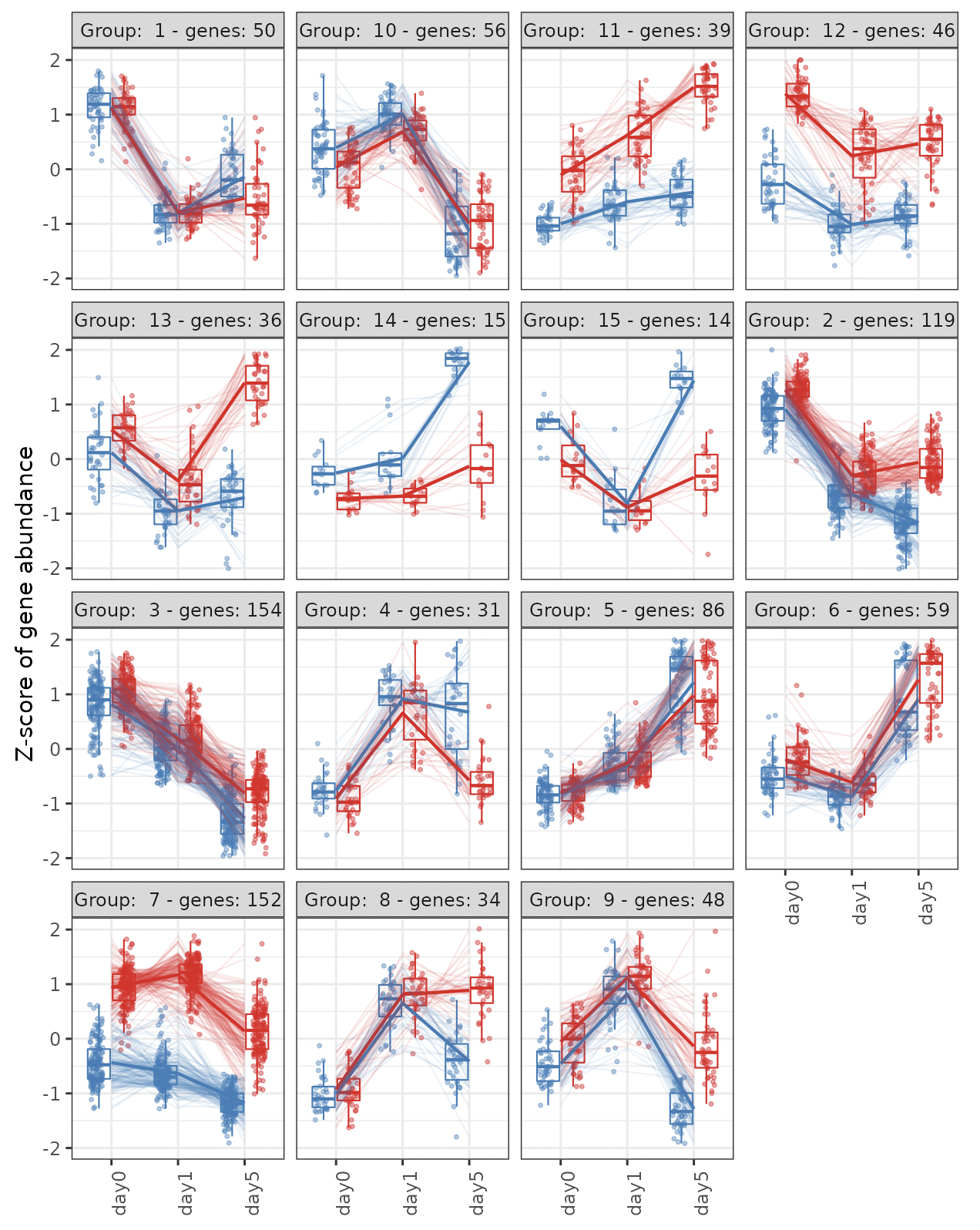
Hierarchical clustering is performed using a top-down clustering approach.
The cluster number is automatically determined.
Boxplots showing the gene expression patterns of each cluster are shown.
