VS Integration with GitHub AS20 - DigiBP/digibp.github.io GitHub Wiki
This tutorial will demonstrate how project artifacts can be pushed to a GitHub repository directly from Visual Studio Code.
- Pre-requisites - Visual Studio Code, Git, GitHub account
- 1. Cloning a remote GitHub repository
- 2. Committing changes to the remote repository
- 3. Synchronizing the repository
- 4. Managing and collaborating changes to the repository
- 5. Editing Wiki documentation locally
- 6. Adding images to Wiki documentation
Please install Visual Studio Code and register to GitHub before following this tutorial.
Check if Git is already installed:
Please verify if you already have Git installed by typing git --version in Terminal/Command Prompt. If not, please install Git.
Windows:
After you have installed Git, it is important to configure your Github username and email address for commitments. In this way, Visual Code Studio will allow you to upload local repository changes to Github.
Set global username/email:
-
Open Git command line (Git Bash)
-
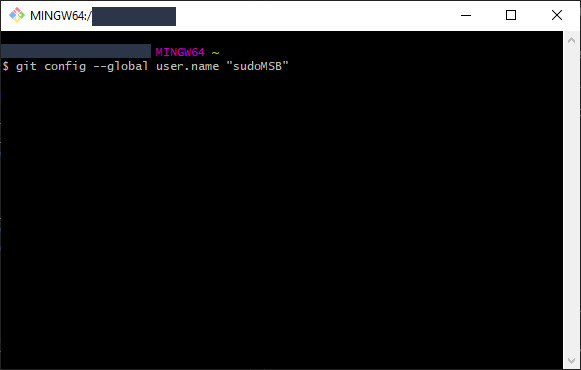
Set user name:
Type the following command:
git config --global user.name "YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME"
-
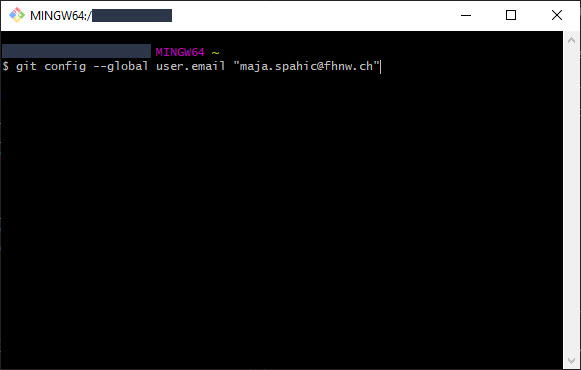
Set user email:
Type the following command:
git config --global user.email "YOUR_@EMAIL_ADDRESS"
MacOS: No additional configuration is needed on MacOS.
In order to work on your local machine, you need to clone an existing GitHub repository, specifically the team repository that will be used for the final DigiBP project.
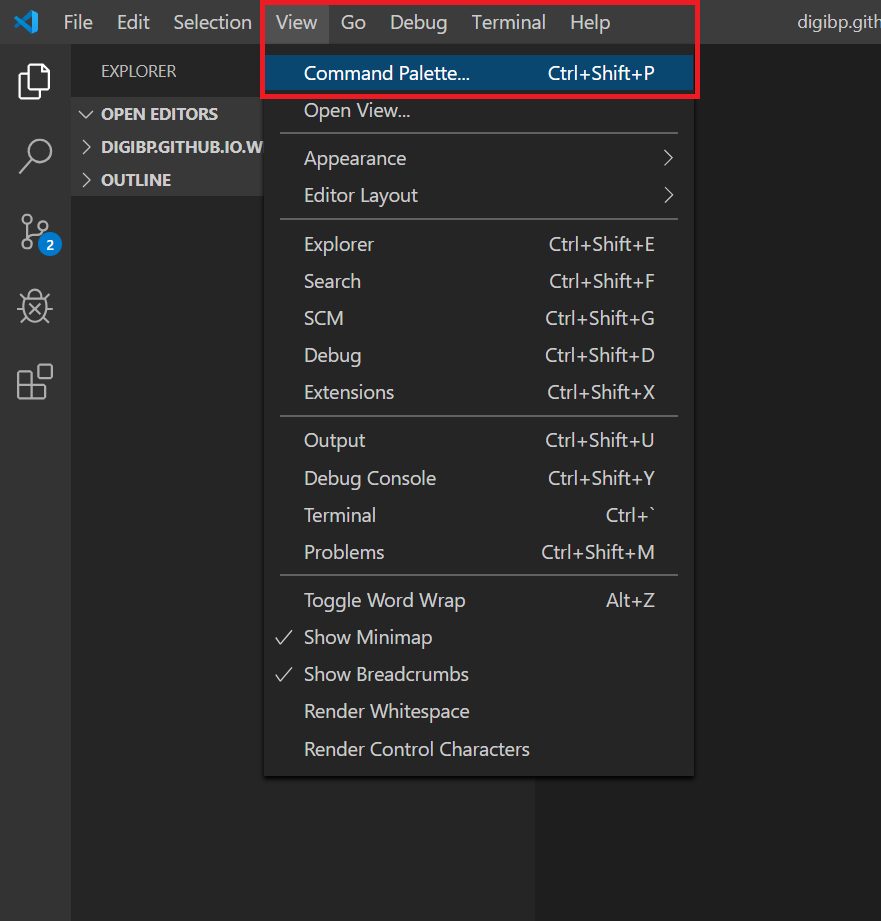
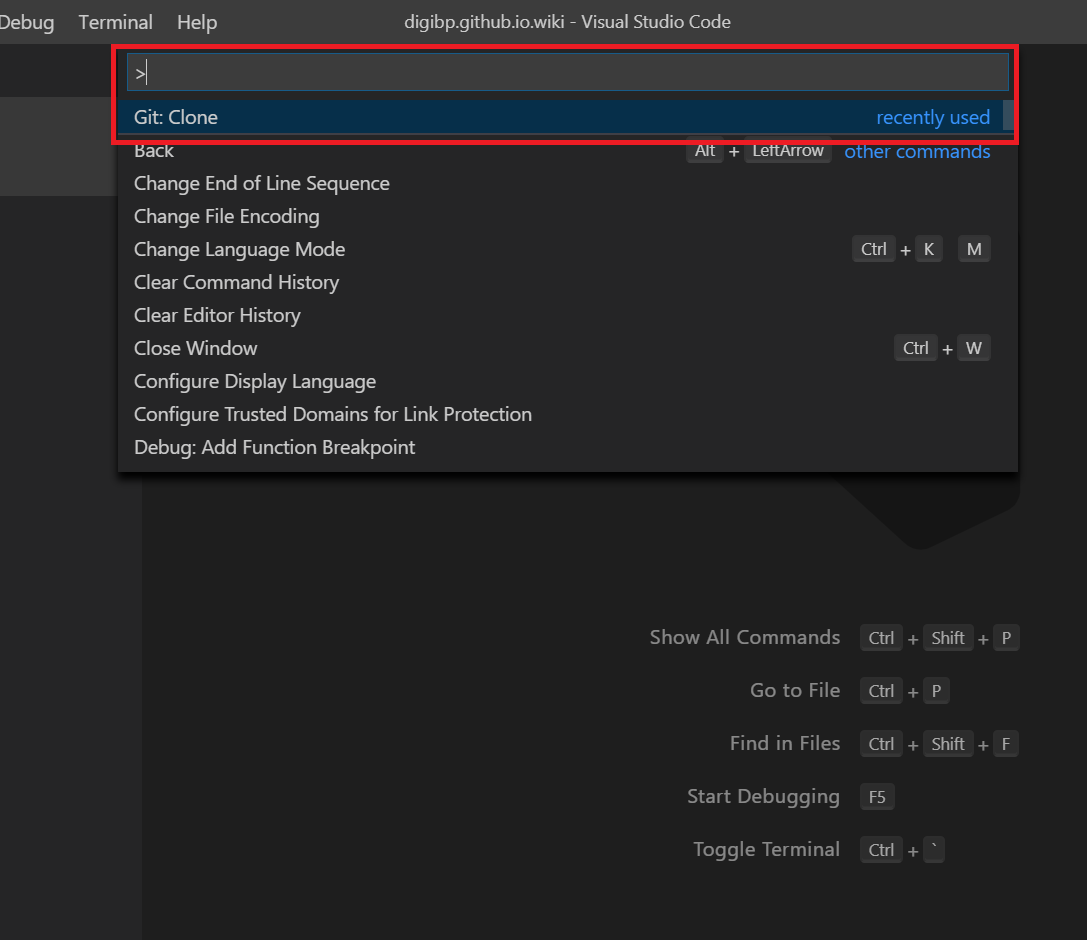
Click on the View Menu and select Command Palette...
Type Git:Clone in the textbox that opens.
