FreeBSD 14 Pi 5 MAX‐M8Q - BYO-NTP/recipes GitHub Wiki
| date | server | os | gnss | daemon | 🎯 | 🗣️ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-06 | Pi 5 | FreeBSD 14 |
Waveshare MAX-M8Q | chrony NTPsec ntp |
2 ms | discuss |
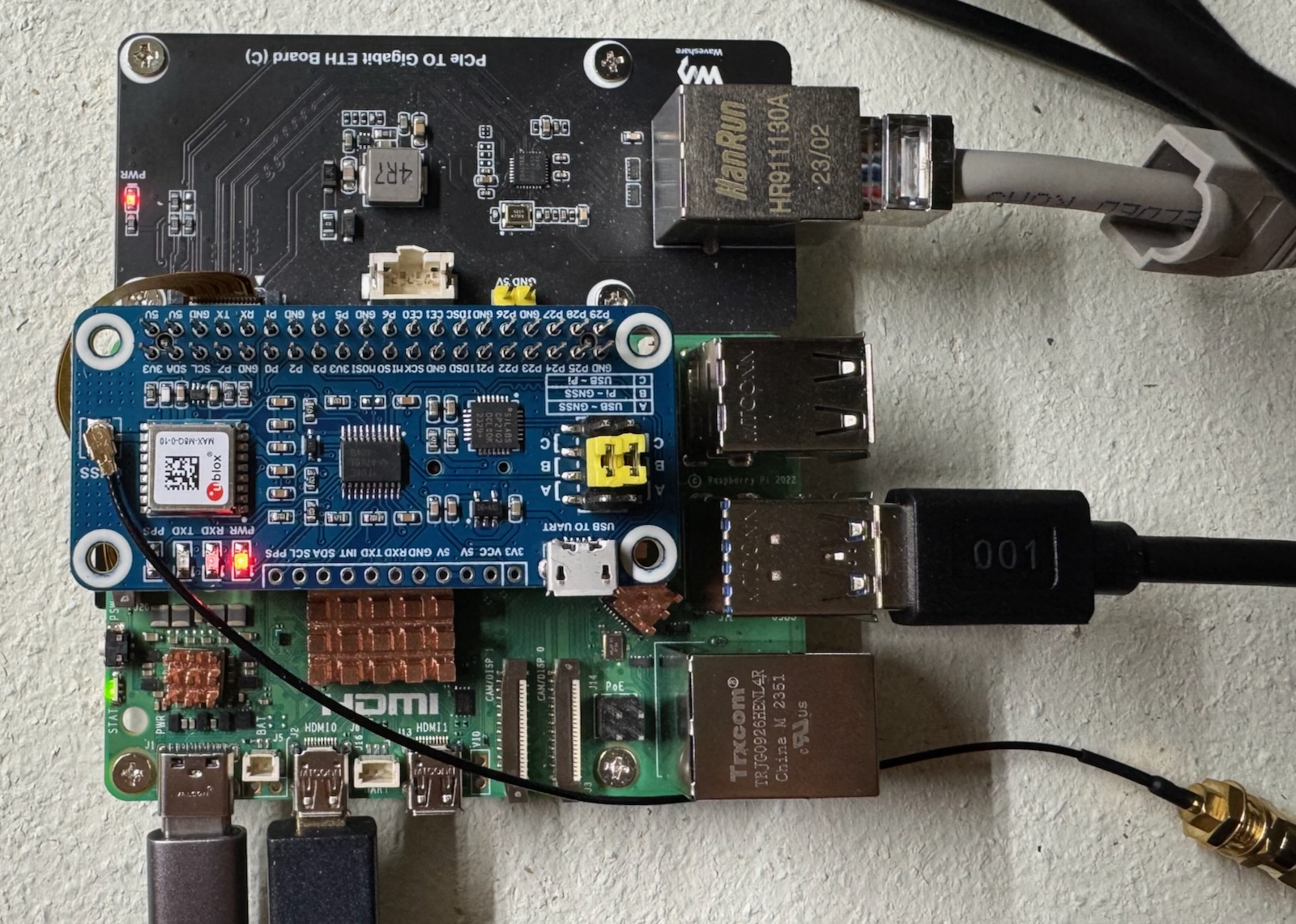
Although the Waveshare HAT works fine on the Pi 5 with Pi OS, my attempts to get serial communication with the GPIO serial ports have failed. I suspect that the one PL011 that shows up is the console/debug port. That leaves connecting via USB, with a major loss of precision. 🤷🏼 A better choice for a Pi 5 is running Pi OS.
Install FreeBSD for Pi 5
Configure the jumpers to A mode and plug a USB cable into the HAT and a Windows computer with u-blox u-center installed. Configure the GNSS per the recommendations on the gnss page.
See the Assembly photo if needed.