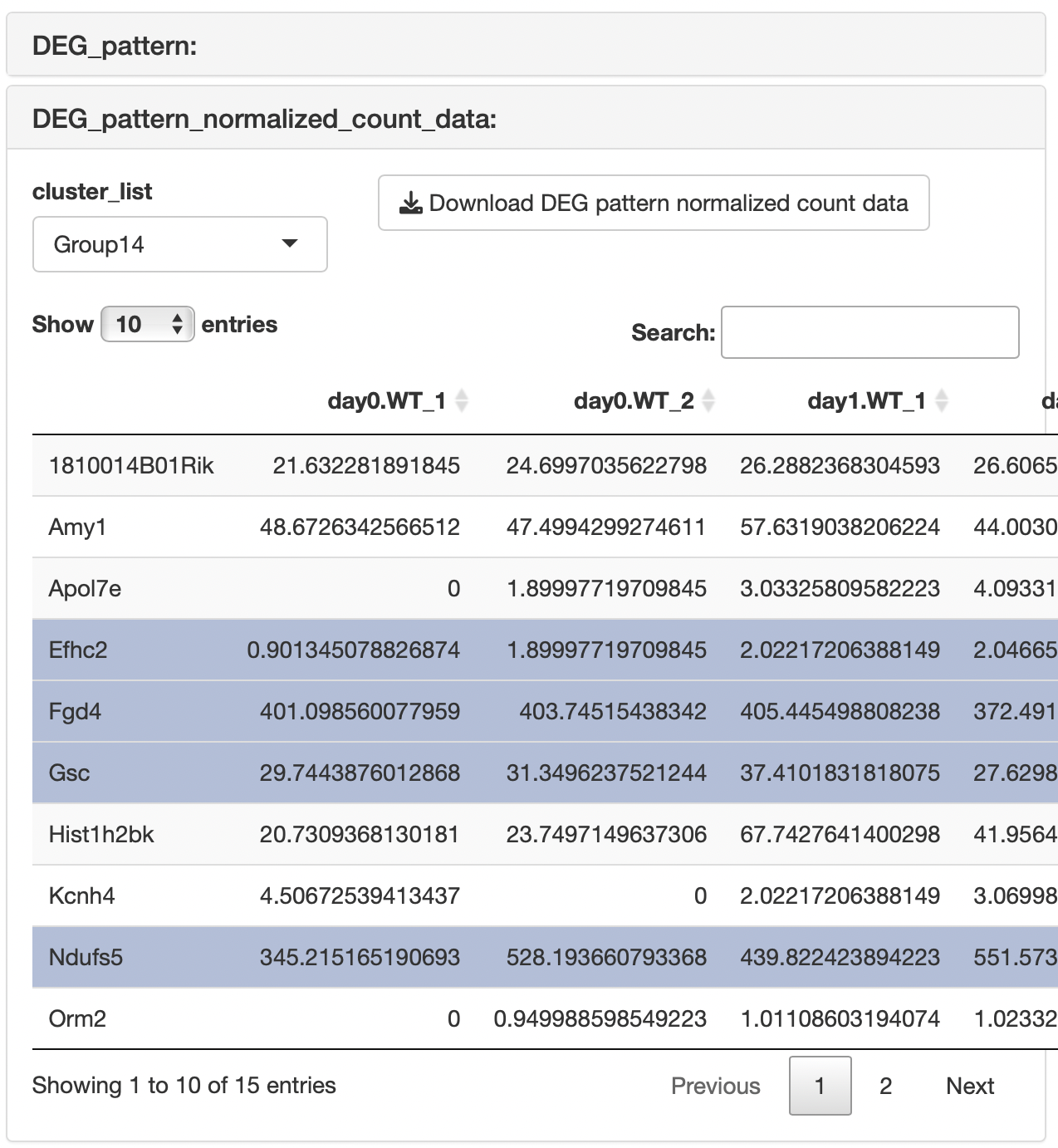
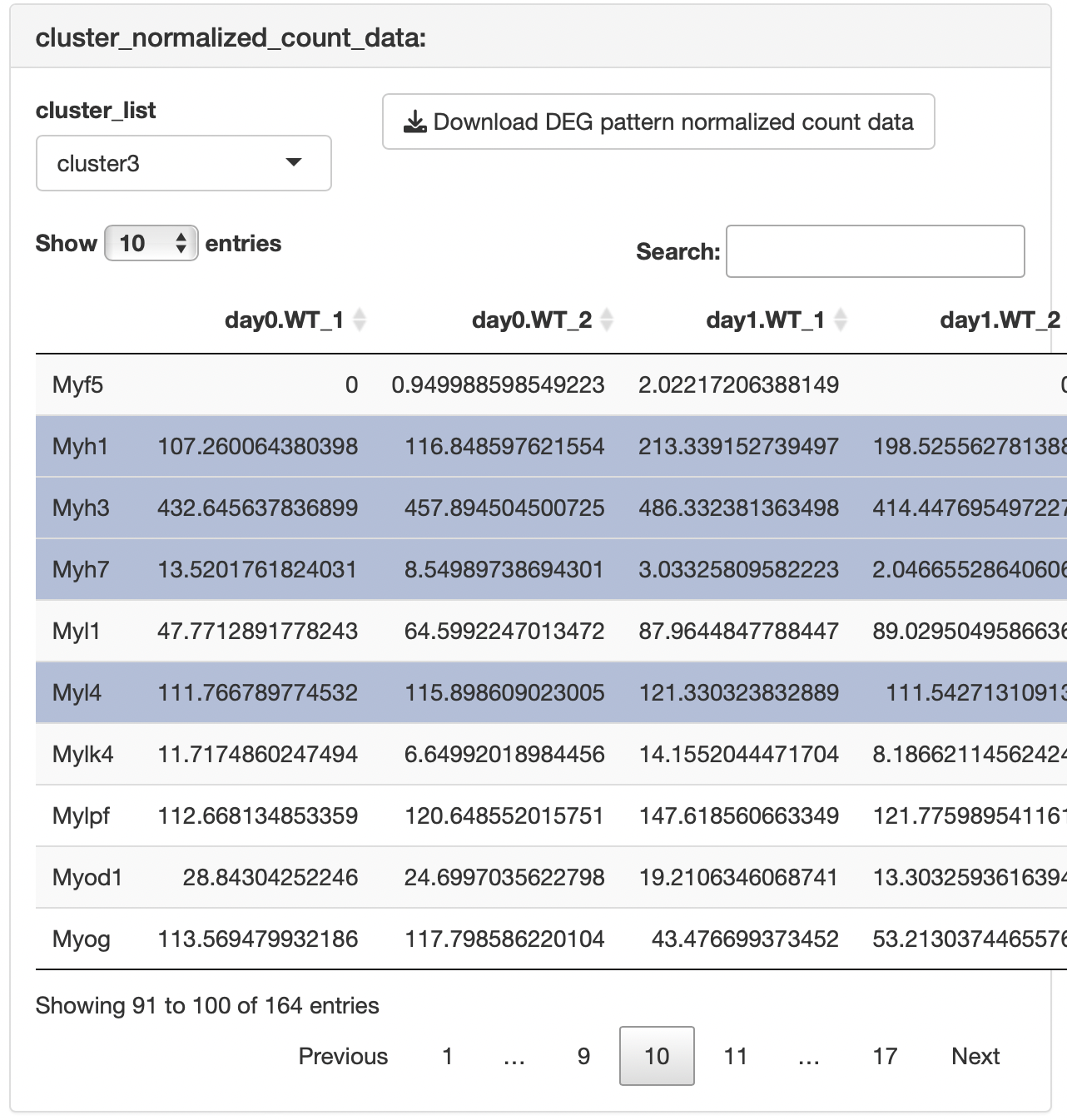
The result table data showing