UG_Special Topics_SearchFilter - GoldenCheetah/GoldenCheetah GitHub Wiki
Special Topics: Search & Filter
Searching and Filtering are ways to find activities which fulfill specific criteria (e.g. to limit the number of activities shown in the activity navigator - or to find a particular activity). But also to only consider specific activities in summary and cumulative charts, like on the Trends view.
Before going into any details, here the common functions available for both Search and Filter queries. The logic for Search and Filter is similar in all places of GoldenCheetah:
The input box for Search/Filter functionality contains multiple functions. It has
- a selector to switch between
SearchandFiltermode, - a drop-down menu contain the pre-defined queries and related functions,
- and is the text input field to enter your queries.
Note: Please do always check if you have chosen the right type for your query Search or Filter as they have a slightly different query syntax and purpose.
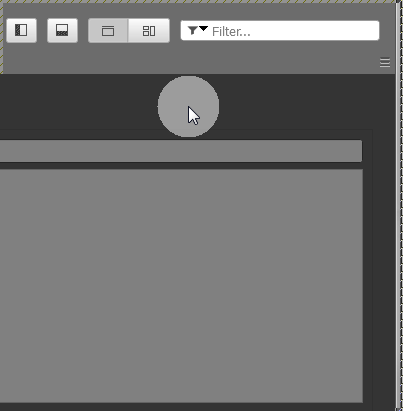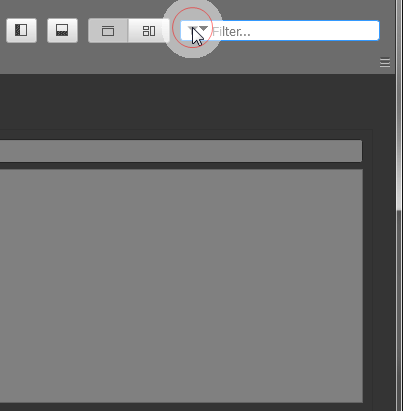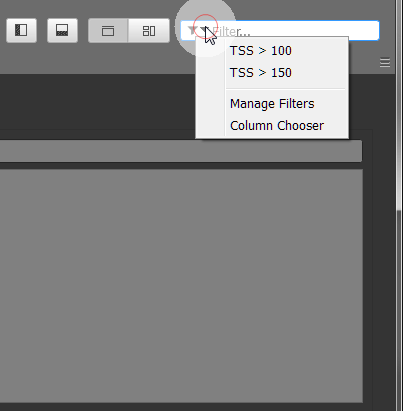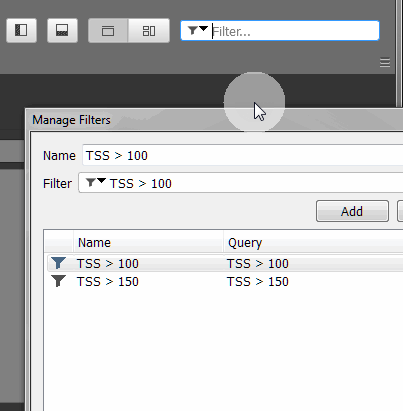
You can create and store Search and Filter queries using the Manage Filters menu. Queries stored here appear in the drop-down menu for faster access.
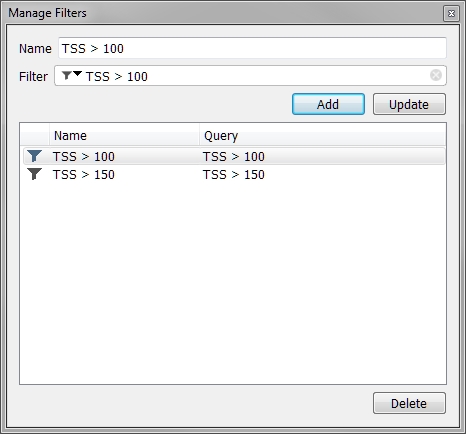
-
Add- adds the query defined in the Name/Filter input field to the list -
Update- updates an existing query with changes from Name/Filter input fields -
Delete- deletes the query selected in the list
Note: Please be sure to use the correct query type (Search/Filter).
You can always just enter the query into the text field and press Enter to run the query. Or use a pre-defined queries which applies directly and saves the time of typing.
