Ford Fulkerson Algorithm - David-Chae/Algorithms_Notes_Solutions GitHub Wiki
In this tutorial, you will learn what Ford-Fulkerson algorithm is. Also, you will find working examples of finding maximum flow in a flow network in C, C++, Java and Python.
Ford-Fulkerson algorithm is a greedy approach for calculating the maximum possible flow in a network or a graph.
A term, flow network, is used to describe a network of vertices and edges with a source (S) and a sink (T). Each vertex, except S and T, can receive and send an equal amount of stuff through it. S can only send and T can only receive stuff.
We can visualize the understanding of the algorithm using a flow of liquid inside a network of pipes of different capacities. Each pipe has a certain capacity of liquid it can transfer at an instance. For this algorithm, we are going to find how much liquid can be flowed from the source to the sink at an instance using the network.
Terminologies Used Augmenting Path It is the path available in a flow network.
Residual Graph It represents the flow network that has additional possible flow.
Residual Capacity It is the capacity of the edge after subtracting the flow from the maximum capacity.
How Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm works?
The algorithm follows:
-
Initialize the flow in all the edges to 0.
-
While there is an augmenting path between the source and the sink, add this path to the flow.
-
Update the residual graph.
We can also consider reverse-path if required because if we do not consider them, we may never find a maximum flow.
The above concepts can be understood with the example below.
Ford-Fulkerson Example
The flow of all the edges is 0 at the beginning.
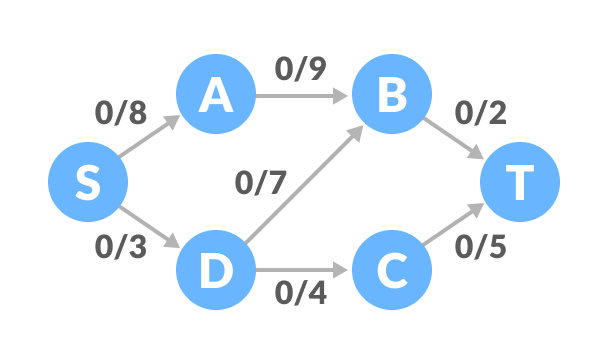
- Select any arbitrary path from S to T. In this step, we have selected path S-A-B-T.

The minimum capacity among the three edges is 2 (B-T). Based on this, update the flow/capacity for each path.

- Select another path S-D-C-T. The minimum capacity among these edges is 3 (S-D).

Update the capacities according to this.

- Now, let us consider the reverse-path B-D as well. Selecting path S-A-B-D-C-T. The minimum residual capacity among the edges is 1 (D-C).

Updating the capacities.

The capacity for forward and reverse paths are considered separately.
- Adding all the flows = 2 + 3 + 1 = 6, which is the maximum possible flow on the flow network. Note that if the capacity for any edge is full, then that path cannot be used.
Ford-Fulkerson Applications
- Water distribution pipeline
- Bipartite matching problem
- Circulation with demands
Implementations
Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm - Java Implementation
Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm - Python Implementation