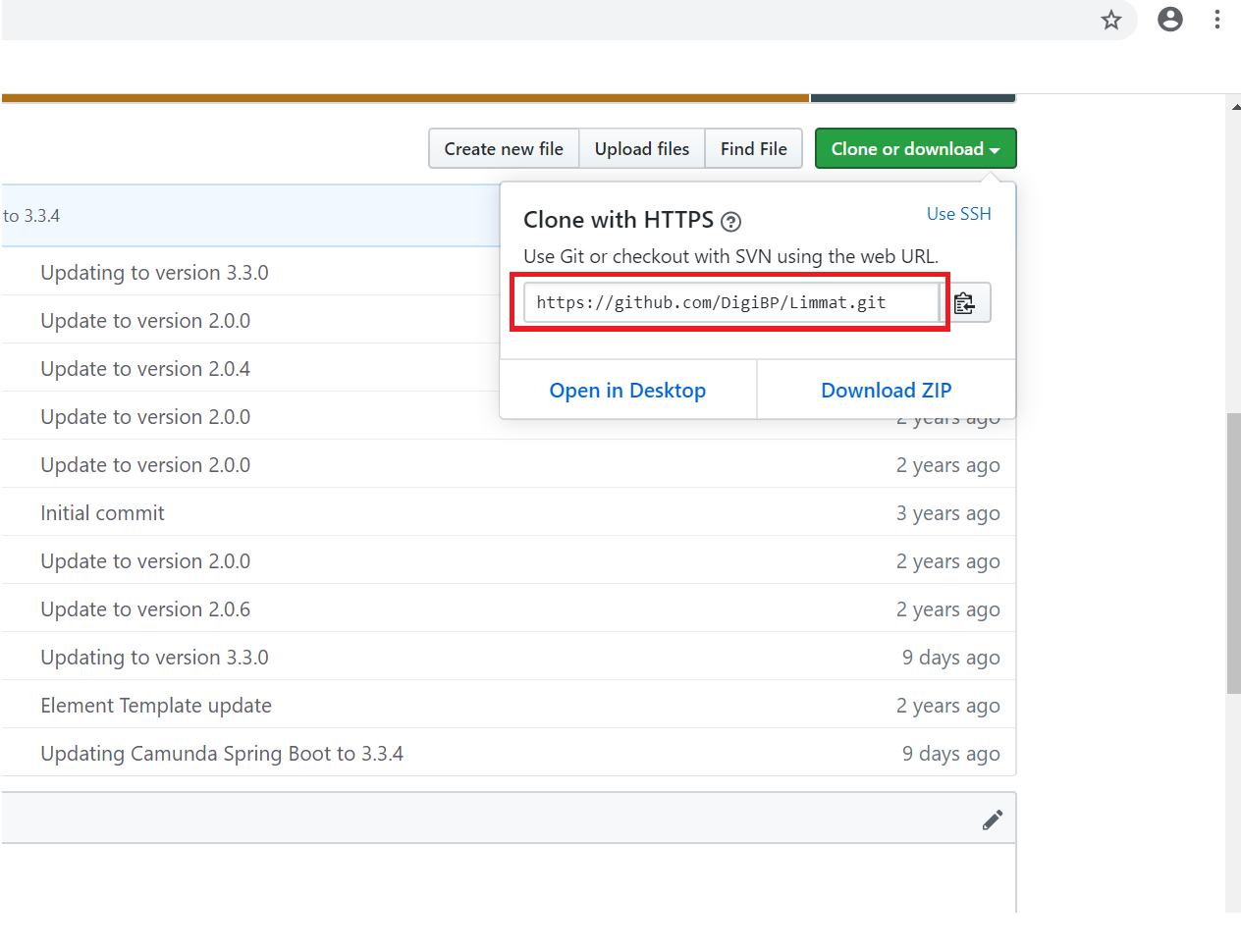
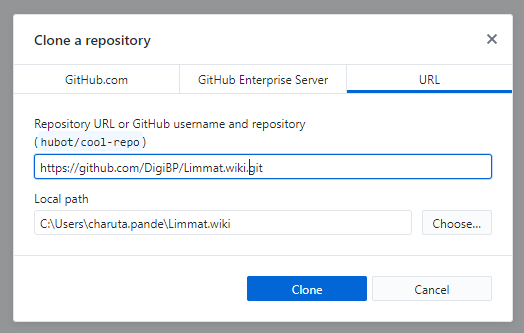
Copy the URL from the GitHub repository of your team.