Avoid interference from the USB mouse:
sysrc devmatch_blocklist+="ums"The NTP daemons look to /dev/gps0 by default, so link gps0 to the serial port using devfs:
test -L /dev/gps0 && rm /dev/gps0
grep -q gps0 /etc/devfs.conf && sed -i '' -e 's/^link.*gps0$//g' /etc/devfs.conf
echo 'link cuaU0 gps0' >> /etc/devfs.conf
service devfs restartVerify the USB serial adapter
dmesg | egrep '(uart|pps|CP2102)'uart0: <PrimeCell UART (PL011)> iomem 0x107d001000-0x107d0011ff irq 0 on acpi0
ugen0.2: <Silicon Labs CP2102 USB to UART Bridge Controller> at usbus0
uslcom0: <Silicon Labs CP2102 USB to UART Bridge Controller, class 0/0, rev 1.10/1.00, addr 1> on usbus0Each section heading is a link with many more details about installing, configuring, and verifying that particular NTP daemon.
export NTP_REFCLOCKS=$(cat <<EO_CHRONY
refclock SHM 0 refid NMEA precision 0.02 offset 0.052 poll 4 trust
EO_CHRONY
)
curl -sS https://byo-ntp.github.io/tools/chrony/install.sh | shexport NTP_REFCLOCKS=$(cat <<EO_NTPSEC
#refclock nmea refid NMEA minpoll 2 maxpoll 4 time2 0.060 baud 115200 mode 8 prefer
# gpsd via SHM
#refclock shm unit 0 refid NMEA minpoll 2 maxpoll 4 time1 0.055 prefer
# gpsd via JSON driver
refclock gpsd mode 2 refid NMEA minpoll 2 maxpoll 4 time2 0.055 prefer
EO_NTPSEC
)
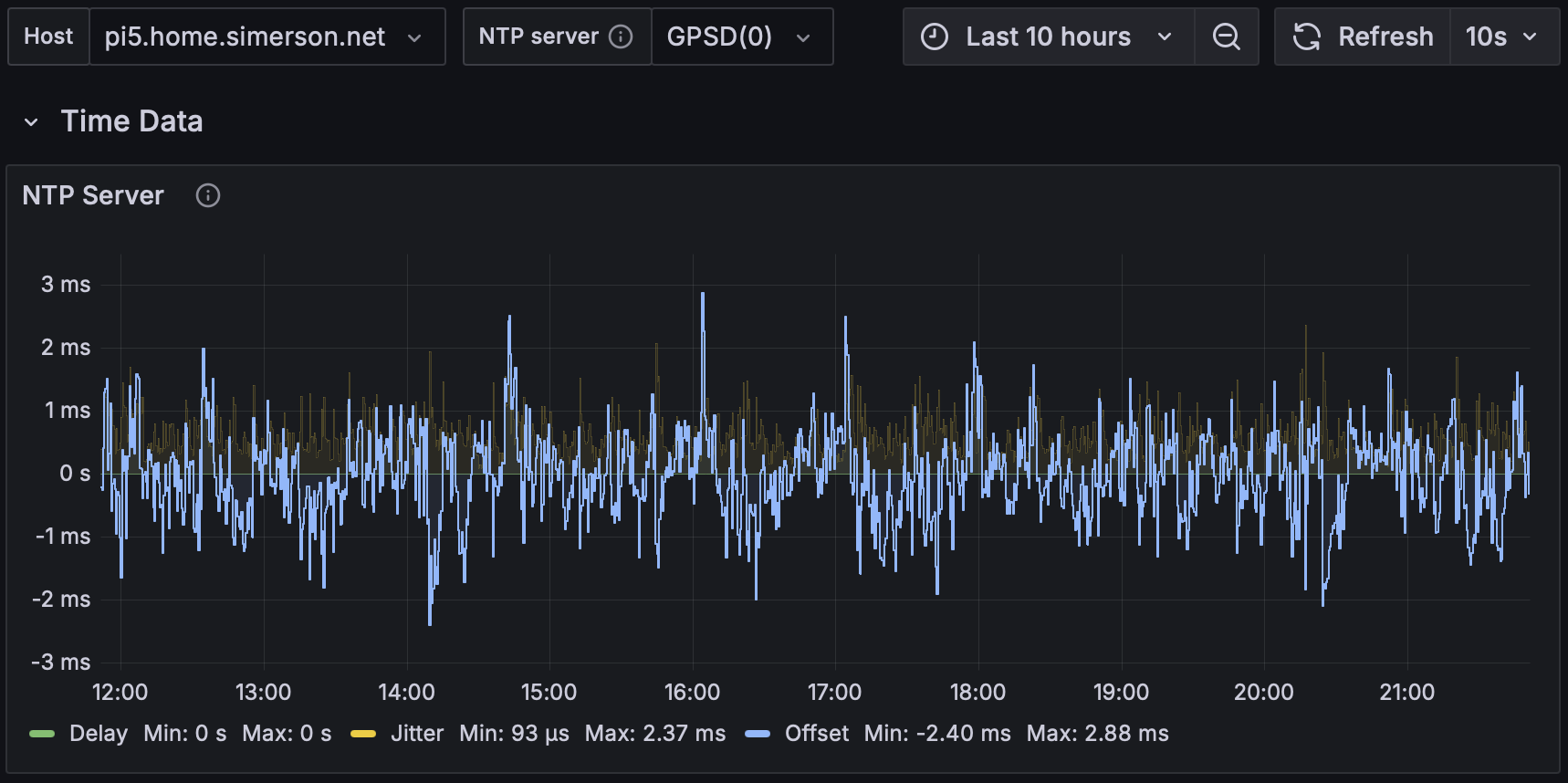
curl -sS https://byo-ntp.github.io/tools/ntpsec/install.sh | shOver 12-hour collection intervals, changing only the driver from direct NMEA (0.0134) to shm or gpsd (0.00288) made a notable improvement in the accuracy.
