The OSI Model: An overview - GravocCO/TryHackMe---Introductory-Networking GitHub Wiki
OSI Model: Open Systems Interconnection Model - a standardized model which is used to demonstrate theory behind computer networking. This standardized model has been accepted by most institutions and organizations.
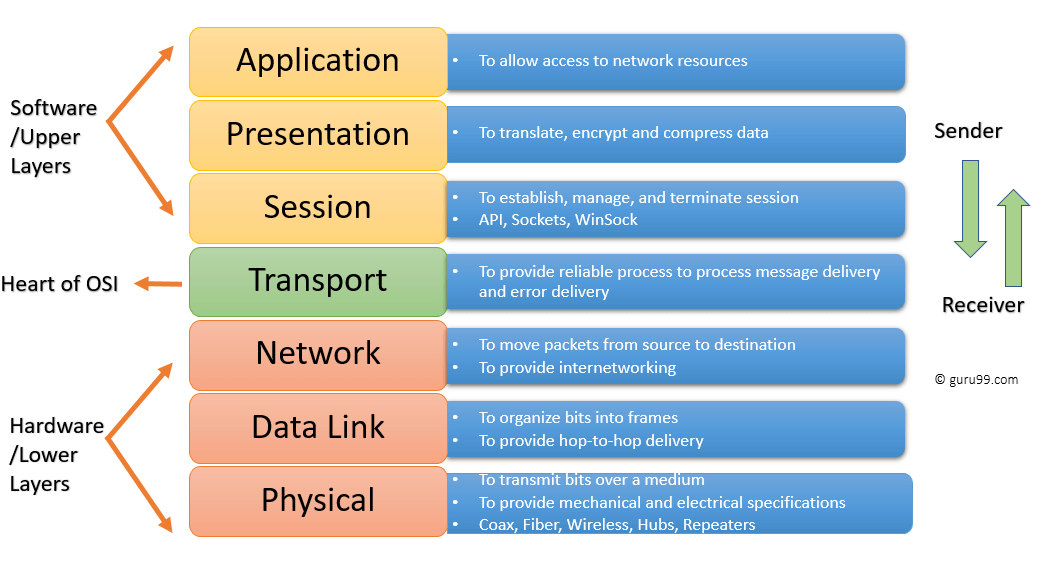
OSI Model Layer Order
7: Application - 6: Presentation - 5: Session - 4: Transport - 3: Network - 2: Data Link - 1: Physical

Mnemonic: (A)ll (P)eople (S)eem (T)o (N)eed (D)ata (P)rocessing
Layer 7: Application
Application Layer is where applications and humans interact with the network/internet. It's an intermediary that provides networking options to programs between say: Google Chrome and it's destination across a network.
Layer 6: Presentation
Presentation layer receives data, and translates it into a standardized format. It also handles encryption, compression, and other transformations to the data.
Layer 5: Session
Session layer is responsible for facilitating and maintaining connections between the sender and receiver across the network/internet.
Layer 4: Transport
Transport Layer chooses the protocol over which the data will be transmitted, divides the transmission into bite-sized pieces, and is responsible for the actual transmission of the data. The two most common protocols used are TCP and UDP.
Layer 3: Network
Network layer is responsible for locating the destination of a request. It's like a phone book of the internet. It catalogs IP addresses (Internet Protocol), referred to as Logical Addressing. It uses this IP address catalog to locate and set destinations for data transmission. It can set both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Layer 2: Data Link
Data Link layer focuses on physical addressing of the transmission. It adds the MAC address to the data for the endpoints. Every device has a Network Interface Card (NIC) which comes with a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address to identify it. It is also the data link layers job to present the data in a format suitable for transmission. It also acts as an integrity check for received information.
Layer 1: Physical
The hardware/wiring responsible for transmission and receipt of data. It's electrical pulses are the data that are being sent and received over the network/internet. It's job is to convert binary data of the transmission into signals and transmit them across as network, as well as receiving transmissions and converting them back to binary data.
Quiz Questions & Answers
Which layer would choose to send data over TCP or UDP?
Layer 4: Transport - Transport layer is responsible for choosing the protocol in which the data will be sent.
Which layer checks received packets to make sure that they haven't been corrupted?
Layer 2: Data Link - Data Link layer is responsible for verifying the integrity of received transmission packets.
In which layer would data be formatted in preparation for transmission?
Layer 2: Data Link - Data Link layer is responsible for ensuring data is suitable for transmission.
Which layer transmits and receives data?
Layer 1: Physical - Physical layer is responsible for receiving or transmitting the electrical impulses/data across the network/internet.
Which layer encrypts, compresses, or otherwise transforms the initial data to give it a standardized format?
Layer 6: Presentation - Presentation layer is responsible for presenting data in a readable format for the application layer, compresses, and encrypts data.
Which layer tracks communications between the host and receiving computers?
Layer 5: Session - Session layer is responsible for establishing and maintaining sessions between two devices/endpoints.
Which layer accepts communication requests from applications?
Layer 7: Application - Application layer serves as an intermediary between users/applications, and provides them networking options that give them connection to the network/internet.
Which layer handles logical addressing?
Layer 3: Network - Network layer is responsible for finding and adding the appropriate IPv4 or IPv6 endpoint destination to the transmission.
When sending data over TCP, what would you call the "bite-sized" pieces of data?
When bite-sized data is sent over the internet via TCP, it's called Segments. When it's sent via UDP, it's called Datagrams.
Which layer would the FTP protocol communicate with?
Layer 7: Application - The File Transfer Protocol is a standard in which many 3rd party software application platforms operate.
Which transport layer protocol would be best suited to transmit a live video?
UDP - Live video needs as fast as possible connections in order to better simulate real-life conversation, and it's okay if some packets don't arrive. It allows a persistent communication without risk of failure, unless the connection cuts off entirely.