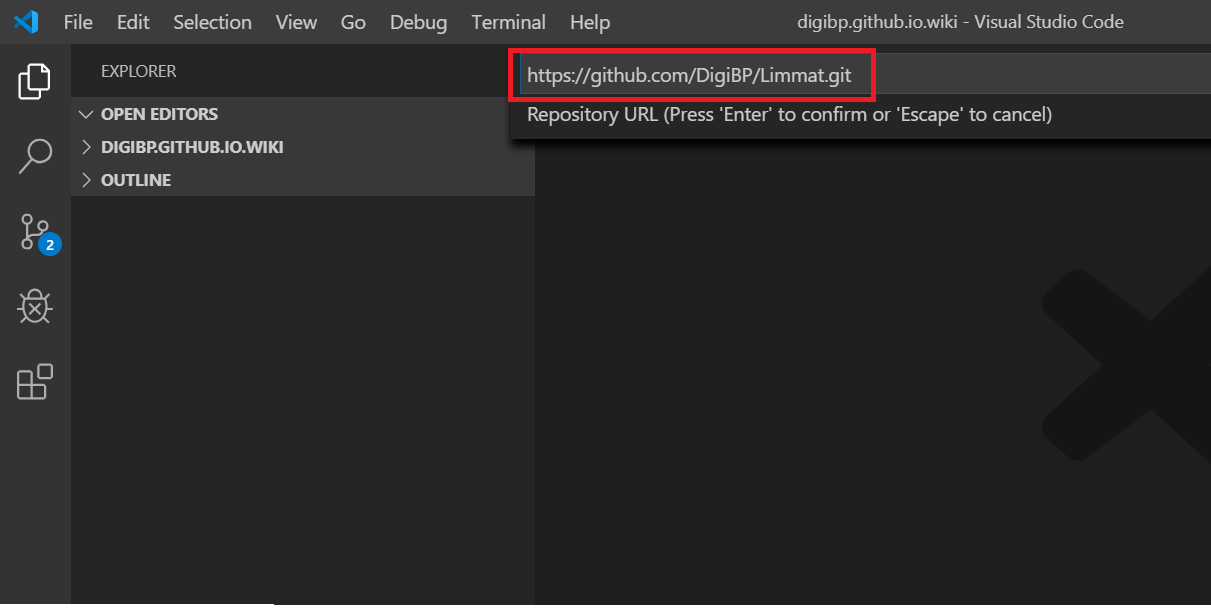
Paste it in VS as shown below:
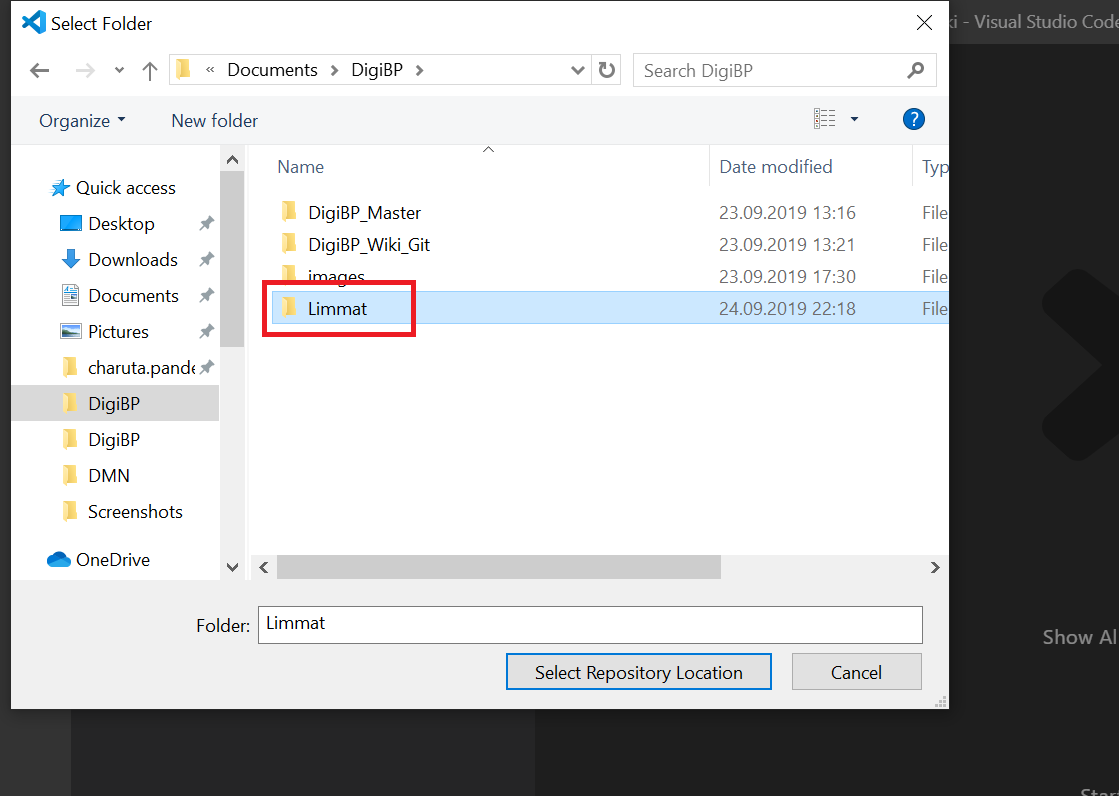
Select a local folder where the repository will be cloned. The local folder should be created in advance.
