1) PERTINENT INFORMATION - Anirudh-123/LOADING-AND-UNLOADING-MACHINE GitHub Wiki
LOADING AND UNLOADING MACHINE
NEED STATEMENT
- One of the warehouse in your town opts to go for automation of loading and unloading of goods you have to design a machine that detects when a goods vehicle parked and then loads as per requirements.
ABOUT LOADING AND UNLOADING MACHINE
-
It is an intermittent-operation or continuous-operation hoisting and conveying machine used to perform loading-unloading, conveying, and stacking operations with bulk and unit goods.
-
They may be stationary, mobile, or self-propelled, depending on the operations performed. They may be driven by internal-combustion engines or electric motors , whose power transmitted to the working and drive elements through mechanical or hydraulic transmissions.
-
Loading-unloading machines are divided into two basic groups: loaders, which primarily perform loading operations but are often also used for conveyor goods, and unloaders, which are generally used only for unloading bulk goods.
-
Load-lifting machines are stationary, self-propelled, or movable, depending on their application. They may have continuous or intermittent action and may be driven electrically, by an internal-combustion engine, or by some other power source.
-
The principle parts of load-lifting machines are frame, the lifting mechanism, and the carrying system. Self-propelled are equipped with mechanism for movement; rotating types are equipped with rotation mechanism.
-
For lifting and lowering people the machine is equipped with cabins and cages; for moving piece goods it has hooks and various special grips; and for moving piece goods it has hooks and various special hooks; and for bulk materials, it has buckets, dippers, or graders.
THE EXISTING SOLUTIONS FOR LOADING AND UNLOADING MACHINES
- MARINE LOADING ARM
- WAGON TPPLER
- MOBILE WAGON LOADER
- ROBOTIC AGV
1] MARINE LOADING ARM
-
A marine loading arm, also known as a mechanical loading arm, loading arm, or MLA is a mechanical arm consisting of articulated steel pipes that connect a tankship such as an oil tanker or chemical tanker to a cargo terminal.
-
A marine loading arm is an alternative to direct hose hookups that is particularly useful for larger vessels and transfers at higher loading rates and pressures. Controlled manually or hydraulically, a loading arm employs swivel joints and can, to some extent, follow the movement of a moored vessel.
-
Many loading arm systems feature quick-connect fittings. Gasket or o-ring arrangements are required to make a secure seal to the ship's manifold flange. A loading arm must be drained or closed off before the connection is broken off.
-
This is usually done in two ways. For fuels such as gas oil and diesel, the lines can be blown out with high pressure air. In the case of fuels such as kerosene or petrol, the lines can be stripped with pumps.
-
Loading arms can handle both liquids and gases, in a wide range of viscosities and temperatures.[6] Cargoes from liquid-sulphur to liquefied natural gas are moved through marine loading arms. Loading arms service vessels in a wide range of sizes, from small river barges to the largest supertankers.
-
Various designs exist, and specific installations can be tailored for a given port based on considerations such as vessel size, cargo flow rate and cargo temperature. Environmental constraints, such as the range of tide, wind conditions, and earthquake tolerance, can also affect choice of loading arm.
-
A loading arm installation may include add-ons such as hydraulic or manual quick connect couplers, position monitoring systems, emergency release systems, and piggyback vapor return lines. Compared to cargo hoses, the loading arm's main drawback is its comparative lack of flexibility.