the relationships between genes and clusters are displayed.
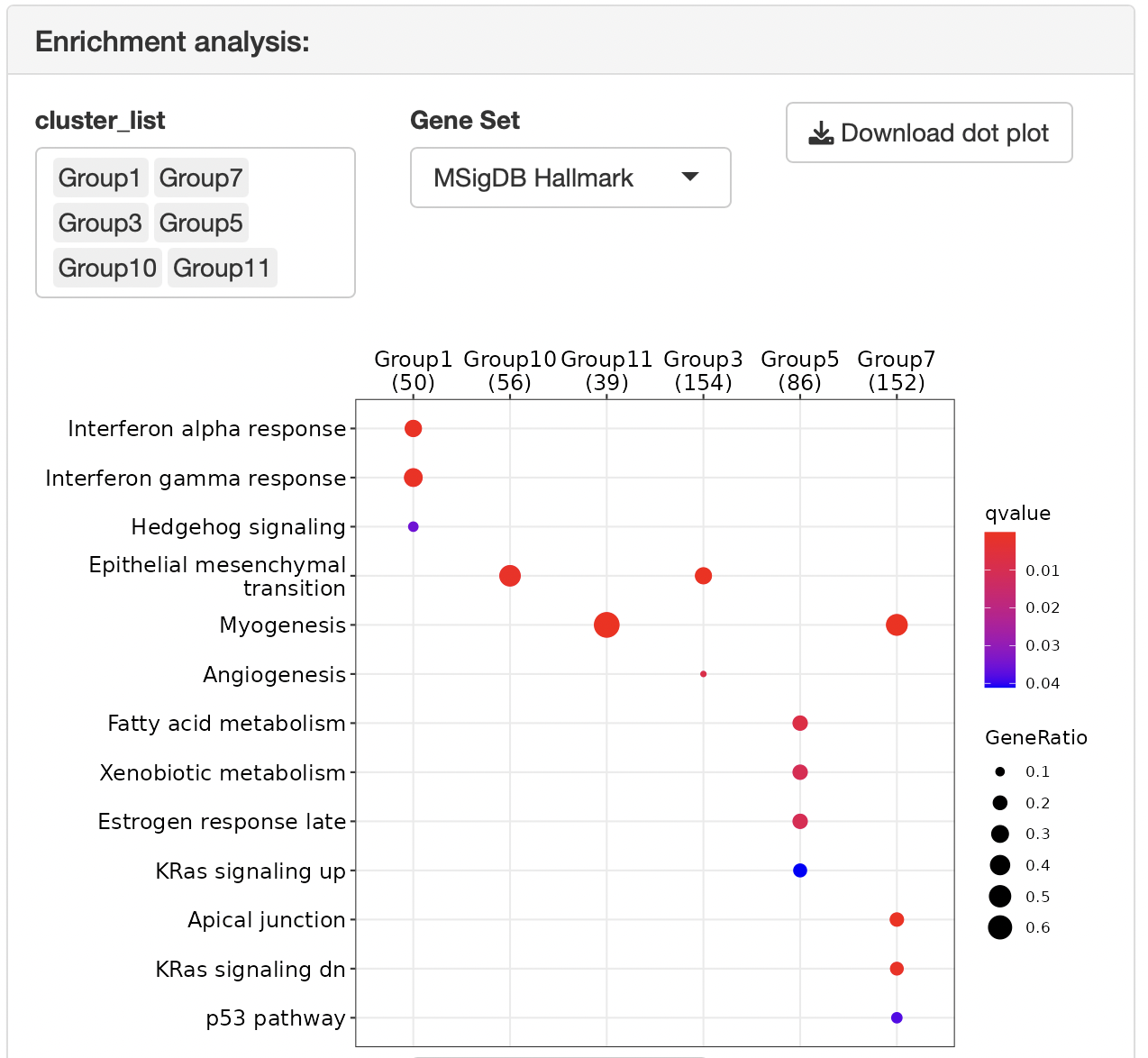