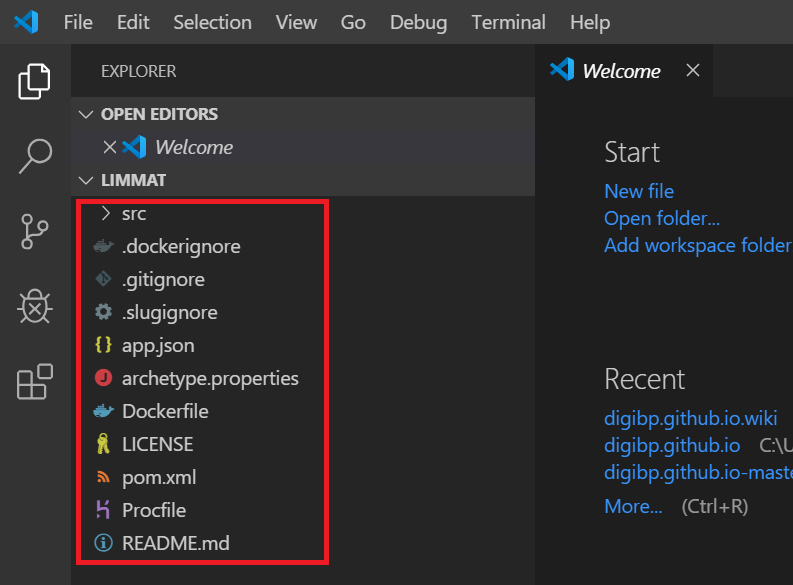
The folder structure of your repository will be displayed in VS.
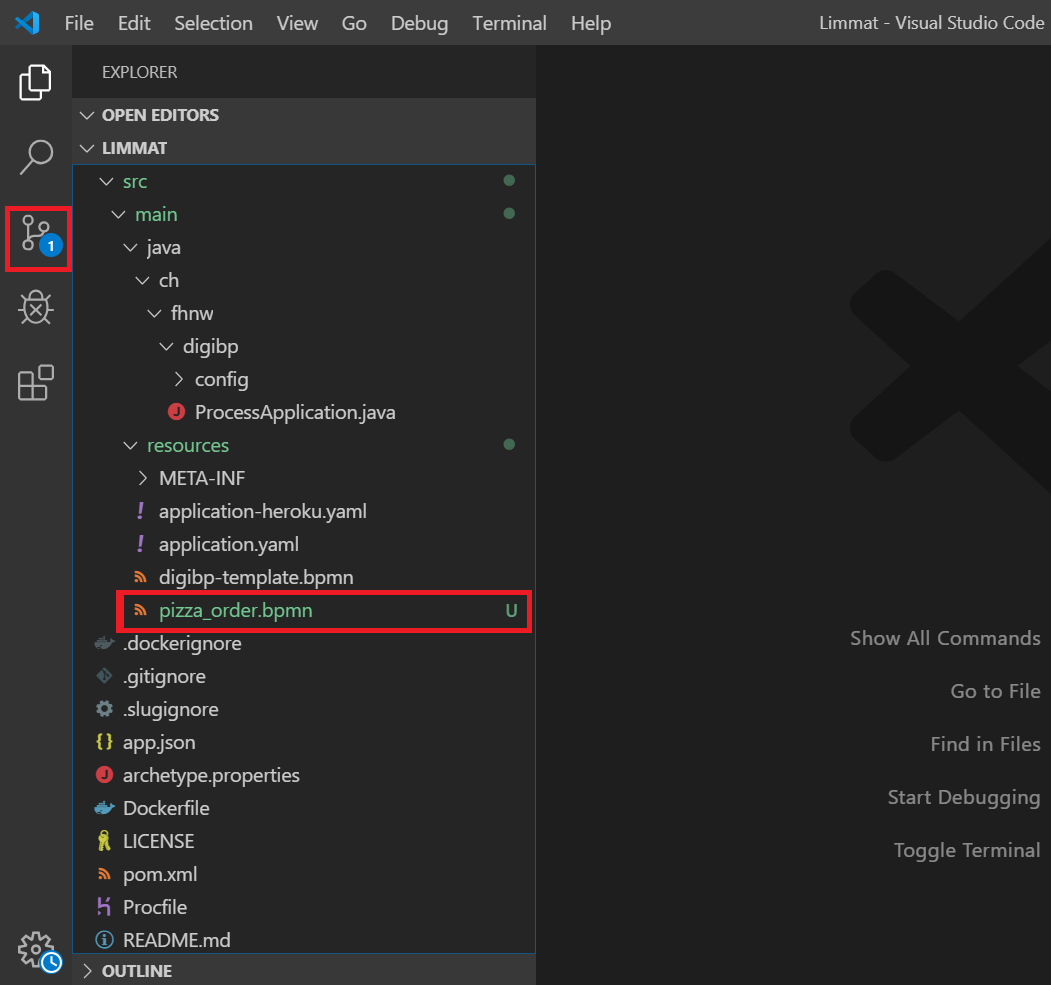
Add a file to one of the folders, for example, the pizza_order.bpmn model to the resources folder. VS displays this file with an indicator "U" and a number 1 as shown in the image below, indicating that one file has been added/modified in the local repository.
