Module 1 (Queue) - Algoritma-dan-Pemrograman-ITS/StrukturData GitHub Wiki
- front - the node that is located in front of the queue.
- rear - the node that is located at the back of the queue.
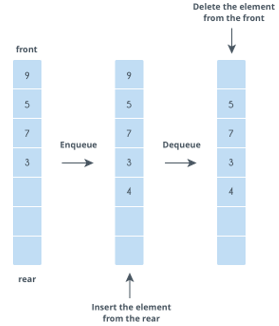
Queue is a linear data structure that works under the First In First Out (FIFO) principle. Under that principle, the first element to be inserted into a queue will be the first element to be removed. Every element within a queue will always be added at the back of the queue and be removed when it is at the front of the queue. One real life example of a queue, is an orderly queue of bus passengers waiting for a bus in a bus station. The first person to enter the queue will be the first to get on the bus.
A Queue data structure can be used to implement a Breadth-First-Search (BFS) on a transversal search within a Graph.
- isEmpty - to check whether a queue is empty or not.
- size - to get the data of a queue's size.
- push/enqueue - to add new data at the back of the queue.
- pop/dequeue - to remove a data in the front of the queue.
- front - to get the data located in the front of the queue.
The Time Complexity of every operation on a Queue is done constantly O(1).
As mentioned previously, Queues can be used within a Breadth-First-Search (BFS) on a transversal graph, it will be explained on the next module so you do not have to worry about it for now. Another example of a problem that can be used by using a Queue is to generate binary numbers from 1 to N.
A complete implementation of Queue can be accessed here.
A Queue can be implemented by making use of the Singly Linked List data structure by having two pointers, rear to refer to the back of the queue and front to refer the front of the queue.
-
A Queue's node can be represented by having a node named
QueueNodethat stores anintdata and a pointer to point to the next node.typedef struct queueNode_t { int data; struct queueNode_t *next; } QueueNode;
-
A Queue has two pointers within its structure, that is
rearandfront.typedef struct queue_t { QueueNode *_front, *_rear; unsigned _size; } Queue;
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ queue<int> q; return 0; }
-
Simply check whether the
frontand therearof the Queue isNULLor not, to know if a Queue is empty or not.bool queue_isEmpty(Queue *queue) { return (queue->_front == NULL && queue->_rear == NULL); }
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ queue<int> q; if(q.empty()){ cout << "this queue is empty" << endl; } return 0; }
-
To insert a new node, do the following steps:
-
make a new node.
-
if the queue is empty, make the new node as the
frontand therear. -
if it is not, then the
nextof the currentrearnode is the new node and treat the newly inserted node as therear.void queue_push(Queue *queue, int value) { QueueNode *newNode = (QueueNode*) malloc(sizeof(QueueNode)); if (newNode) { queue->_size++; newNode->data = value; newNode->next = NULL; if (queue_isEmpty(queue)) queue->_front = queue->_rear = newNode; else { queue->_rear->next = newNode; queue->_rear = newNode; } } }
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ queue<int> q; q.push(1); q.push(2); q.push(3); q.push(4); return 0; }
-
-
To remove a node, do the following steps:
-
store the current
frontnode within a temporary node. -
change the
frontof the node to thenextof the currentfront. -
delete the node stored in the temporary node.
-
if the
frontis empty, then therearshould be empty as well.void queue_pop(Queue *queue) { if (!queue_isEmpty(queue)) { QueueNode *temp = queue->_front; queue->_front = queue->_front->next; free(temp); if (queue->_front == NULL) queue->_rear = NULL; queue->_size--; } }
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ queue<int> q; q.push(1); q.push(2); q.push(3); q.push(4); q.pop(); return 0; }
-
-
int queue_front(Queue *queue) { if (!queue_isEmpty(queue)) { return (queue->_front->data); } return 0; }
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ queue<int> q; q.push(1); q.push(2); q.push(3); q.push(4); while(!q.empty()){ cout << q.front() << endl; q.pop(); } return 0; }
More on std::queue could be read here or in C++ Language documentation here.