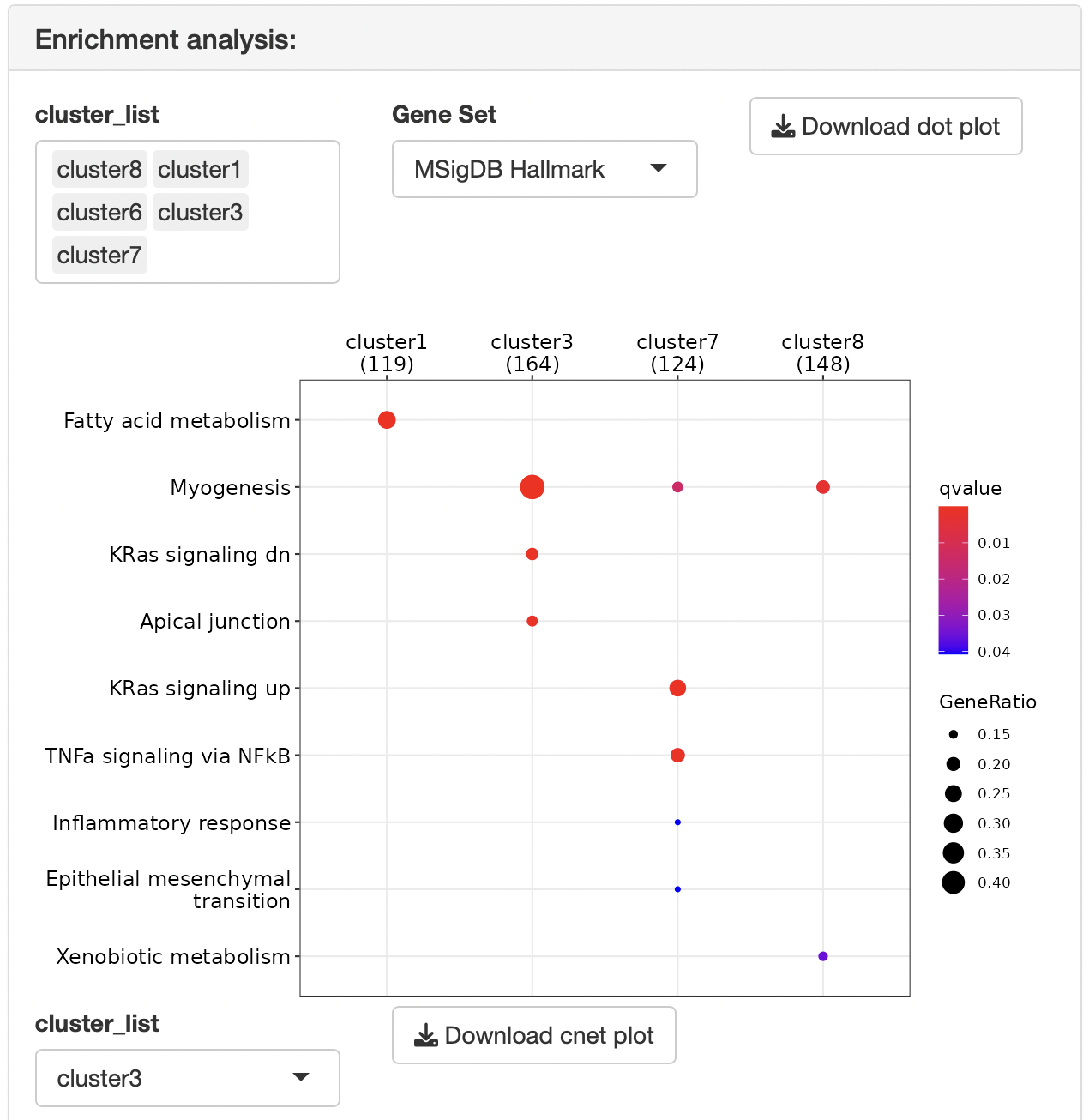
Overrepresentation analysis is performed to identify the function of each cluster.
