Research: Audio Attenuation - Jelmerrr/DeepDive-SFX-Manipulation GitHub Wiki
Audio attenuation and its effect on 3D sound mapping.
The main way 3D sound effects are used to immerse a player is through audio attenuation. The concept of audio attenuation is spatializing sound and adjusting volume (and potentially other things) to mimmick the effect of having a sound appear from far away. In real life, when soundwaves travel through the air not only does the soundwave lose amplitude (volume) over time. Additionally at a distance certain frequencies become weaker (especially higher ones) making the sound appear muffled. Adding realistic audio attenuation comes down to two parts: 1. the spacializing based on volume and 2. the cutting of higher frequencies at a distance. Combining these two effects creates realisitc audio attenuation.
Why should we use audio attenuation for SFX?
As mentioned before audio attenuation is used to give off the illusion of sound mapped in 3D space. Without audio attenuation it will become difficult to accurately map sounds in accordance to where the emitter and player are located. Proper audio attenuation also helps to highlight nearby sounds meaning the player will give them more priority. Through attenuating distant and less important sounds the player can better focus on the sounds right in front of them.
What does audio attenuation achieve for video games?
Audio attenuation is usefull to make how sound traverse the 3D space more realistic. Additionally it can help make a soundscape feel less chaotic and can guide the focus of the player towards what is deemed important by the developers. A quick showcase how audio attenuation could be used on a water ambient effect can be found here: Water Attenuation Showcase
Through using audio attenuation to gradually fade out frequencies the overall soundscape becomes percieved as less loud and easier to follow. Certain frequencies and sound preassure levels are precieved differently which can be seen in an equal-loudness contour.
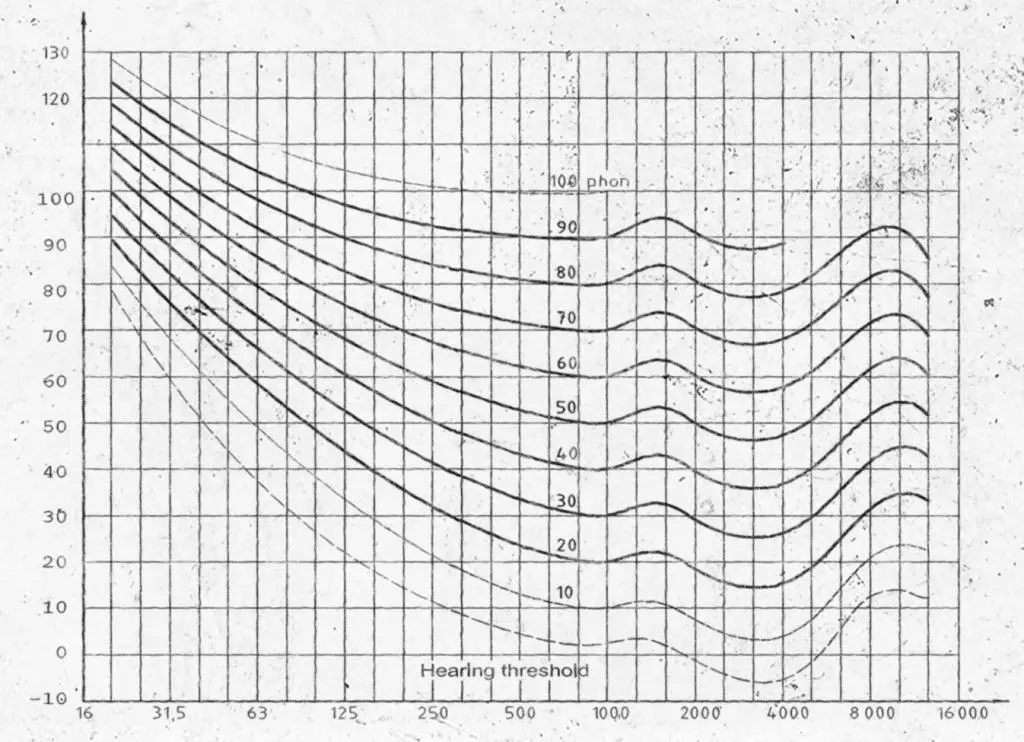 The image above showcases a Fletcher Munsom curve, it showcases how loud frequencies are percieved, if you want two frequencies to sound the same you need to play them at different amplitudes so they allign.
The image above showcases a Fletcher Munsom curve, it showcases how loud frequencies are percieved, if you want two frequencies to sound the same you need to play them at different amplitudes so they allign.
How to implement audio attenuation in FMOD?
Adding audio attenuation in FMOD is quite simple when working with 3D events. FMOD handles a lot of the dirty work already in the spatializer.

The spatializer handles the distance aspect of audio attenuation itself, you can however change the distance the audio attenuation activates at so it fits your project better. The next step after setting up the spatializer accordingly is to add a distance parameter. Click on the "+" sign, hover over "add parameter sheet" and click on add parameter.

After that select the preset "Built in: Distance" and set the range in accordance to the values set in the spatializer. When the parameter is setup you can add autmation on an equalizer in order to achieve the muffle effect.


When that is done you can check the result in FMOD through playing your sound while adjusting the distance parameter to what you want.
Conclusion
In conclusion audio attenuation is the primary method of making sound feel realistic in a 3D space. Through usage of adjusing volume based on distance and mapping out certain frequencies you can create a more natural soundscape.
Sources:
What is attenuation? the definition for attenuation. Music Production Glossary: Audio and Music Production Terms. (2023, October 6). https://musicproductionglossary.com/what-is-attenuation/
Wikimedia Foundation. (2023, October 4). Attenuation. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attenuation
Wikimedia Foundation. (2023b, October 8). Equal-loudness contour. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equal-loudness_contour
Indomitable Music. (2021, October 8). Better distance attenuation in Fmod (why your rpg sounds bad). YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GD-p6mbo5Z4