export NTP_REFCLOCKS=$(cat <<EO_NTP
server 127.127.20.0 minpoll 3 maxpoll 4 mode 88 prefer
fudge 127.127.20.0 refid NMEA time2 0.050
EO_NTP
)
curl -sS https://byo-ntp.github.io/tools/ntp/install.sh | sh- watch the status in near real time (requires installing gnu-watch):
- printf '\e[8;9;80t'; ssh -t pi5 gnu-watch -n2 chronyc sources
- printf '\e[8;9;80t'; ssh -t pi5 gnu-watch -n2 ntpq -c peer
- Measure the offset
- Gather statistics with telegraf + influxdb + grafana or similar.
Regrettably not pictured, the USB cable running from the GNSS HAT to the Pi.
NTPsec
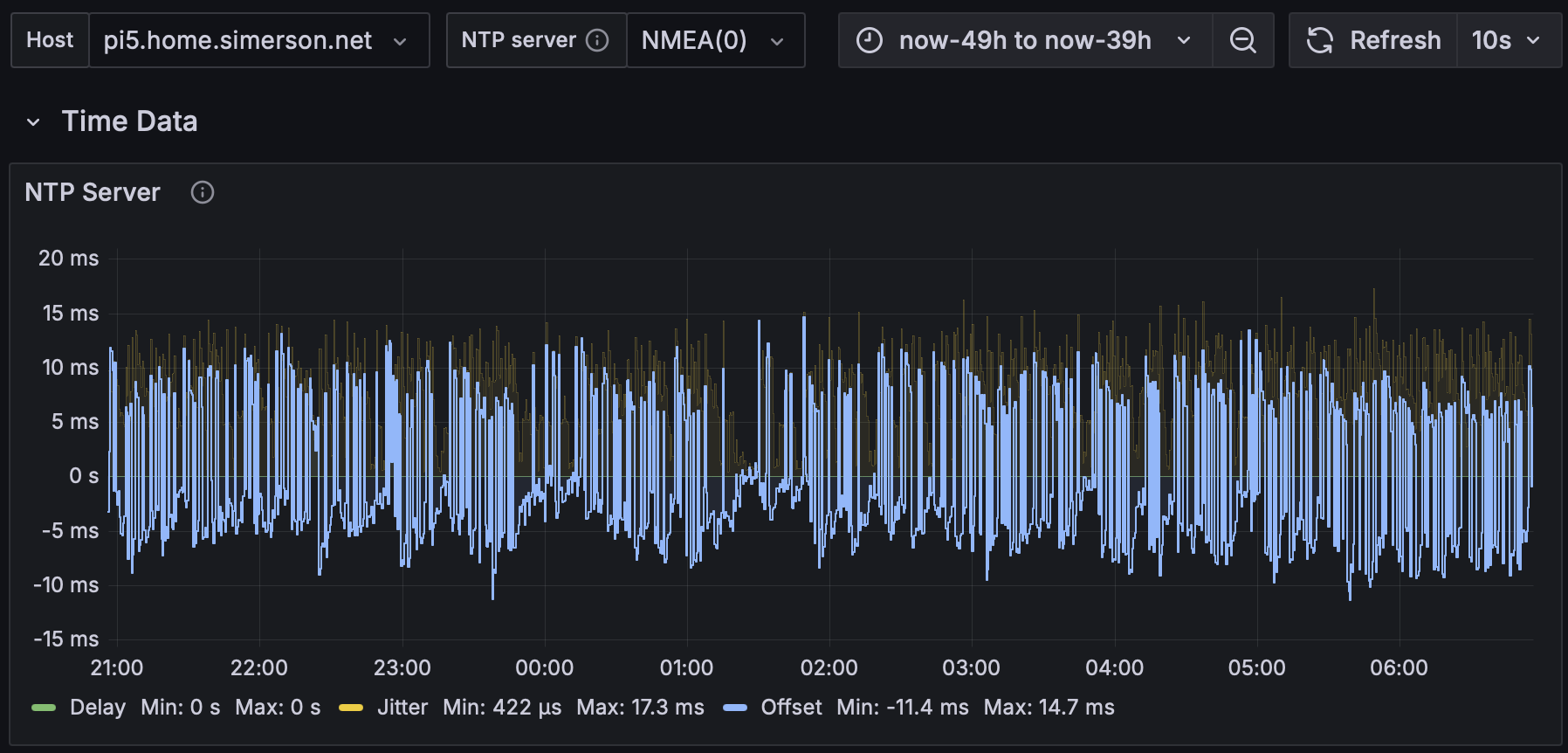
Note that the NTPsec performance would be just as bad as the ntp results below were it not for switching to the gpsd driver.
ntp