The gene set can be selected from the following:
MSigDB hallmark gene
KEGG
Reactome
PID (Pathway Interaction Database)
BioCarta
WikiPathways
GO (biological process, cellular component, and molecular function)
Human phenotype ontology
DoRothEA regulon (activator)
DoRothEA regulon (repressor)
Transcription factor targets
miRNA target
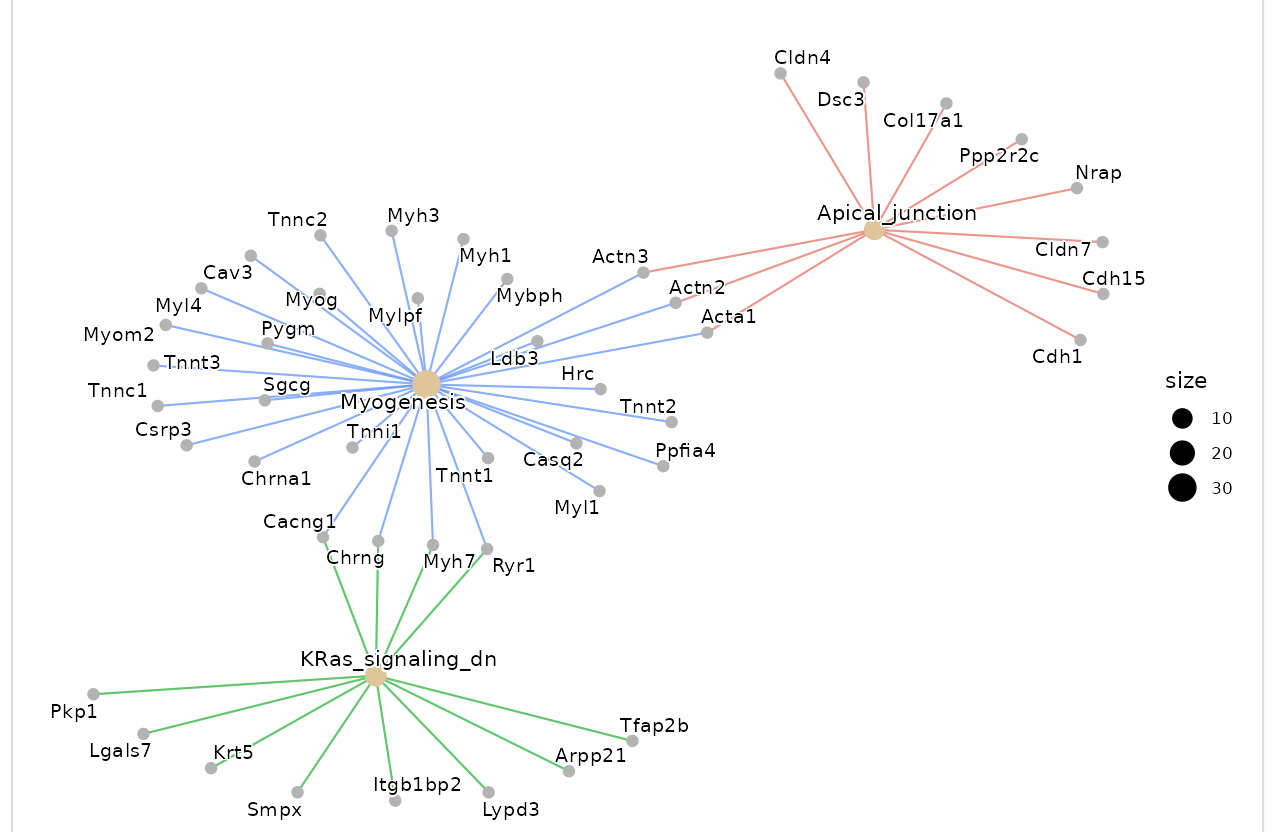
Dotplots and gene-concept network, cnet, plots are displayed as the result.
The group displayed by the cnet plot can be switched by selecting from the "Group" list.
Enrichment analysis depends on ClusterProfiler.