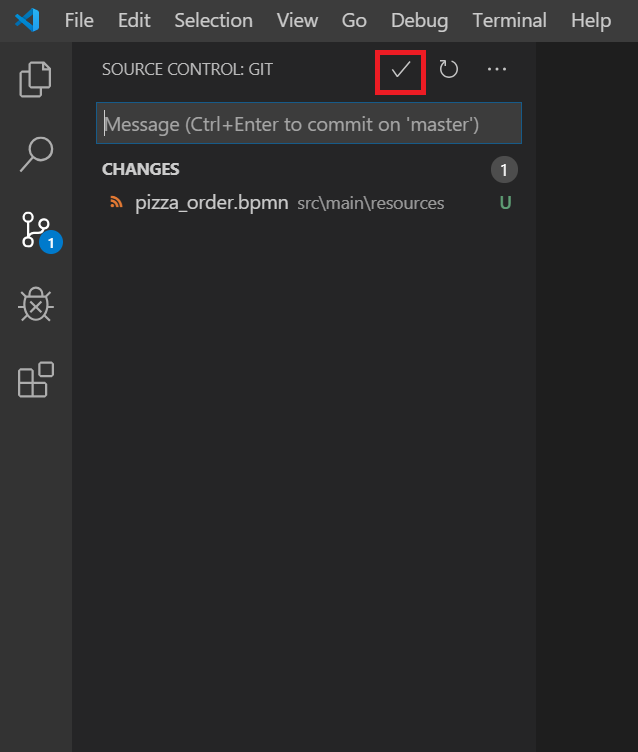
Click on the Fork icon on the left to go to the Source Control View. Then click on the tick sign as highlighted in the image below.
Click Yes for staging the file and enter a commit message. The commit message should be a meaningful text that summarizes the change to the repository.
Click on synchronize changes icon at the bottom left and click OK for pushing the changes to GitHub repository - please refer to the image below.
If you are not logged in to GitHub, a notification to enter GitHub userid and password will appear.
Step 2 and 3 are both required in order to successfully push a change to the GitHub repository.
The team members can pull changes from the repository by synchronizing as described above.
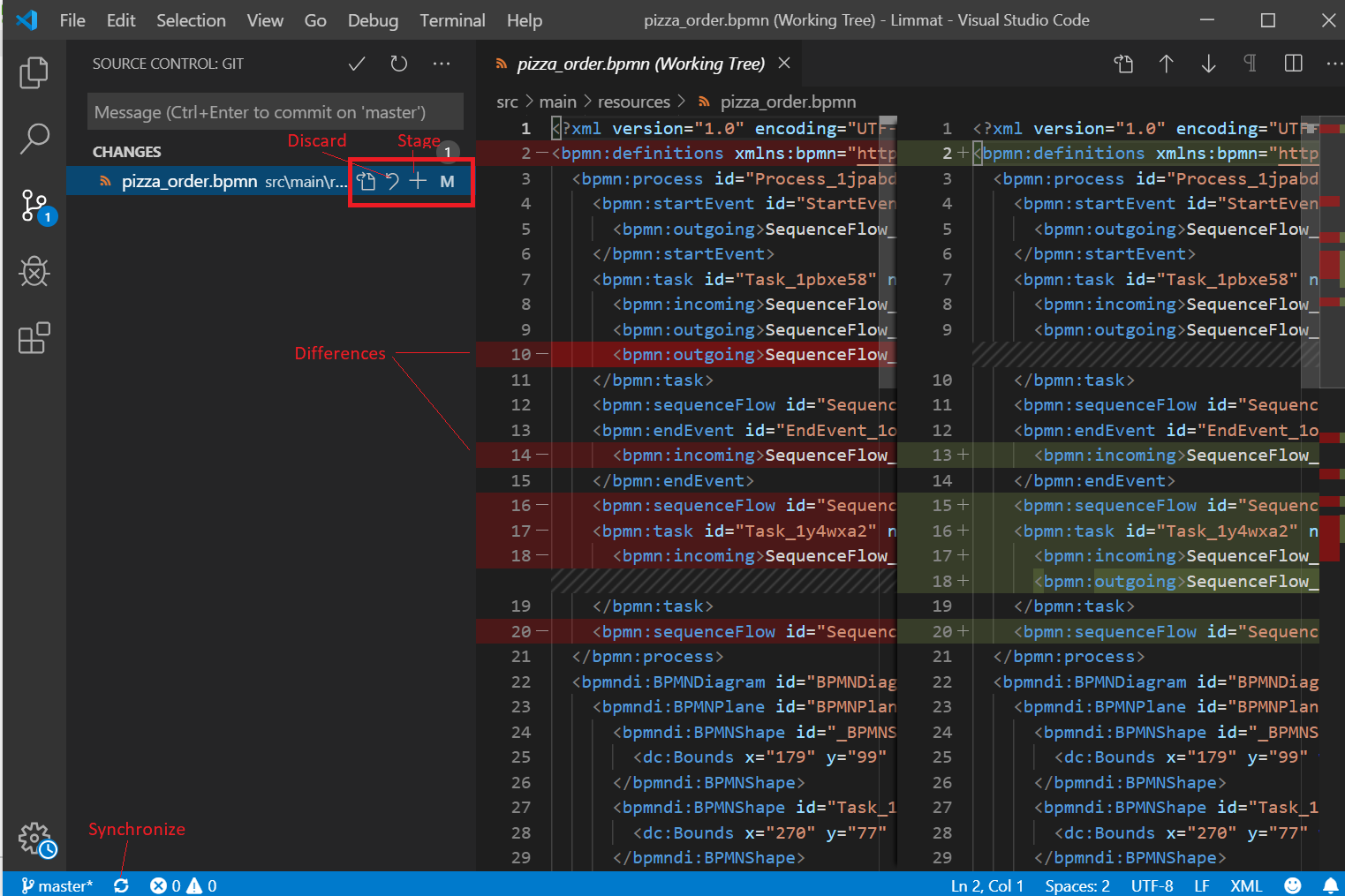
In the Source Control view, if clicked on the changed file, you can see the difference as compared to the version in the GitHub repository.
Staging enables committing selected files. Unstaged files do not get committed to GitHub and can be continued to edit. To stage a file, click on the '+' icon next to the file. Refer to the image above.