Loading Arms for Refinery Products:
For a berth handling Refinery products which are stored at ambient conditions, it is common to have two pairs of loading arms to handle all non-refrigerated/pressurised products. Each pair of arms has a manifold such that one pair is dedicated to ‘white oils’ and one pair is dedicated to ‘black oils’. Product contamination is avoided by stripping and draining as part of the loading process, as follows:
-
After pumping to the tanker is complete, the MOV upstream of the manifold is closed. These MOVs are generally the double seal design, to ensure product segregation.
-
Liquid remaining in the manifold and the inboard section of the loading arm is then pumped out by the stripping pump. The stripping pump discharges either into the outboard section of the selected loading arm (i.e. onto the tanker) via a small ‘piggy back’ line, or back into the supply pipeline upstream of the MOV, or to the on-shore slops system.
-
Any unpumpable material in the manifold is drained into an on-shore slops drum at the berth, leaving the manifold and loading arms empty. For hydrocarbons stored at ambient conditions, the stripping pump should discharge into the outboard section of the loading arm because generally speaking the material has already been metered and therefore belongs to the customer.
How Marine Loading Arm Works (Fig. 2):
- Marine loading arm is designed based on its Operating envelop
- Marine Loading Arms is operated by using the hydraulic system.
- Heart of the marine loading arm is swivel Joint. Which plays a important role in operating the Marine loading arms.
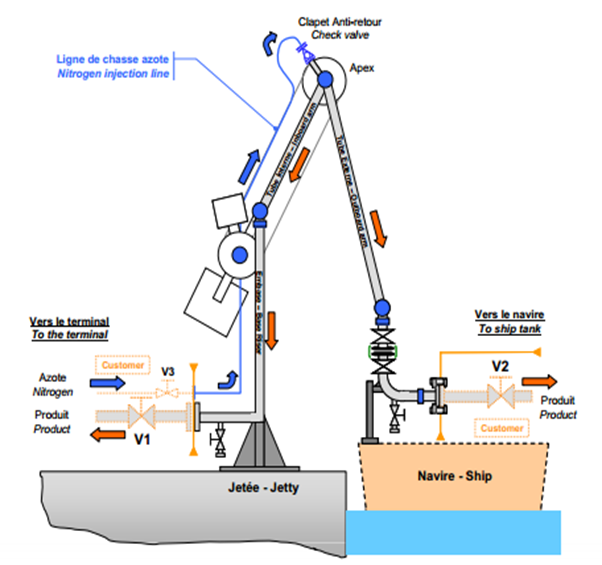
Swivel Joints (Fig. 3):
-
Enabling the loading arm once connected, to follow the movements of the vessel within the working envelope.
-
Allow the rotation between two items of a product line whilst ensuring no product leakage, even under external pressure.
-
ln a standard marine arm there are six swivel joints with the direction of rotation in three planes giving the arm six degrees of freedom. This allows the arm to be maneuvered to and from the vessel and, once connected, allows the arm to follow all the motions of the vessel.
-
Each swivel joint is made up of a male and female part joined by two or three bail bearing raceways allowing the free rotation of the joint. A compression type packing seal is used to seal the two parts of the swivel joint.
-
Swivel Joints are available in various materials including carbon steel, LTCS, Hastelloy, Titanium etc.

End Connection (Fig. 4) of Marine Loading Arm:
-
The End connection of the MLA is a standard ASME B16.5 flange.
-
It is available in various size and rating.
-
It is also called as Quick connect / disconnect coupling (QCDC)
-
End connections are of two types: Manually operated; Hydraulically Operated.

| S.No | Components | Work | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Apex Swivel Joint | Heavy-duty materials allow for matching the various kinds of product to be transffered, they be toxic, explosive liquids or gases. With help of lining or heating, they can handle most criticle products. | https://www.whatispiping.com/an-article-on-marine-loading-arm. |
| 2. | Inboard Arm | The inboard counterweights are fixed to the inboard counterweight extension beam and adjusted to assure correct balancing of the loading arm assembly | http://www.mechanicalengineeringsite.com/marine-loading-arm-types/ |
| 3. | Slewing Drive | It is a gearbox that can safely hold radial and axial loads,as well as transmit a torque for rotating. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Slewing_drive |
2] WAGON TIPPLER
-
Tippler is used for emptying the loaded wagons by tipping it. Tippler retains wagon from top as well as from side by using clamping devices provided on it. Apart from that track stops, wheel grippers and different type of limit switches are provided as features of wagon tippler.
-
Tippler is driven by either Hydraulic drive or by electro-mechanical drive OR Hydro Mechinical Drive .
-
Placement of wagon, on tippler platform, is accomplished by wagon marshalling equipment like Side Arm Charger or Bettle Charger or Pussher Car deppending on Type of Wagon Tippler application.
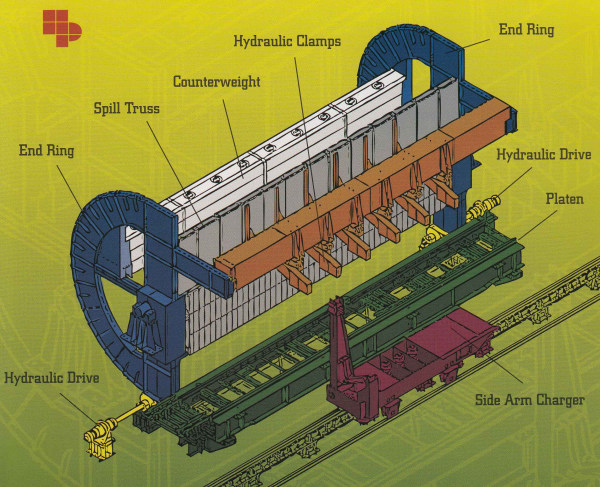
-
The platen assembly is a fabricated steel structural frame, which consists of an inner platen and an outer platen. The inner platen is placed on top of the outer one, and the weigh bridge cells are mounted between the two.
-
The end rings are fabricated steel frames of semi-circular shape. Two end rings are connected by the spill girder, top clamp beam and counterweight box girder. The end rings support the platen assembly, along with the loaded wagon to be tipped. Each end ring is supported on a trunnion shaft mounted on plummer blocks, which are supported on a steel stool or pedestal.
-
The wagon tippler is equipped with six hydraulically-operated steel clamping arms moving through the hydraulic cylinder. All the clamps are designed to more into position as the wagon tippler begins to rotate, and they clamp on the top of the wagon at a pre-determined angle and hold the wagon firmly until it returns to its normal resting position, when the clamps release the wagon.