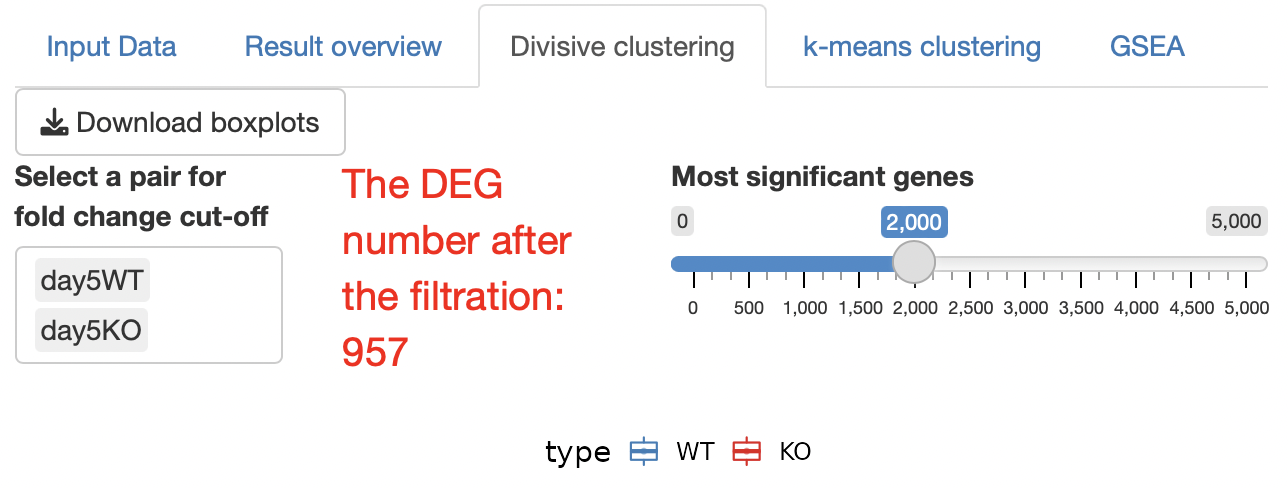
Select a pair for fold change cut-off
The fold change between the two groups is subject to “the cut-off condition” in the setting panel
This function is effective for extracting genes that change remarkably between specific groups.
Most significant genes
The DEGs after cut-off are extracted in ascending order of FDR, and clustering analysis is performed.
If there are too many DEGs after the cut-off, there is a risk of freezing due to server memory, thus narrowing down the genes to be analyzed.

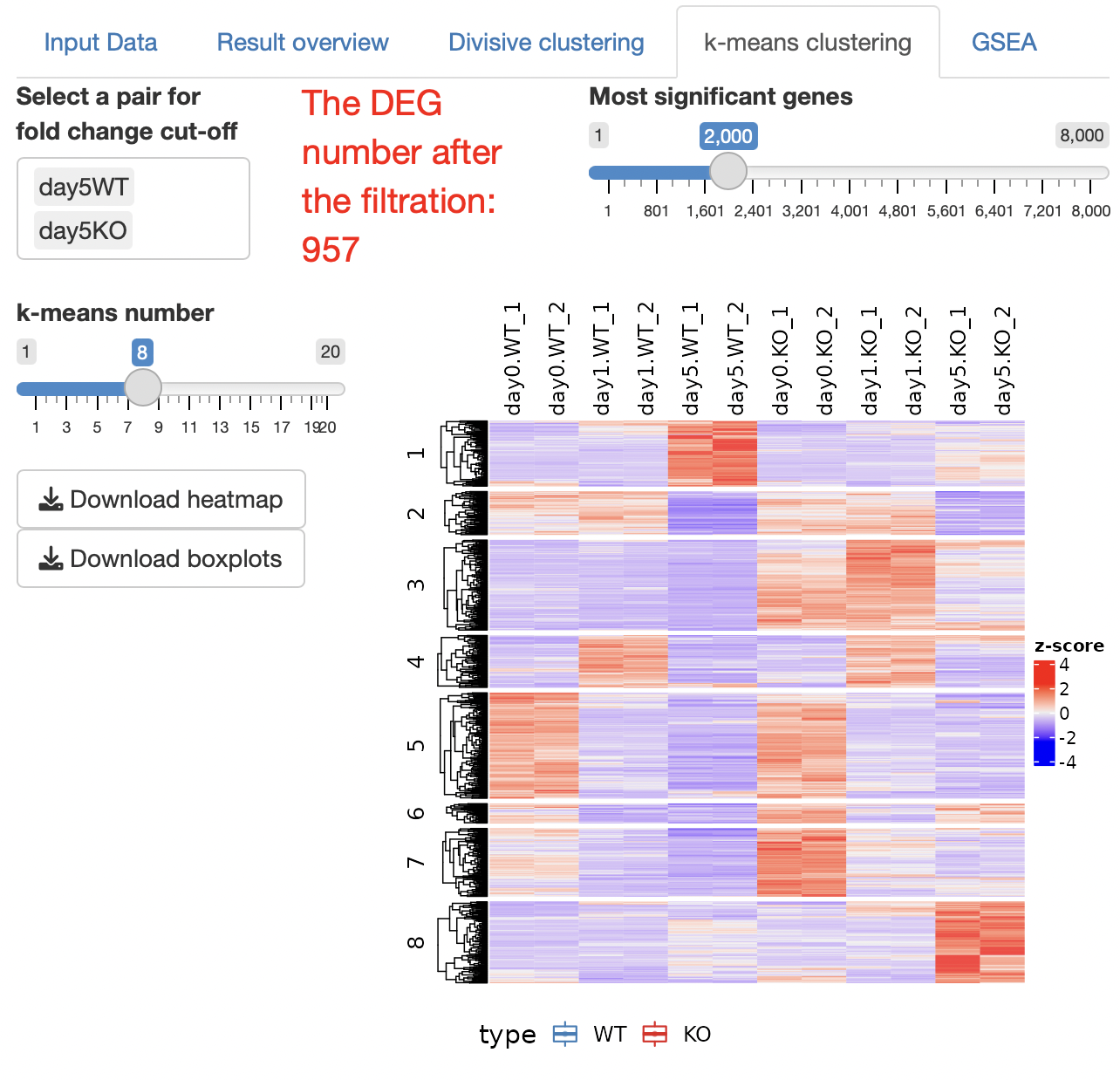
k-means clustering is performed.
The number of clusters can be changed by operating a slide bar.