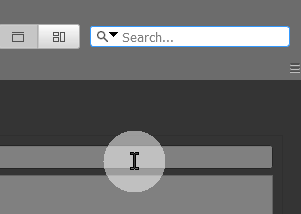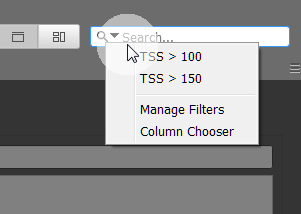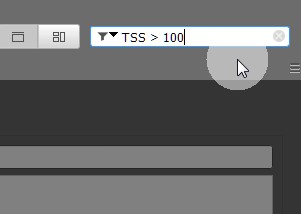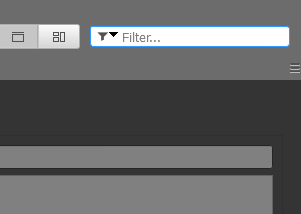
Note:To de-activate a Search/Filter query, just click on the little (x) on the right side of the input field.
The Search function in GoldenCheetah is pretty straight forward. If Search is active (check if the correct icon - "magnifying glass" is shown) and just enter the text you are search for. The activity list will be reduced/filtered to those activities where the text appears in any of the text fields.
Filtering is like searching, a way to find activities which fulfill specific criteria. Where searching mainly works on text fields, filtering can do a lot more. But this more also means you have to make yourself familiar with the query syntax for filtering.
In a simplified way, a filter query is a bit like a database query - (which is different to free-text search engines). As a minimum you need to define
- the field you want to look at (FieldName)
- a rule how to look at that field (Operator)
- a comparison value (Value)
Easy example: The query TSS >= 100 - finds all activities where TSS is 100 or more. This example already illustrates the major point of what a Filter can do better than a Search. You cannot define a search which can do this (in GoldenCheetah). (But, also Filter queries cannot do it all and easy. E.g. Search makes most sense for text fields and is perfect if e.g. you do not even know in which field you have stored your text - Search will find it.)
Note: You need to separate field names, operator, keywords, function as well as values or string by " " (Space) so that the query parser can recognize them - otherwise you will see the query text color changing to "red". To see the error text, just click into the query text and wait until an error text appears.
A simple query is structured: <field_name> <operator> <value_or_string>
GoldenCheetah uses a "semi"technical field name for the queries - which is basically the English metric or field name, where all spaces are substituted by _ to get the <field> as one text string. Since it iss difficult to remember all the field names, and (for longer field names) to type the name correctly, you can "Drag&Drop" field name in the required format using the Column Chooser tool. (It is in the filter menu - next to Manage Filter).
Note: The field has to be defined in Preferences > Data Fields with a non blank Screen Tab. Some technical fields, s.t. Start Date and Start Time, are not available this way and can be accessed via builtin functions s.t. Date and Time instead.
-
Text Operators (make only sense for text fields/strings)
-
MATCHES- checks if the field text has a exact match with the regular expression inMATCHES(<reg_expr>) -
BEGINSWITH- checks if the field text begins with the text you are comparing to -
ENDSWITH- checks if the field text ends with text your are comparing to -
CONTAINS- checks if the field text at any position contains the text you are comparing to -
!- used before any expression that contains the above operators, gives the opposite results. For example the filter: Notes CONTAINS "hills", returns all the activities that contain the word hills in the notes. The filter !(Notes CONTAINS "hills"), returns all the activities that DO NOT CONTAIN the word hills in the notes.
-
-
Value Operator (work for value fields and text fields)
-
=- Equal -
<>- Not equal -
<- Smaller -
<=- Smaller or equal -
>- Greater -
>=- Greater or equal
-
Note: For text fields mainly = and <> make sense, comparison of text on greater or smaller works as well, but uses the character codes to compare
-
<string>can be a single word, or a sequence of words (which then need to be put into quotes "" or '') -
<value>can be aninteger(like 123 or -456) or afloat(like 123.567 or -123.456 or 123.567e3 or 123.567e-3 )
You can combine multiple simple queries with
- Boolean operators
-
ANDor&&- both simple queries have to be fulfilled -
ORor||- either one or both simple queries have to be fulfilled
-
Note: This can be done as often as the query input field allows for a text size perspective. In contrast to the Search queries, the filter queries don't care on upper/lower case for the operator keywords.
