Security - Jonaath/EmergingTechnologiesMendix GitHub Wiki
Mendix Environment Security
Even before application development begins, Mendix implements a wide range of security measures at the infrastructure level, within its cloud services, and in its runtime environment. These controls are designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the applications built on the platform.
Compliance with International Standards
Mendix is certified under several well-established standards for information security and risk management:
-
ISO/IEC 27001: A global standard for information security management systems (ISMS), focusing on managing risks related to data security (access, confidentiality, availability).
-
ISO/IEC 27017: A standard providing guidelines for cloud-specific security controls, aimed at reducing data processing risks in cloud environments.
-
GDPR and HIPAA: Mendix supports organizations in achieving compliance with these data protection regulations by offering the necessary safeguards across its services.
Additional certifications and frameworks are also supported. For the full list, refer to the official documentation:
👉 Mendix Security Compliance Overview
Cloud Security
Regardless of the cloud environment used (Mendix Cloud, private cloud, AWS, Azure), Mendix ensures robust security mechanisms are in place:
-
Data Encryption: Data is encrypted both in transit (via TLS) and at rest (disk and database encryption).
-
Environment Segregation: Each application is isolated in its own container with dedicated resources, reducing risks of interference or unauthorized access.
-
Access Controls: Strong authentication (SSO, SAML, OAuth) and fine-grained permission management are natively supported.
-
Backup and Resilience: Automatic backups are regularly performed, with fast recovery procedures available.
-
Monitoring: Real-time monitoring and alerting systems help detect suspicious behavior or security incidents.
Runtime Security
The Mendix runtime environment includes built-in protections to mitigate common attack vectors:
-
Attack Prevention: The runtime engine blocks common attacks such as injection, XSS, CSRF, and other known threats by default.
-
Patching and Updates: Mendix regularly delivers security updates to address identified vulnerabilities.
-
Auditability: System-level logging enables traceability of critical events for audit and investigation purposes.
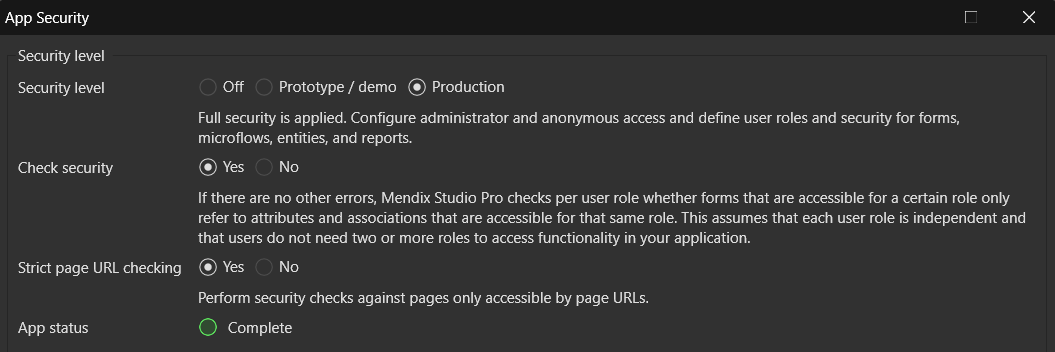
Application Security Modes
Mendix provides three security modes that govern the overall security posture of your application:
-
Off Mode
This mode disables all security features, making it suitable only for quick prototypes or local testing. In Off Mode, any user can access any part of the application without restriction. It is never recommended for production scenarios. -
Demo Mode
In Demo Mode, a minimal level of security is enabled, allowing for basic authentication and role assignments. This mode is appropriate for demonstrations or early testing, where the application’s data and functionality are not yet sensitive. However, it still lacks many of the advanced security checks necessary for a production environment. -
Production Mode
Production Mode enforces a comprehensive security framework. All pages, entities, and microflows require explicit access rules, which helps maintain the principle of least privilege. This mode is essential when deploying your application to real users or storing sensitive information. Developers must configure:- Project Roles and Module Roles
Align each user role (e.g., Administrator, Manager, Employee) with the correct permissions at both the project and module level. - Entity-Level Access Rules
Control read, write, and delete permissions on domain entities and optionally restrict specific attributes. - Page Security
Ensure only authorized roles can view or interact with certain pages. - Microflow Permissions
Limit execution of critical business logic to users with the proper clearance.