Boxplots showing the gene expression patterns of each cluster are shown.
The result table data showing the relationships between genes and clusters are displayed.
Overrepresentation analysis is performed to identify the function of each cluster.
Select a pair for fold change cut-off
The fold change between the two groups is subject to “the cut-off condition” in the setting panel
This function is effective for extracting genes that change remarkably between specific groups.
Most significant genes
The DEGs after cut-off are extracted in ascending order of FDR, and clustering analysis is performed.
If there are too many DEGs after the cut-off, there is a risk of freezing due to server memory, thus narrowing down the genes to be analyzed.
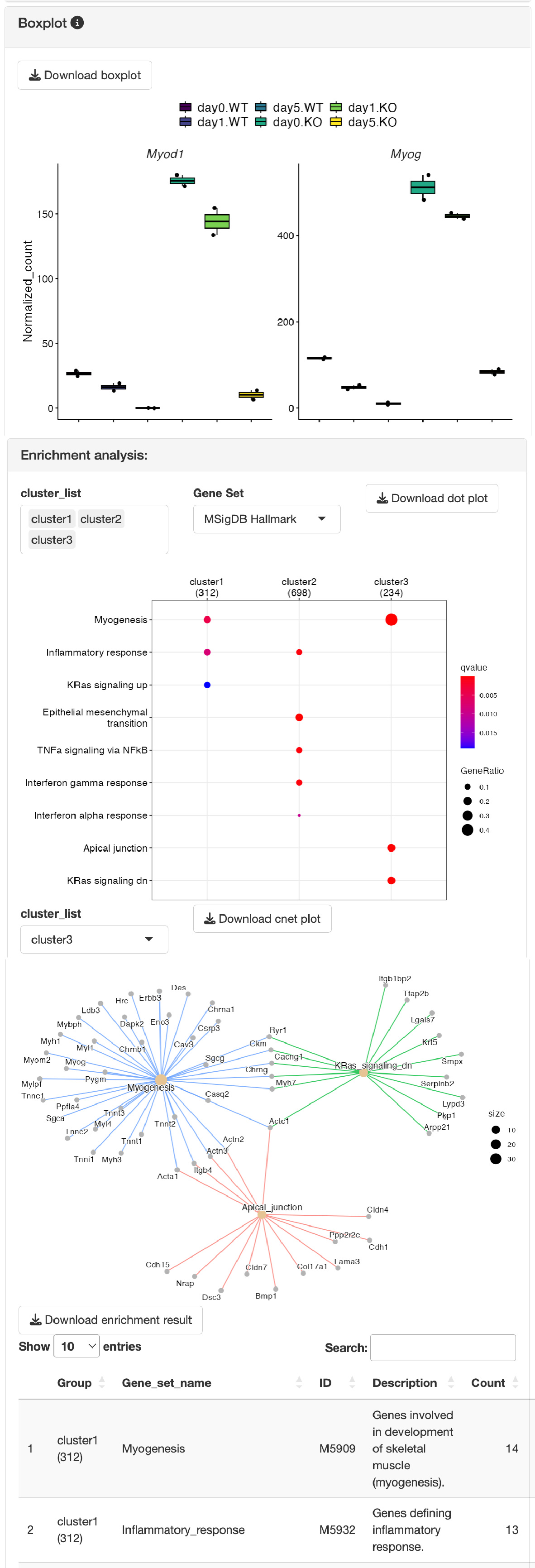
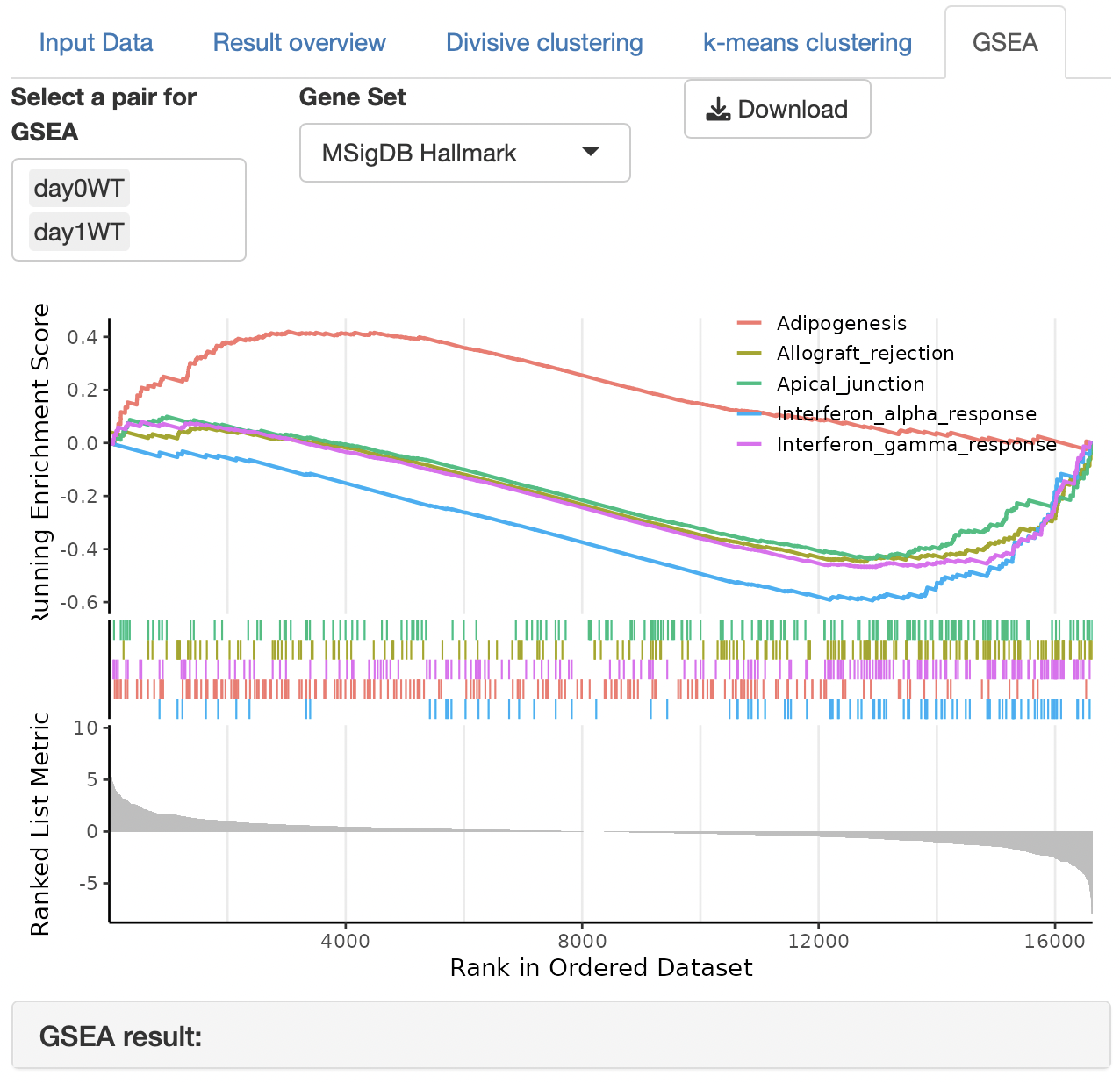
GSEA (gene set enrichment analysis) is performed to identify the function of each cluster.
The gene set can be selected from the following:
MSigDB hallmark gene
KEGG
Reactome
PID (Pathway Interaction Database)
BioCarta
WikiPathways
GO (biological process, cellular component, and molecular function)
Human phenotype ontology
DoRothEA regulon (activator)
DoRothEA regulon (repressor)
Transcription factor targets
miRNA target
Enrichment analysis depends on ClusterProfiler.