Contributing Guidelines - AyranIsTheNewRaki/Herodot GitHub Wiki
Create a local clone of your fork
- Fork the repository.

- Navigate to your fork of the Herodot repository and click Clone or download.
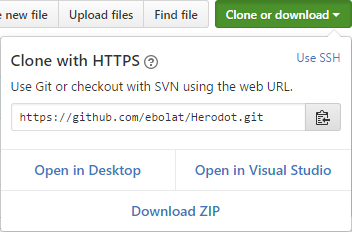
-
Copy the clone URL for the repository.
-
Open Git Bash.
-
Change directories to the location where you want the local project folder will be created.
-
Type
git clone, and then paste the clone URL you copied. It will look like this, with your GitHub username instead ofYOUR-USERNAME:
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/Herodot
- Press Enter. Your local clone will be created.
Sync your fork with the original Herodot repository
-
Open Git Bash.
-
Change directories to the location of the fork you cloned.
-
Type
git remote -vand press Enter. You'll see the current configured remote repository for your fork.
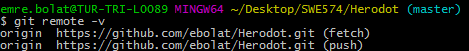
- Type
git remote add upstream, and then paste the URL you copied from the original repository:
git remote add upstream https://github.com/AyranIsTheNewRaki/Herodot.git
- To verify the new upstream repository you've specified for your fork, type
git remote -vagain. You should see the URL for your fork asorigin, and the URL for the original repository asupstream.
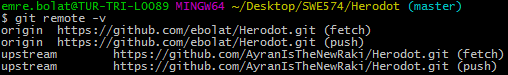
Keep your local fork up-to-date
- Navigate to your local
masterbranch.
git checkout master
- Fetch the branches and their respective commits from both
upstreamandlocalrepositories.
git fetch --all
- Merge the changes from
upstream/masterinto your localmasterbranch. This brings your fork'smasterbranch into sync with theupstreamrepository, without losing your local changes.
git merge upstream/master
Making Changes and Creating Pull Requests
- Never work on your
masterbranch even if it is your localmaster. First sync your localmasterwithupstream/masterand branch off a feature branch from localmasterby typing:
git checkout -b myfeaturebranch master
-
Make your changes and commit. (If your commit is related to an issue, please add issue reference number to your commit)
-
Push your changes.
-
Submit a pull request as described here.