- Project Roles and Module Roles
When you switch to Production Mode, Mendix automatically checks for any missing or misconfigured security settings, prompting you to address them before deployment. This helps ensure your application is thoroughly locked down.
Module-Level Security
Entity Access
At the heart of Mendix’s data security model is Entity Access. Within each module, you can define which user roles have permission to create, read, update, or delete data. You can even refine these rules further by specifying attribute-level constraints or by using XPath expressions. For example, you might allow a “Manager” role to see and update all records but restrict an “Employee” role to only see records they created.
Page Security
Pages represent the user interface of your Mendix application. By configuring Page Security, you can decide which roles are allowed to open or interact with specific pages. This ensures that sensitive interfaces—like administration dashboards or HR forms—are only accessible to authorized personnel. If you attempt to open a page without sufficient permissions, Mendix will automatically block access.
Microflow Permissions
Microflows encapsulate your application’s core business logic. Since they often modify data or trigger important processes, it is crucial to protect them. Microflow Permissions determine which roles can execute or debug a given microflow. This prevents unauthorized users from running processes that could, for instance, delete records, calculate financial data, or generate sensitive reports.
User Roles and Access Management
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Mendix uses a layered approach to roles:
- Project Roles: Defined at the application level (e.g., Administrator, Manager, Employee).
- Module Roles: Defined within each module (e.g., “User”, “ReadOnly”, “Approver”) and then mapped to Project Roles.
By mapping Project Roles to Module Roles, you can grant or restrict access to different parts of the application based on each user’s responsibilities. This ensures that users have only the privileges they need, reducing the risk of accidental or malicious misuse.
