Realtime facedetect - FatigueDetecting/Fatigue_detecting GitHub Wiki
1. Face capture technique
The main technique used is the MAT class in OPENCV to define the frame and the CAPture class to capture the frame, through testing I found that as this fatigue detection system is mainly used for single face detection. For single face detection, the main difficulty lies in the change of ambient light and the deflection of the user's face, especially at night when facing oncoming traffic, the ambient light changes abruptly and creates a big obstacle for recognition
The solution to this problem is to use OPENCV's greyscale processing for the frames, which is found through the detection of single frames. For RASPberry there is a large optimisation and it does not take up too much space.
For face feature acquisition, the DLIB algorithm was used at the beginning, by compiling the DLIB parser and importing the landmark file, 68 feature points of the face could be acquired and annotated.
2. Multi-threading technology.
Through the design of a multi-threaded scheduler, so that the actual threads of the system can be observed when the class is initialised. As opencv captures frames faster, and face feature point recognition is much slower than opencv captures frames, the algorithm of multi-thread scheduling class is proposed, by separating opencv capture thread::detach, and for feature point capture is automatically scheduled. A thread blocking technique is designed using buffers to block the feature point class. The class is blocked and released according to the thread scheduler, which can be run at full cpu load.
3. Circular buffers, due to the speed of capture and slow recognition.
At the beginning of the design, I designed the buffer with a buffer length of 3 frames and emptied the buffer after each recognition, but this would cause the cpu load to rise and the recognition would not be smooth. Later, the circle--buffer technique in BOOST was used to elicit the circle_buffer buffer created by inspiration. Since MAT uses the default constructor, a matrix is generated and used by the functions provided by OpenCV (typically Mat::create() and cv::imread() ) to allocate the storage space.
Buffer design: Since multi-threading can lead to mismatches in the speed of camera frame writes, and since the processing time cannot be timed to the stack when multi-threading, the template class buffer was designed to balance the speed difference between writing to frames and reading from fatigue states.
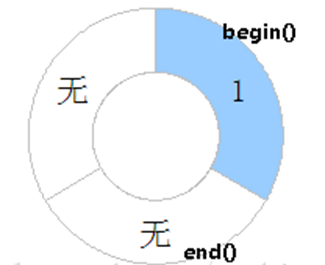
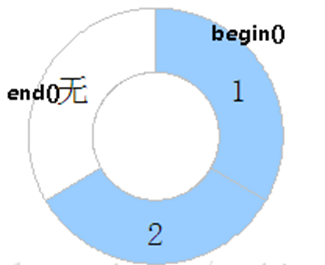
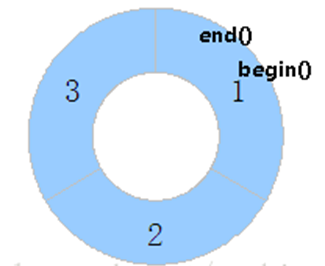
The internal memory of the ringbuffer is only the pointer address. The ringbuffer is designed with five class functions:
CRingBuffer::Clear
CRingBuffer::ReSetBufferSize
CRingBuffer::WriteData
CRingBuffer::ReadData
CRingBuffer::GetLength
Where writeData is called to write the address of the pointer within the location selected by the subscript in memory. Also write the length bits required for the subscript advance pointer and wait for the next data to be written. When ReadData is called, the pointer address is read at the location selected by the read subscript. Also reads the length position currently read by the subscript advance.