Vectors vs. Arrays: Fun Time!! - Casady-ComSci-Seminar/Seminar-Notes GitHub Wiki
Vectors (Not the orange fella from Despicable Me): Used in Random Numbers Assignment
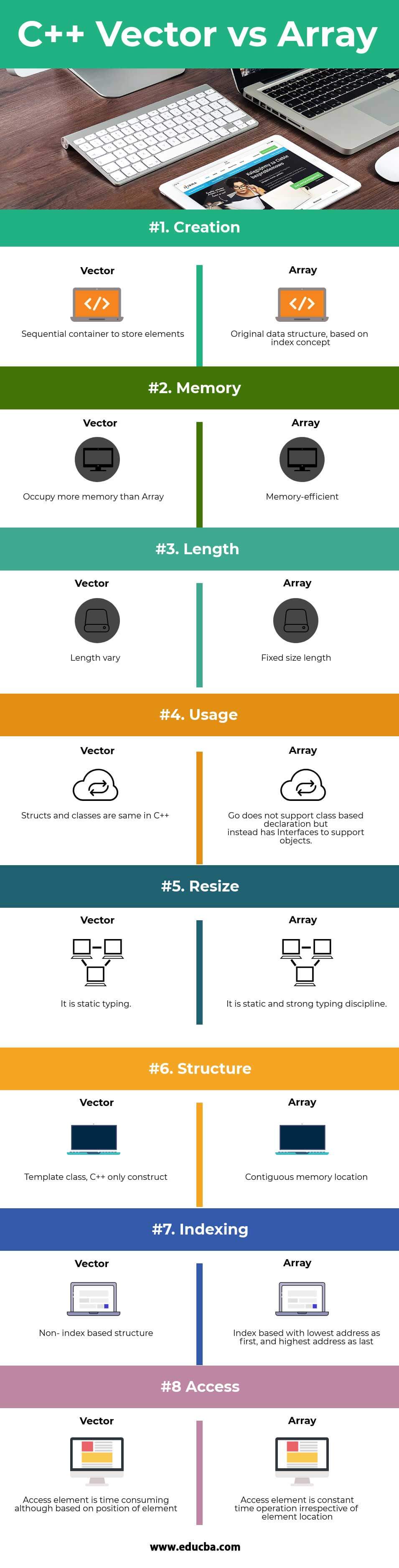
- Vectors hold as many things as you want. They grow dynamically with what you add to them.
- Sad Part: They take up a lot of your memory 😢
- Vectors are a template class so it is necessary to use "#include "
- Vectors are automatically deallocated.
- Vectors can be returned from a function.
- Vectors can be copied or assigned directly.
- Vectors can get the size using a built in function.
Example(initialization):
std::vector<int> vector;
vector.push_back(6); //pushes it onto the end
cout<<vector[0]<<endl; //gets the first thing
vector.pop_back(); //pops the thing on the end offArrays (Not as cool as vectors): Used in Using Arrays Assignment
- Arrays only hold a finite value that is declared during initialization.
- Arrays take up a very small amount of space in your memory because they do not grow dynamically like vectors. However, this does add restrictions to how you use the array.
- Arrays are built in to C++ so there is no need to include them, this is unlike vectors.
- Arrays need to be deallocated explicitly.
- Arrays are passed into functions as pointers.
- Arrays cannot be returned unless dynamically allocated from a function.
- Arrays cannot be copied or assigned directly.
- No size function. Have to do it yourself.
Example Code:
int array[5] = {0}; // makes the array full of zero
int array[5] = {2,3,5,7,11}; // array with numbers in it (mind💥)Citations(this is proper Heath Style Citation):
Image Address: https://cdn.educba.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/C-Vector-vs-Array.jpg
Helped From: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/advantages-of-vector-over-array-in-c/