Auditing and Logging
Mendix maintains comprehensive logs that track user actions, failed login attempts, and data changes. These logs help you monitor suspicious activity, investigate issues, and demonstrate compliance with internal or external regulations. Coupled with an RBAC strategy, auditing ensures transparency and accountability.
Security in ShopInOne
In our application, we implemented Production Mode to manage security at all levels of the app. While this approach requires more configuration effort during development, it allows for fine-grained control and significantly improves overall security across the entire system.
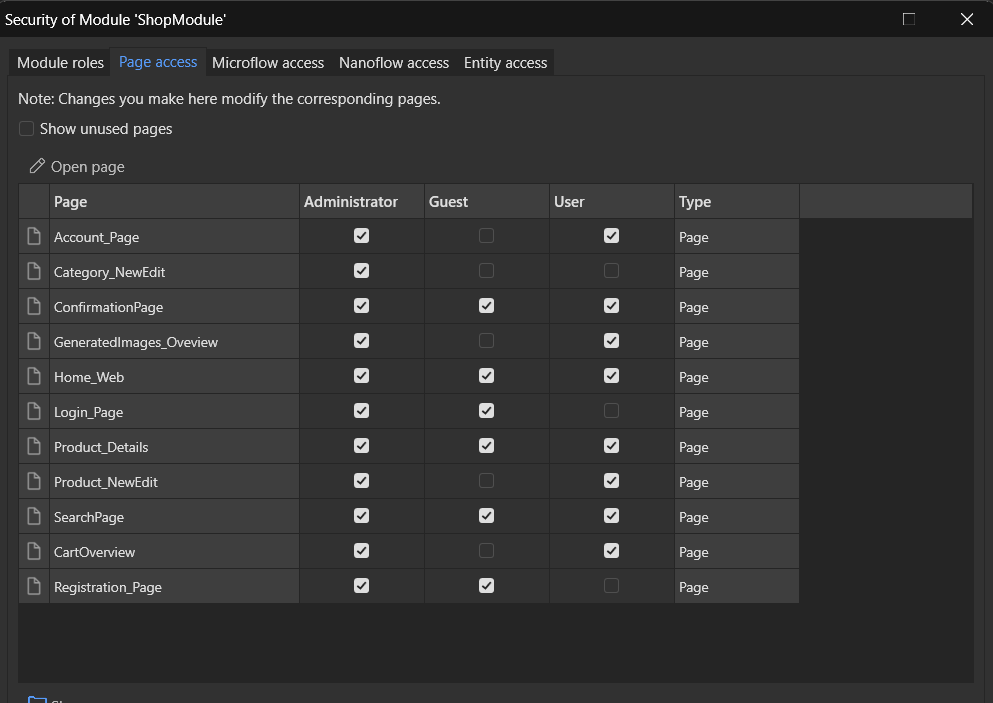
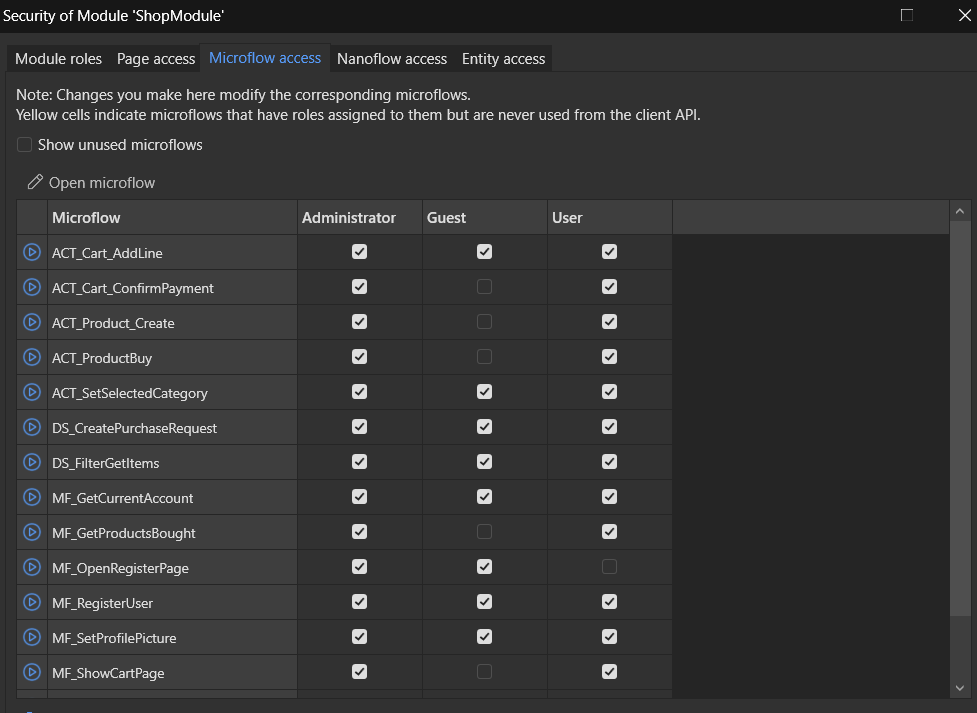
User Roles and Access Control
We defined three distinct user roles in ShopInOne, each with tailored access rights:
-
Administrator:
- Used exclusively during development.
- Has unrestricted access to all pages and views for testing and configuration.
- This role is is not used during deployment to prevent unintended exposure in production.
-
Guest:
- Represents a visitor without an account.
- Can browse products, but with limited information and no ability to interact with core features (e.g., offers, purchases).
-
User:
- A registered user with full access to platform features.
- Can create offers, view detailed product information, make purchases, and manage their content.
Role-Based Access Configuration
Access rights are explicitly defined across all application layers to ensure each user role only interacts with authorized components. Permissions are applied at the level of:
- Pages: Only relevant pages are accessible depending on the user's role.
- Microflows / Nanoflows: Logic execution is restricted to roles that require it.
- Entities and Attributes: Read, write, and delete permissions are carefully configured to prevent data leakage or unauthorized modification.
This role-based approach ensures data privacy, limits potential misuse, and aligns with the principles of least privilege and security by design.
Next page → Cost Analysis