In cases of conflict, the changes to the local file can be discarded by clicking on the discard icon as shown in the image above.
The changes made by other team members can be pulled by synchronizing the repository. To view the history of changes, an additional extension 'GitHub History' (see instructions) needs to be installed.
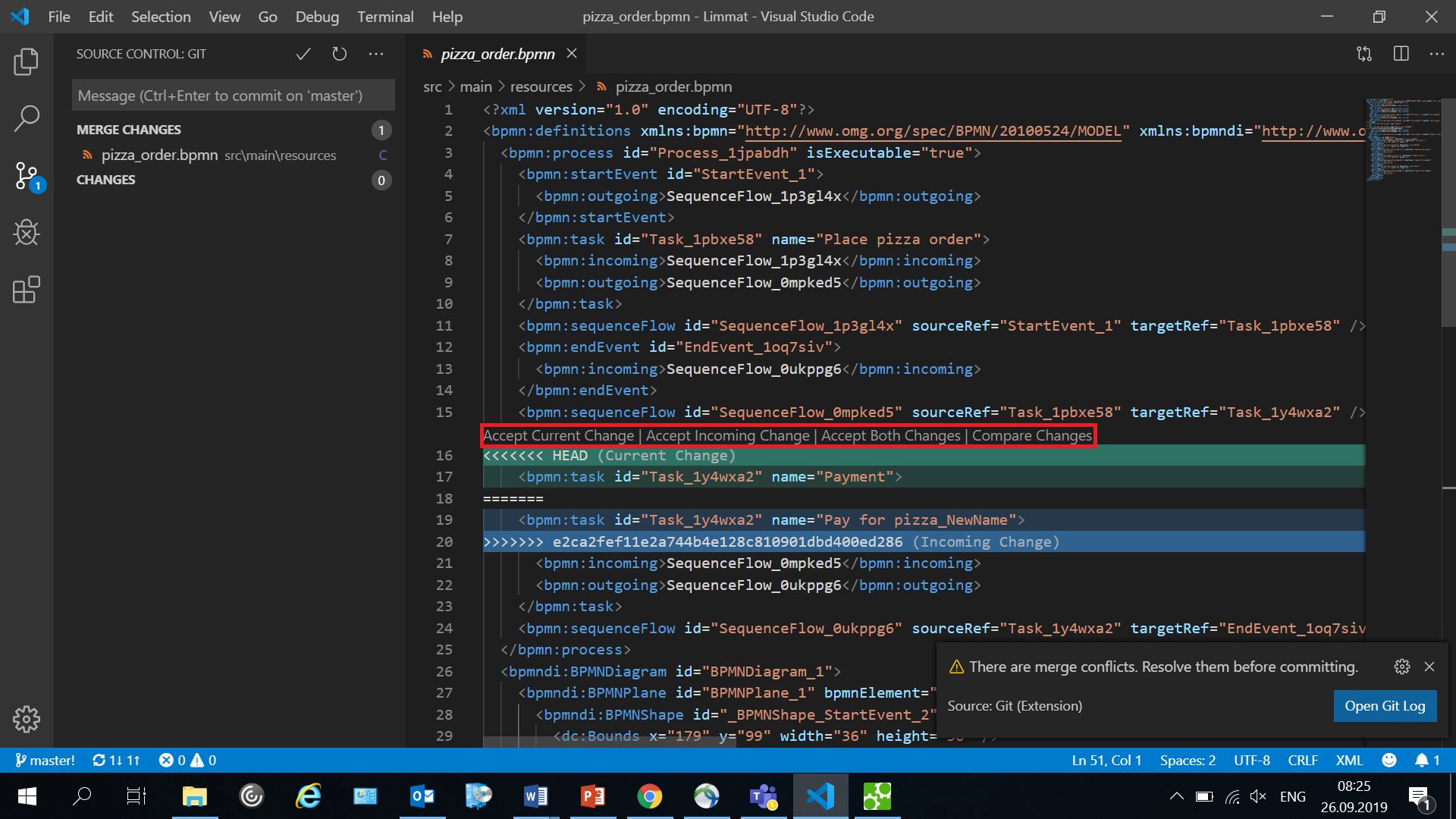
While working in collaboration, a very likely scenario is to face conflicts while modifying the same file. If multiple members commit changes to the same file, Git identifies it as a conflict. Visual Studio code provides the possibility of resolving conflicts by either accepting current (local) changes, accepting the incoming changes (by other members) or accept both changes (if the changes are not interfering with each other). The following image illustrates this behavior:
The wiki documentation can be created and edited locally from your computer using VS Code.
The first page of your Wiki documentation should be created directly in your Github repository by clicking on the Wiki link and then on the "Create the first page" and then "Save".
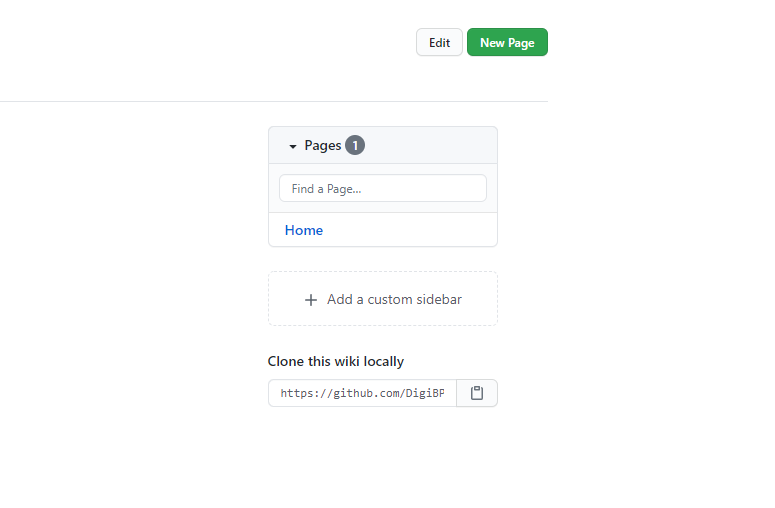
As soon as the first page is created, you will notice a Github link that can be cloned (Clone this wiki locally).
Next, you can simply copy the link to the Wiki and clone it using VS code by following the similar steps as above. Alternatively, you can use a tool like Github Desktop and use it to clone the Wiki repository.
Once you have cloned the Wiki locally, you can start adding/editing the markdown pages (*.md). The wiki pages can be committed and pushed to Github by following steps similar to Step 2 and 3 above.
Quite often you might want to include images in your wiki documentation. You can follow the two step approach given below for this purpose.
Create a new folder <image_folder_name> in your main repository (not the Wiki repository) and add your images in this folder. You can create a structure by adding further folders inside this <image_folder_name>.
You can include the images in your Wiki documentation by using one of the following coding styles
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DigiBP/<your_repository_name>/master/<image_folder_name>/<image_name>" alt="" width="500">or
[](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DigiBP/<your_repository_name>/master/<image_folder_name>/<image_name>)