| S.No | Components | Work | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clamp Assembly | It is designed so that it can clamp both the maximum and the minimum height of the wagon tipped. The clamping system is capable of holding a fully loaded wagon at any poasition during operation. | https://info.heylpatterson.com/blog/bid/104157/Rota-Side-Wagon-Tipplers-Handle-Bulk-Materials-for-the-Indian-Market |
| 2. | Spill Truss | It is also known as spill grinder.It connects and supports the loaded wagon lengthwise during operation.It also toouches wagaon standing without pressure. | https://info.heylpatterson.com/blog/bid/104157/Rota-Side-Wagon-Tipplers-Handle-Bulk-Materials-for-the-Indian-Market |
| 3. | Wheel Grippers | They are fitted on the platform to grip the wagon wheels and prevent dearling during tippling operation. | https://info.heylpatterson.com/blog/bid/104157/Rota-Side-Wagon-Tipplers-Handle-Bulk-Materials-for-the-Indian-Market |
| 4. | Wheel Chocks | They are operated hydraulically on the inhaul and outhaul side of the platen prevent the wagon wheels from rolling back on the platen. | https://info.heylpatterson.com/blog/bid/104157/Rota-Side-Wagon-Tipplers-Handle-Bulk-Materials-for-the-Indian-Market |

3] MOBILE WAGON LOADER
-
The wagon unloading systems are required in the process plants for unloading material received from the mines / ports by the railway wagons. Two types of wagons are generally used in the Indian Industry viz. BOXN wagons and BOBRN wagons.
-
The loading systems under this type could be further classified into two types viz. (i) the mobile loader will be travelling for the complete length of the rake (ii) series of loaders will be provided with limited travel and would load a particular number of loaders at a time
-
The type of wagon loading system depends on the properties of the material to be loaded and limitations in the layout. Hence each type of wagon loading systems mentioned above are applicable and are being adopted on different occasions.
-
The mobile wagon loader consists of a long conveyor, a travelling tripper, a cross belt conveyor mounted on the tripper and a loading chute. This system will be provided parallel to the rail track where the rake containing 58 wagons will be parked.
-
The travelling tripper will be travelling along the conveyor for loading the material into the wagons. The storage silo will be located at the tail end of this conveyor and feeds the material continuously onto the conveyor.

WORKING
-
At the start of the loading operation, travelling tripper will be located at the starting edge of the first wagon of the rake. The material from the silo will be fed onto the conveyor which will be conveyed to the cross conveyor mounted on the tripper.
-
The material will be loaded into the wagon through the loading chute. The travelling tripper moves forward while discharging the material into the wagon at a constant speed.
-
When the loading chute approaches the end of the wagon, the loading chute changes over from one wagon to the next wagon and thus there will not be any spillage between the wagons. The loading operation will continue to the next wagon without any interruption.
-
This process will be continued till the loading of the last wagon of the rake.
| S.No | Components | Work | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Long Conveyor | It works by using two pulleys that continually loop over the material that rotates over them and hence transports the loads from one place to another. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conveyor_belt |
| 2. | Travelling Tripper | They are provided in conveyor system that have one or more chutes to discharge the material from conveyor belt. | https://www.tradeindia.com/manufacturers/travelling-trippers.html |
| 3. | Cross Belt Conveyor | They are very efficient for transport of goods over considerable distance compared to long conveyor belts | https://www.tce.co.in/Wagon%20Loading%20And%20Unloading%20System.pdf |

