LPET - EDM-Project/EDM GitHub Wiki
What is LPET?
LPET - Low Priority Eviction Thread, is aimed to manage eviction of pages in case app is soon to be out of memory.
When is LPET triggered?
LPET is triggered when number of pages in memory reaches a user-configured variable named high_threshold, and goes to sleep when it reaches low_threshold.
How does LPET decide which page to evict?
LPET intends to imitate operating system's high-level algorithm to decide if a specific page should be evicted or not:
Let's say we order all pages in a cyclic linked list. Upon first LPET's run we will start from the first page inserted into memory, and iterate the list cyclically.
For every page:
- If it is idle => evict
- Else - mark it as idle and continue to the next page
When enough pages are evicted (amount of pages is low_threshold) - save the last iterator as the starting point for next LPET's call.
This algorithm ensures that we keep hot pages in the instance, and evict cold (idle) ones. Furthermore, evictions are made from all space addresses equally, thanks to the fact that each iteration has a different starting point. For more info about the way we detect idle pages.
Interface to other Modules
A single-page eviction flow which involves creating a channel between LPET and DMS is well-described in this scheme (WITHOUT reference to how LPET chooses a page to evict):
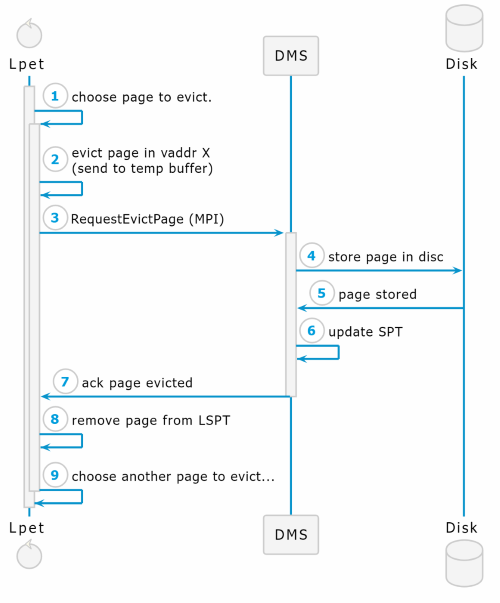
How does LPET evict a page?
The actual eviction (step 2) is made by mremap() with MREMAP_DONTUNMAP flag. LPET remaps the page to buffer, each eviction overrides the latest data in the buffer. With MREMAP_DONTUNMAP flag, mremap() doesn't unmap the old address (i.e. the address of the page we evict).
In EDM environment, evicted pages are pages that were registered before to userfaultfd. Therefore, when the app accesses a page that was evicted, it will result in a page fault that will be handled by DM-Handler.