- Using bracket "(" ")" - in more complex queries it is often either required / and useful to put certain sub-query or calculations in brackets - so that execution is done in the right sequence.
In addition to the quite common operators before, GoldenCheetah has some build-in extras you can use.
- Calculation Operators
-
+- plus -
-- minus -
*- multiply -
\- divide -
^- power
-
The syntax is <value_or_field> <calculation_operator> <value_or_field>. With this you can create queries like: "show me all activities where the sum of L2_Time and L3_Time is more than 2 hours: ( L2_Time_in_Zone + L3_Time_in_Zone ) > 7200. Please note that duration fields (here 2h) are always assumed to contain their value in "seconds" (here 7200 seconds).
GoldenCheetah provides two functions which return activities specific metrics very easily:
-
BEST- syntax isBEST ( <data_series>, <duration)and returns the MEAN MAX value of the chosen data series for the activity to filter. This value then can be used in a query e.g. to compare to a <value>.
The supported <data_series> are: "apower", "power", "hr", "cadence", "speed", "torque", "vam", "xpower", "np", "wpk"
Example: You want to select all activities, where your 5min mean max power was higher than 200 watts. This query then looks: BEST ( power, 300) > 200. Again the duration (5min) has to be entered in seconds (300sec) into the query.
-
TIZ- (Time in Zone) - syntax isTIZ ( <tiz_series>, <zone>)and returns the time you have spend in a particular zone for the activities to filter. This value then needs to be used in the complete query e.g. to compare to a<value>.
The supported <tiz_series> are: "power" and "hr"
Example: You want to select all activities, where you have spend 60min or more in power zone 4. This query then looks: TIZ ( power, 4 ) > 3600. Again the duration (60min) has to be entered in seconds (3600sec) into the query.
-
SBorTSB- (Stress Balance / Training Stress Balance) - syntax isSB(<metric>)orTSB(<metric>)and returns the PMC value for the metric in question for the date of the activity and therefore allows to select activities based upon PMC data. -
LTSorCTL- (Long Term Stress / Continuous Training Load ) - syntax isLTS(<metric>)orCTS(<metric>)and returns the PMC value for the metric in question for the date of the activity and therefore allows to select activities based upon PMC data. -
STSorATL- (Short Term Stress / Acute Training Load) - syntax isSTS(<metric>)ATL(<metric>)and returns the PMC value for the metric in question for the date of the activity and therefore allows to select activities based upon PMC data.
The supported <metric> are e.g. TSS, and the similar ones.
- set(symbol, value, filter) - set
symboltovaluefor activities that matchfilter, e.g.set(Sport, "Bike", Data contains "P") - unset(symbol, filter) - clear
symbolfor activities that matchfilter - isset(symbol) - if
symbolis set to nonzero or non-blank returns true
- autoprocess(filter) - run processors configured as automatic/import on activities selected by the filter parameter.
- postprocess(processor, filter) - run the specified processor on activities selected by the filter parameter, the processor parameter is the data processor name in English, as a string constant.
- tests() - returns the number of intervals in the activity that are marked as performance tests.
- daterange(start) - returns the start date of the currently selected date range in Trends view.
- daterange(stop) - returns the stop date of the currently selected date range in Trends view.
XDATA("name","series", sparse|repeat|interpolate|resample) will return true/false when filtering rides to indicate if the xdata is present in the activity.
NOTE: XDATA "name" and "series" can be specified using wildcards. such as "*" or "[Pp][Oo][Ww][Ee][Rr]*". This is NOT a regular expression, it is the same format of pattern used to match filenames.
- Duration fields and values - always have to be provided in "seconds" in a query.
- Date values can be entered as
“yyyy/mm/dd”in comparisons and there are builtins for the date of the activity (Date) and current date (Today), see also Working with Dates and Times. For example to filter activities between two dates:Date >= "2022/08/01" and Date < "2022/09/01" - Some technical fields (s.t. Start Date and Start Time) are also not supported - when you enter such a field with the
Column Chooseryou will get asyntax errore.g. "field not known" - You can use built in functions Date and Time instead. - Syntax errors - when a query is invalid, the query input field text color changes to "red". By clicking at any part of the query text with your mouse and waiting a short moment, an error text will appear, telling you why GoldenCheetah failed to parse your query.
For further information see: Formula Syntax and Expressions
BACK: Special Topics: Overview
BACK: Table of contents