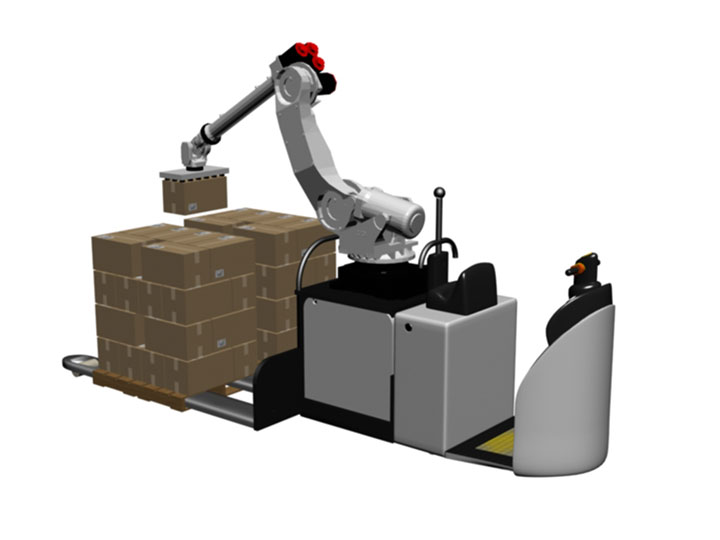
4] ROBOTIC AGV
-
An automated guided vehicle or automatic guided vehicle (AGV) is a portable robot that follows along marked long lines or wires on the floor, or uses radio waves, vision cameras, magnets, or lasers for navigation.
-
They are most often used in industrial applications to transport heavy materials around a large industrial building, such as a factory or warehouse. Application of the automatic guided vehicle broadened during the late 20th century.
-
The AGV can tow objects behind them in trailers to which they can autonomously attach. The trailers can be used to move raw materials or finished product. The AGV can also store objects on a bed.
-
The objects can be placed on a set of motorized rollers (conveyor) and then pushed off by reversing them.
-
AGVs are employed in nearly every industry, including pulp, paper, metals, newspaper, and general manufacturing. Transporting materials such as food, linen or medicine in hospitals is also done.
-
AGVs used in Warehouses and Distribution Centers logically move loads around the warehouses and prepare them for shipping/loading or receiving or move them from an induction conveyor to logical storage locations within the warehouse. Often, this type of use is accompanied by customized warehouse management software.
-
AGVs can be applied to move materials in food processing (such as the loading of food or trays into sterilizers) and at the “end of line,” linking the palletizer, stretch wrapper, and the warehouse. AGVs can load standard, over-the-road trailers with finished goods, and unload trailers to supply raw materials or packaging materials to the plant. AGVs can also store and retrieve pallets in the warehouse.
-
Wireless charging A very efficient and maintenance-free way to charge the AGV batteries is wireless power transfer (WPT). Typically the system works as an inductive power transmission system with a sender and receiver coil. The power transmitted can reach up to 300KW. Typical AGV systems range around 3KW of charging power.

| S.No | Components | Work | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hydraulic System | It provides the necessary lifting power to transfer pallets between destinations in a facility. | https://youtu.be/yGhmOfAbi_U |
| 2. | Load Sensors | There are three photoelectric sensors. Two sensors are designated as "load off-board" sensors and they are responsible for detection of load, or a lack of load at pick or drop location. The "load on-board" sensors communicate to AGV computer that a load is onboard or not. | https://youtu.be/yGhmOfAbi_U |
| 3. | Warning Lights | There are four amber warning lights. A steady, alternating left/right flashing indicates normal operation. An intermittent, alternating left/right flashing pattern indicates that AGV has come to some form of stop. If both sides are flashing simultaneously a system error has occurred. | https://www.myodesie.com/wiki/index/returnEntry/id/3077 |
| 4. | Contact Obstacle Detectors | The four side sensors are photoelectric sensors that communicate to AGV computer that some contact has been made with obstacle. | https://www.myodesie.com/wiki/index/returnEntry/id/3077 |

REFERENCES
1.https://www.whatispiping.com/an-article-on-marine-loading-arm 2.http://www.mechanicalengineeringsite.com/marine-loading-arm-types/ 3.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Slewing_drive 4.https://info.heylpatterson.com/blog/bid/104157/Rota-Side-Wagon-Tipplers-Handle-Bulk-Materials-for-the-Indian-Market 5.https://youtu.be/eciq2qRz9oo 6.https://www.tce.co.in/Wagon%20Loading%20And%20Unloading%20System.pdf 7.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conveyor_belt 8.https://www.myodesie.com/wiki/index/returnEntry/id/3077 9.https://youtu.be/yGhmOfAbi_U