Module 1 (Priority Queue) - AlproITS/StrukturData GitHub Wiki
- Top - is a node with the highest priority within the queue.
Priority Queue is a unique variation of the Queue data structure, as it will sort the stored data by default. Data stored within a Priority Queue will be sorted based on their priority, which means the first data to come out is the one with the highest priority, regardless of when they got inserted. Knowing this, we can utilize Priority Queues to solve problems where different priorities exist.
"pqueue" might be used to shorten "Priority Queue" for the duration of this module.
- isEmpty - to check whether the pqueue is empty or not.
- push - to insert new data.
- pop - to remove data with the highest priority.
- top - to get the data with the highest priority/located at the top.
Pqeues could be used to solved the following problems:
- CPU program scheduling.
- Implementation of Dijkstra Shortest Path and Prim's Minimum Spanning Tree algorithms.
- Problems where the data have different priority levels.
A complete implementation of Priority Queue can be accessed here.
In this module, the Min-Priority Queue will be implemented, where nodes with the smaller numbers will be prioritized.
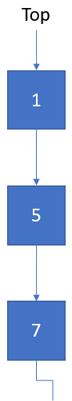
The simplest way to implement such pqueue is by modifying the Singly Linked List data structure, where the top pointer is used to refer to the node with the highest priority.
Sidenote: Implementing a Priority Queue data structure by using Linked List is not the most efficient implementation. One way to achieve higher efficiency is by implementing it with the Heap Tree data structure.
-
Nodes of a pqueue can be represented by a struct named
pqueueNodethat stores anintvariable and a pointer to refer to the next node.typedef struct pqueueNode_t { int data; struct pqueueNode_t *next; } PQueueNode;
-
A pqueue has one pointer
topto refer the node with the highest priority within its structure.typedef struct pqueue_t { PQueueNode *_top; unsigned _size; } PriorityQueue;
-
To check whether a pqueue is empty or not, simply check whether its
toprefers toNULLor not.bool pqueue_isEmpty(PriorityQueue *pqueue) { return (pqueue->_top == NULL); }
-
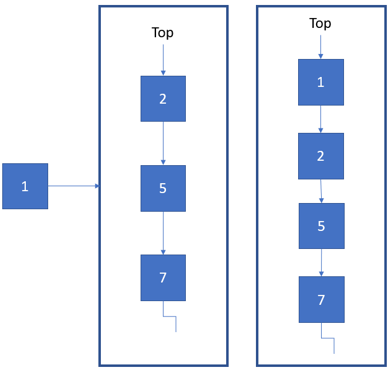
To do a push, kindly follow these steps:
- store the current
topnode within a temporary variable - make a new node.
- if the pqueue is empty, make the new node as the
top. - if it is not empty, there can be two cases.
First case, the new node contains smaller data than the one stored at the
top(higher priority)- make the next of the new node refer to the current
top. - make the
toprefer to the new node.
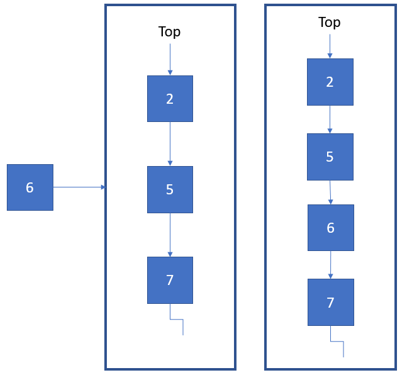
Second case, the new node contains bigger data than the one stored at the
top(lower priority)- iterate through the queue until the data within new node isn't bigger.
- or iterate until the end of pqeueu, where next is
NULL. - make the next of the new node refer to the next of the temp node.
- make the next of the temp node to the new node.
void pqueue_push(PriorityQueue *pqueue, int value) { PQueueNode *temp = pqueue->_top; PQueueNode *newNode = \ (PQueueNode*) malloc (sizeof(PQueueNode)); newNode->data = value; newNode->next = NULL; if (pqueue_isEmpty(pqueue)) { pqueue->_top = newNode; return; } if (value < pqueue->_top->data) { newNode->next = pqueue->_top; pqueue->_top = newNode; } else { while ( temp->next != NULL && temp->next->data < value) temp = temp->next; newNode->next = temp->next; temp->next = newNode; } }
- store the current
-
To do the pop, follow these steps:
- make sure that the pqueue is not empty.
- make a
temp(temporary) node that points to thetopnode. - make the
topto point to the currenttop's next node. - remove the
tempnode.
void pqueue_pop(PriorityQueue *pqueue) { if (!pqueue_isEmpty(pqueue)) { PQueueNode *temp = pqueue->_top; pqueue->_top = pqueue->_top->next; free(temp); } }
-
int pqueue_top(PriorityQueue *pqueue) { if (!pqueue_isEmpty(pqueue)) return pqueue->_top->data; else return 0; }